par Maham Saif - T L Kennedy SS (2352) Il y a 3 années
854
Math Summative
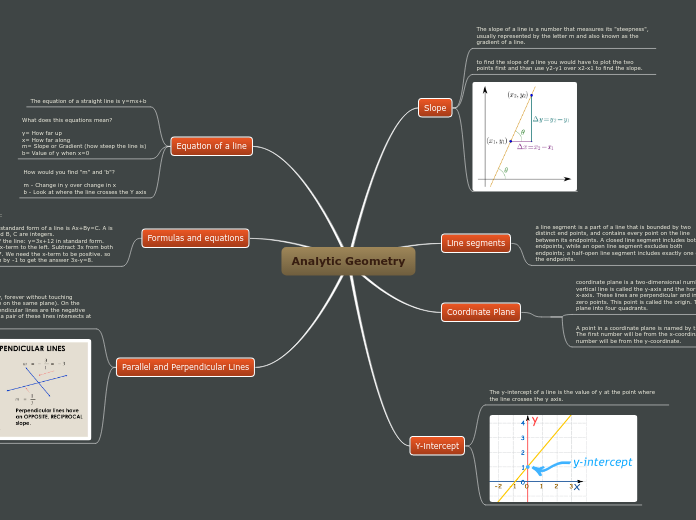
Analytic geometry involves the study of the coordinate plane, which is a two-dimensional number line divided by the x-axis and y-axis. These axes intersect at the origin, creating four quadrants.