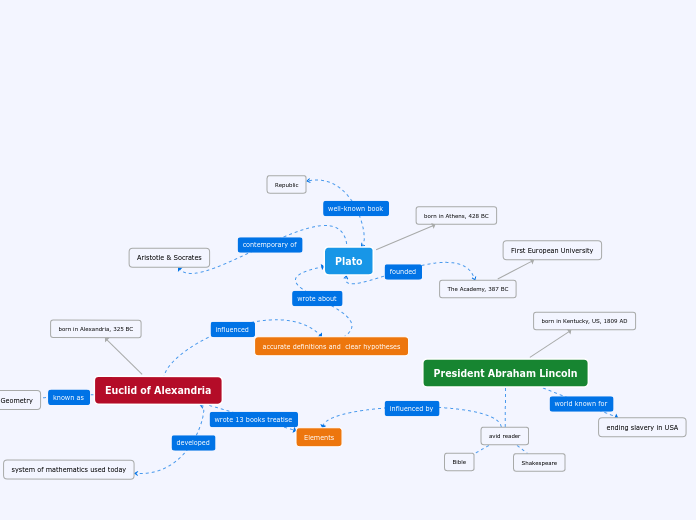
History/Social Science Curriculum for 8th Grade (United States History and Geography: Growth and Conflict)
Content
History
Discuss the importance of the slavery issue as raised
by the annexation of Texas and California's admission
to the union as a free state under the Compromise of
1850
8.9.4
Understand the political and economic causes and
consequences of the War of 1812 and know the
major battles, leaders, and events that led to a
final peace
8.5.1
Describe the relationship between the moral and political
ideas of the Great Awakening and the development of revolutionary fervor
8.1.1
Geography
Examine the location and effects of urbanization, renewed immigration, and industrialization
(e.g., the effects on social fabric of cities, wealth and economic opportunity, the conservation movement)
8.12.5
Trace the boundaries constituting the North and the South, the geographical differences between the two regions, and the differences between agrarians and industrialists
8.10.2
Subtopic
Describe the country's physical landscapes, political divisions, and territorial expansion during the terms of the first four
presidents
8.4.1
Economics
Explain how states and the federal government encouraged business expansion through tariffs, banking, land grants, and subsidies
8.12.3
Describe the development of the agrarian economy in the South, identify the locations of the cotton-producing states, and discuss the significance of cotton and the cotton
gin
8.7.1
Enumerate the advantages of a common market among the states as foreseen in and protected by the Constitution’s clauses on interstate commerce, common coinage, and
full-faith and credit
8.3.3
Citizenship
Evaluate the major debates that occurred during the development of the Constitution and their ultimate resolutions in such areas as shared power among institutions, divided state-federal power, slavery, the rights of individuals and states (later addressed by the addition of the Bill of Rights), and the status of American Indian nations under the commerce clause
8.2.3
8.3.6
Describe the basic law-making process and how the Constitution provides numerous opportunities for citizens to participate in the political process and to monitor and influence government (e.g., function of elections, political parties, interest groups)
8.8.1
Analyze the significance of the States’ Rights Doctrine, the Missouri Compromise (1820), the Wilmot Proviso (1846), the Compromise of 1850, Henry Clay’s role in the Missouri Compromise and the Compromise of 1850, the Kansas-Nebraska Act (1854), the Dred Scott v. Sandford decision (1857), and the Lincoln-Douglas debates (1858)
8.9.5
Understand the Thirteenth, Fourteenth, and Fifteenth Amendments to the Constitution and analyze their connection to Reconstruction
8.11.5
Inquiry
H-SS AS: Students understand and distinguish cause, effect, sequence, and correlation in historical events, including the long- and short-term causal relations
8.4.3
Analyze the rise of capitalism and the economic problems and conflicts that accompanied it (e.g., Jackson’s opposition to the National Bank; early decisions of the U.S. Supreme Court that reinforced the sanctity of contracts and a capitalist economic system of law)
H-SS AS: Students use a variety of maps and documents to identify physical and cultural features of neighborhoods, cities, states, and countries and to explain the historical migration of
people, expansion and disintegration of empires, and the growth of economic systems
8.5.2
Know the changing boundaries of the United States and describe the relationships the country had with its neighbors (current Mexico and Canada) and Europe, including the influence of the Monroe Doctrine, and how those relationships influenced westward expansion and the Mexican-American War
H-SS AS: Students assess the credibility of primary and secondary sources and draw conclusions from them
8.7.2
Trace the origins and development of slavery; its effects on black Americans and on the region’s political, social, religious, economic, and cultural development; and identify the strategies that were tried to both overturn and preserve it (e.g., through the writings and historical documents on Nat Turner, Denmark Vesey)
H-SS AS: Students detect the different historical points of view on historical events and determine the context in which the historical statements were made (the questions asked, sources
used, author’s perspectives)
8.10.5
Study the views and lives of leaders (e.g., Ulysses S. Grant, Jefferson Davis, Robert E. Lee) and soldiers on both sides of the war, including those of black soldiers and regiments
H-SS AS: Students frame questions that can be answered by historical study and research
8.12.6
Discuss child labor, working conditions, and laissez-faire policies toward big business and examine the labor movement, including its leaders (e.g., Samuel Gompers), its demand for collective bargaining, and its strikes and protests over labor conditions
Literacy
CCSS.ELA-Literacy.WHST.6-8.1b
Support claim(s) with logical reasoning and relevant, accurate data and evidence that demonstrate an understanding of the topic or
text, using credible sources
CCSS.ELA-Literacy.RH.6-8.1
Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of primary and secondary resources
CCSS.ELA.Literacy.WHST.6-8.2b
Develop the topic with relevant, well-chosen facts, definitions, concrete details, quotations, or other information and examples
CCSS.ELA-Literacy.RH.6-8.6
Identify aspects of a text that reveal an author’s
point of view or purpose (e.g., loaded language,
inclusion or avoidance of particular facts)
CCSS.ELA.Literacy-RH.6-8.8
Distinguish among fact, opinion, and reasoned judgment in a text