par afiqah shalihin Il y a 9 années
495
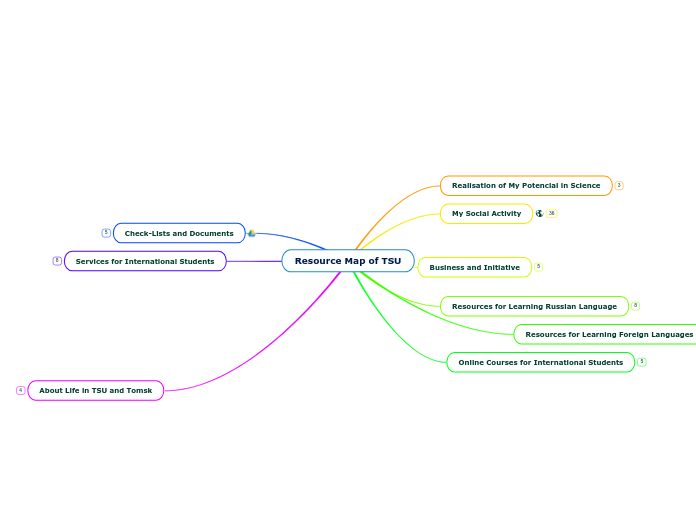
microbial interactions by shalihin
Microorganisms interact in a variety of ways, often forming complex relationships that impact larger biotic communities. These interactions can be mutually beneficial, competitive, or parasitic.