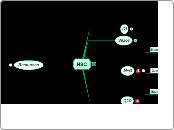
H2O2
Acid is a coumpound that dissolves in water to produce hydrogen ions (H+) in solutions
Note: aq stands for aqueous or dissolved in water
Lewis dot diagram of Sodium and Chlorine Ions (Full valence orbits)
Sodium Ionically bonding with Chlorine
(Electrons moving from sodium to Chlorine)
Lewis dot diagram of a
chlorine atom
Gr.10 Unit 1 Chemistry Summative Assignment
Chemical reactions
Chemical equations
Products
The sum of the reactant
Reactants
The atoms/ions that will form the product
Combustion
In order to burn something
you need the 3 things in
the “fire triangle”:
1) A Fuel (hydrocarbon)
2) Oxygen to burn it with
3) Something to ignite the
reaction (spark)
occur when a hydrocarbon
reacts with oxygen gas. (Burning)
Double discplacement
AB + CD AD + CB
Double Displacement Reactions occur when a
metal replaces a metal in a compound and a
nonmetal replaces a nonmetal in a compound
Balanced double displacement equation
(without symbols clarifying solid, liquid, gas, aqueous)
Single displacement
A + BC AC + B (if A & B are metal) OR
A + BC BA + C (if A & C are nonmetal)
a nonmetal can replace a nonmetal (-)
Single Displacement Reactions occur when
one element replaces another in a compound.
A metal can replace a metal (+)
Balanced Single displacement reaction
Decomposition
Carbonates and chlorates are special case
decomposition reactions that do not go to
the elements.
Carbonates (CO3
2-) decompose to carbon dioxide
and a metal oxide
AB = A + B
Decomposition reactions occur when a
compound breaks up into the elements or in
to simpler compounds
Synthesis
Basically: A + B = AB
Synthesis reactions occur when two
substances (generally elements)
combine and form a compound.
(Sometimes these are called combination
or addition reactions.)
Balanced synthesis reaction
Bonding
Covalent/Molecular
compound
Carbon dioxide
CO
oxygen
O2
Water
H2O
Hydrogen dioxide
mouth wash
https://www.pure-chemical.com/blog/list-of-chemicals-in-daily-life/
Hydrogen peroxide
Some elements may be diatomic
(they exist in nature as double bonded naturally)
H ,O ,N ,Cl ,F, Br
Diatomic elements
Diagram
Unlike formula units, covalent compounds can have multiple combinations, and not be a fixed ratio
When two or more non-metal elements are combined together, it is a covalent compound/molecular compound
The atoms are held together by covalent bonds which is when the atoms share their valence electrons
Ionic Compound
Example
Baking soda
Na(HCO3)
Sodium bicarbonate
Chemical in toothpaste
Sodium Fluoride
NaF
https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/General_Chemistry/Map%3A_A_Molecular_Approach_(Tro)/03%3A_Molecules_Compounds_and_Chemical_Equations/3.05%3A_Ionic_Compounds-_Formulas_and_Names
Table salt
Sodium chloride
NaCl
Polyatomic ions
Bond with a metal to form
an ionic compound
Groups of atoms that stay together and
carry and overall ionic charge
Also known as Radicals
Formula unit
A chemical formula that shows the
lowest whole number ratio of the
atoms (ions) in an ionic compound.
Chemical formula
A representation of the kind
and number of atoms in a substance
Bonds that are formed by transfer of
electrons from one element to the other
Each element (now an ion) will have a
complete octet after the transfer of electrons.
The electrical force between the ions will be opposite with the metal being positivly charged and the gas being negatively charged
Acids and bases
Bases
Naming bases
We use the cross-over rule for the valences
charges but don’t forget the brackets
around the hydroxide
For ammonium Hydroxide
The name for bases starts with a metal and ends with Hydroxide (OH^-1)
Properties of bases
Are basic or alkaline
Bitter taste
Most are solids
Slippery and soapy to the touch
A good conductor of electricity in solution
React with acid to produce salt and water
Indicators
Red litmus turns blue
Blue Litmus paper stay blue
Colourless phenolphthlalein turns pink
Neutral (green) bromthyol blue turns blue
Methyl orange turns yellowish orange
Cabbage Juice turns blue-green
A Base is a Compound that
dissolves in water to produce
hydroxide ions (OH-) in solution
Examples of bases
Baking Soda
Detergent
Soap and Bath products
https://examples.yourdictionary.com/20-common-examples-of-bases-in-everyday-life.html
Acids
Oxyacids
Naming oxyacids
The radical ending "ate"
is dropped
The ending "ic acid" is added to the stem
(SO4)^2-
to H
2(SO4)
Sulfate to sulfuric acid
Contains Hydrogen, Oxygen
and one other element
They are formed with
polyatomic ions (radical like sulfate)
which react with hydrogen
Binary Acids
For all acids, the number of
hydrogen atoms is equal to the
valence or charge on the
element or radical it is bonding with
Naming Binary acids
1. Use Hydro as prefix
2. add the main portion of the second element
3. It will end with "ic"
Examples
HCl(aq) -----> Hydrochloric acid
Contains Hydrogen and one other element
Examples of acids
Citrus fruits
Aspirin
Stomach Acid
Vinegar
Properties of Acids
Sour taste
React with some metals to produce H2
A good conductor of electricity in solution
Reacts with base to produce salt and water
React with pH Indicators & change colour
Blue litmus paper turns red in an acid
Red Litmus paper stay red in an acid
Pink phenolphthlalein turns colourless in an acid
Neutral (green) bromothymol blue turns yellow in an
acid
Methyl orange turns red in an acid
Ions
Ions: Atoms with a charge
Polyatomic Ions
Ions that form with two or more atoms
Anions: Atoms with a negative charge
Cations: atoms with a positive charge
Diagrams
Lewis dot diagram
Bohr-Rutherford Diagram
Bohr-Rutherford diagram of a
oxygen atom
Perodic table
Subtopic
Atoms
Electrons = e-
Valence shell
is the outer ring of an atom
8 Electrons fit in the outer shell
Octet Rule:
Elements tend to acquire 8 (e-) in the
outer most shell to become stable
The noble gasses will always have a filled outer ring
Mass Number = # of e- + # of n°
Mass # (-) # of e- = # of n °
Atomic Mass = # of p+ (+) # of e-
# of e- = number of p+
(In atom)
Neutrons = n°
Protons = p+
The Atomic Number = # of p+
Elements
Common Multivalent Elements
7 Periods and 18 Groups
Group # 2: Alkaline Earth metals
Beryllium
Magnesium
Calcium
Strontium
Barium
Radium
Group # 18: Noble gasses
Helium
Neon
Argon
Krypton
Xenon
Radon
Ununoctium
Group # 1: Alkali metals
Hydrogen
Lithium
Sodium
Potassium
Rubidium
Cesium
Francium
Group # 17: Halogens
Fluorine
Chlorine
Bromine
Iodine
Astatine
Ununseptium