par OLEKSANDRA MOSIICHUK Il y a 1 année
154
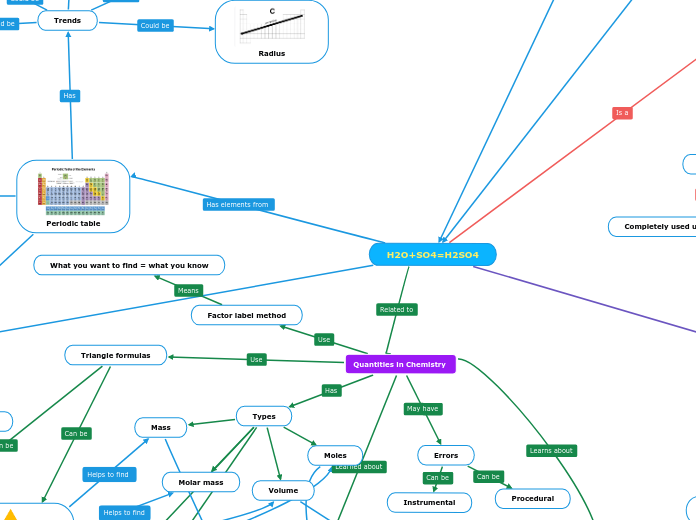
H2O+SO4=H2SO4
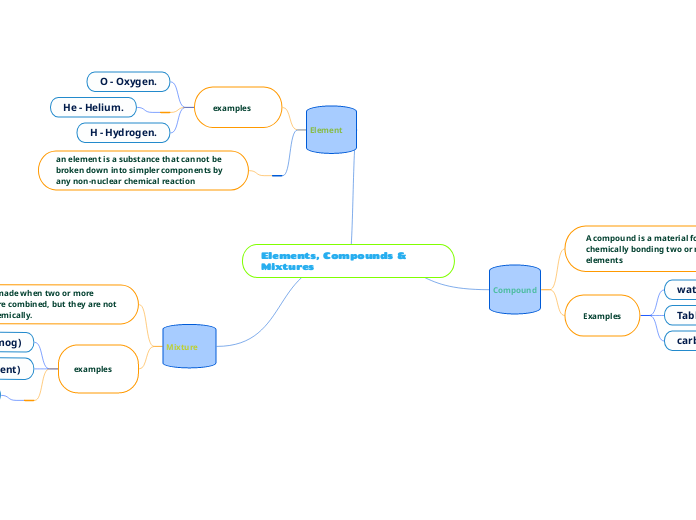
Chemical reactions involve various substances interacting, often resulting in the formation of new compounds. Acids and bases play significant roles in these reactions, with acids donating protons and bases accepting them.