par Olivia Brown Il y a 5 mois
62
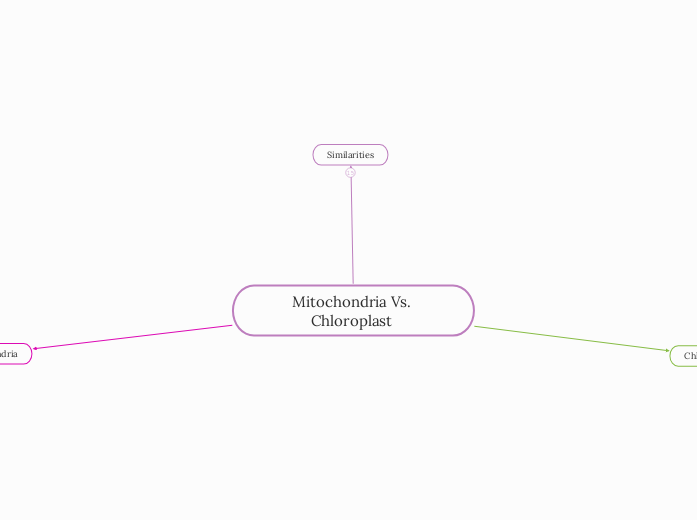
Mitochondria Vs. Chloroplast
Chloroplasts are specialized organelles found exclusively in plant cells, playing a crucial role in photosynthesis by converting solar energy into chemical energy. These organelles contain carotenoid pigments, which assist in trapping solar energy and transferring it to chlorophyll, the primary pigment responsible for absorbing light energy.