par Pravin Arunkumar Il y a 4 années
690
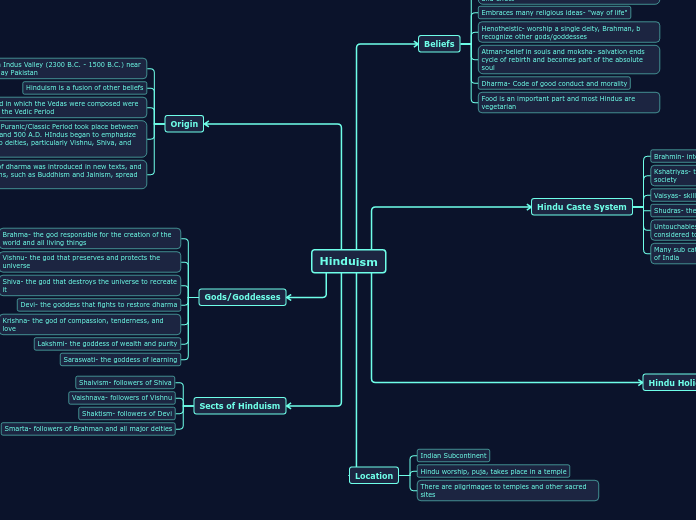
Hinduism
Hinduism, originating in the Indus Valley around 2300 B.C., is a complex fusion of various beliefs and practices. The Vedic Period marked the composition of the Vedas, while the Epic and Puranic periods between 500 B.