par NUR SYAZWANI IZZATI BINTI WAN GHAZALI Il y a 4 années
404
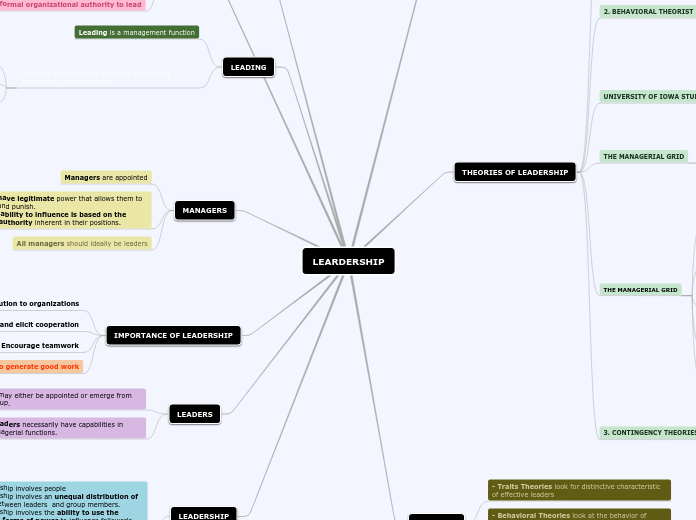
LEARDERSHIP
Leadership theories encompass a variety of perspectives on how leaders emerge and function. Behavioral theories suggest that leadership skills can be taught, focusing on leadership functions and styles.