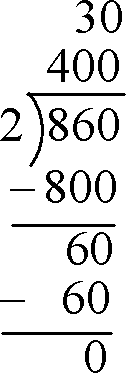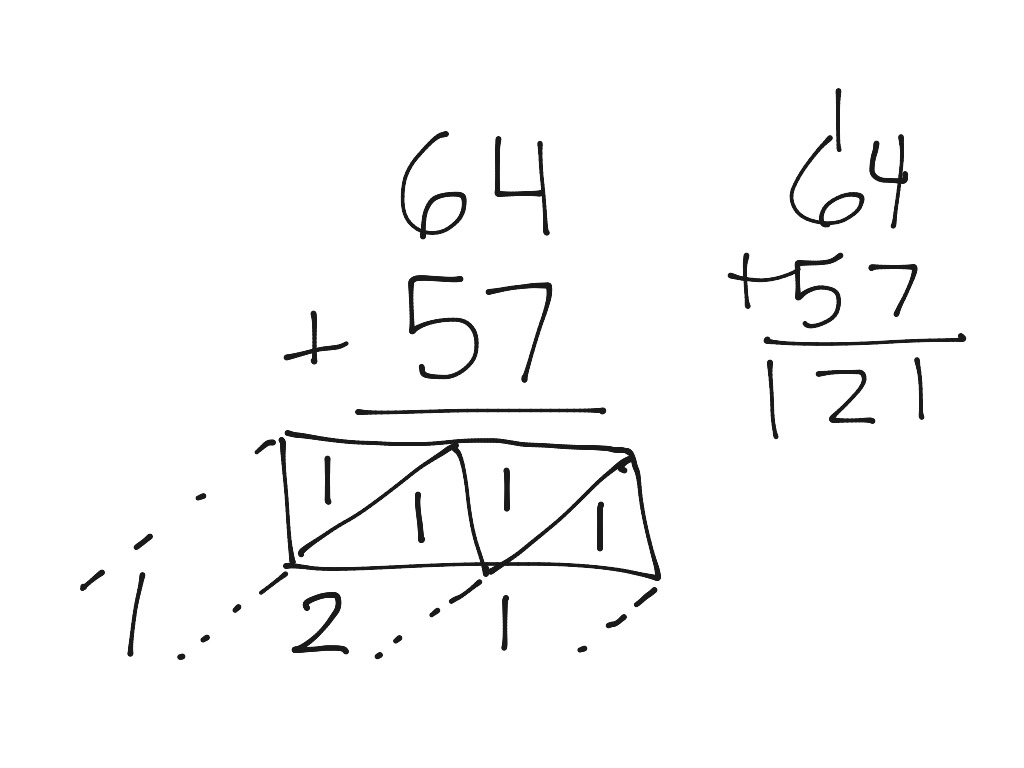MTE 280- Elementary Mathematics
Weeks 4-5
Addition Properties
Commutative Property
- Order does not make a difference in the answer
- Works only for addition/multiplication
Example:
2+9+3+1=15
9+1+1+3=15
Associative Property
- Grouping (parenthesis placement) does not make a difference in the answer
- Works only for addition/multiplication
Example:
(1+4)+6=11
1+(4+6)=11
Alternative Algorithms
- Write out the division problem
- Divide like the traditional algorithm, but with emphasis on place value
Example:
860/2
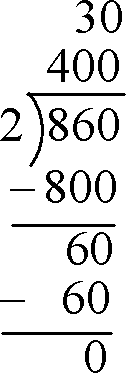
400+30=430
- Works if there is a non-zero remainder
- Repeatedly subtract from the number being divided
- Answer is the number of subtractions completed
Example:
18/6=3
1 subtraction: 18-6=12
2 subtractions: 12-6=6
3 subtractions: 6-6=0
- Draw out the base ten blocks representing the number being divided
- Starting with the largest place value, separate into groups of the what the number is being divided by
- Convert the remainder of that place value into the one below it
- Continue separating into groups and regrouping until there are units left that cannot make a group
- Write out the answer based on how many groups of each shape there are
Example:
726/6
*Brackets represent groupings
7 flats = [6 flats] + 1 flat
1 flat + 2 longs = 12 longs = [6 longs] + [6 longs]
6 units = [6 units]
6 flats + 2(6 longs) + 6 units =121
Expanded Form
- Write each number in its expanded form
- Subtract numbers from the same place value normally
- Add the expanded number together
Example:
525-422=
(500+20+5)-(400+20+2)=
(500-400)+(20-20)+(5-2)=
100+0+3=103
Friendly Numbers
- Goal: change some or all numbers to be multiples of ten
- Add to one number, subtract that from another number
- Subtract new numbers
Example:
57-21=
(57+1)-(21-1)=
58-20=38
- Draw the lattice structure
- Write each digit of each number along the top and right edges of the rectangle
- Multiply each edge, write the first digit in the top section and the second digit in the bottom section
- Add down the diagonals
- Answer is read from top left corner to bottom right corner
Example:

Area Model
- Similar to base ten blocks, but slightly more advanced
- Draw a rectangle
- On adjacent sides of the rectangle, write each number in its expanded form
- Extend lines through the rectangle wherever there are plus signs
- Multiply the numbers on the edges to find the area of each individual square
- Add the areas together to get the total area of the rectangle
Example:

Base Ten Blocks
- Draw a rectangle
- Along two adjacent edges of the rectangle, separate units, longs, and flats (or ones, tens, and hundreds)
- Continue the lines through the rectangle to separate the interior into flats, longs, and units
- Add up each section
- Add the section totals together
Example:

- Write numbers out in their expanded form
- Multiply each separate number
- Add the products
Example:
275+182=
(200)100=20000
(200)80=16000
(200)2=400
(70)100=7000
(70)80=5600
(70)2=140
(5)100=500
(5)80=400
(5)2=10
20000+16000+400+7000+5600+140+500+400+10=50,050
Compatible Numbers
- Same process as friendly numbers
- Subtract an amount from one number and add that amount to another
- Will not get all numbers into multiples of ten
- Goal: to turn some or all numbers into compatible numbers (numbers that are easy to use mentally)
Examples:
24+39+12=
(24+1)+(39+1)+(12-2)=
25+40+10=75
43+62+21=
(43+2)+(62-2)+21=
45+60+21=126
Friendly Numbers/Trade-Off
- Take away some from one number and give that amount to the other
- Goal of getting numbers to multiples of ten
Examples:
37+63=
(37+3)+(37-3)=
40+60=100
28+54+36+22=
(28+2)+(54-4)+(36+4)+(22-2)=
30+50+40+20=140
Left-to-Right
- Instead of adding starting at the ones place and working left, you start from the left and work right.
Example:
348
+ 891
---------
1100
130
+9
-----------
1239
Lattice
- Write numbers vertically
- Draw box underneath each place value
- Draw diagonal line through each box, extending from top right through bottom left corner
- Starting with the ones column, add numbers
- Write the sum's tens digit in the top section of the box and the ones digit in the bottom section
- Move onto the next column and add the same way
- Add down the diagonals, placing sum just outside the box
- Answer is read left to right
Example:
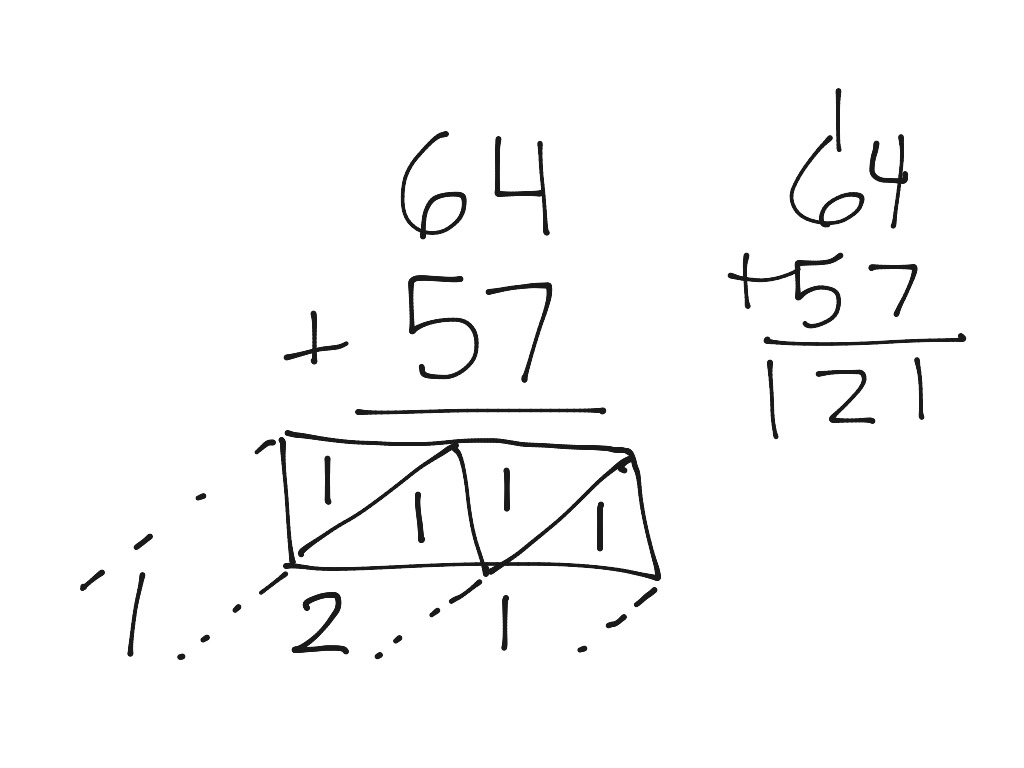
Expanded
- Use for adding large numbers with in hundreds or more
- Write out each number in its expanded form
- Add the expanded numbers
Example:
4615+3548
4000+600+10+5
+3000+500+40+8
________________
7000+1100+50+13=8163
Scratch
- Used for adding many numbers
- Write numbers vertically
- Start in ones column and add going down
- Scratch a number off once you get to 10 (or whatever the base is) and write the remainder next to it
- Continue adding going down and place the last remainder of the ones column under the addition bar
- Count up the number of scratches and write that number on top of the tens column
- Add up the tens column using the same process of scratches and remainders
Example:
2
31
8
27 6
2 51
62
+ 23 2
----------
202
Weeks 1-3
Base Conversions
Converting from Base Ten
Diagram Method (Show)
- Skip count to draw the given number using units, flats, and longs
- Count up the number of each: units, longs, and flats
- Write the number of each shape in their respective place values
Example: Convert 31 to base eight
- Skip count: 8, 16, 24 (draw 3 longs)
- Draw one unit for each remaining number (7 units)
- Write the answer as 37eight
Algorithm Method (Solve)
- Use downwards division, dividing the base number into the given number
Example: Convert 31 to base eight
- 8 goes into 31: 3 times with 7 leftover
- 31=37eight
Example: Convert 47 to base five
- 5 goes into 47: 9 times with 2 leftover
- 5 goes into 9: 1 time with 4 leftover
- 47=142five
Converting to Base Ten
Diagram Method (Show)
- Draw out the given number using units, longs, and flats
- Write down the value of each shape
- Units=1, longs=x, Flats=(x)2
- Where x=number of base
- Add up the value of each shape
Example: Convert 23five to baseten
- 2 longs and 3 units
- Each long=5, each unit=1
- 2(5)+3(1)=13
Algorithm Method (Solve)
- Multiply number of flats by x2
- Multiply number of longs by x1
- Multiply number of units by x0
- Sum the numbers
Example: Convert 23five to baseten
2(51)+3(50)=13
Example: Convert 4,120,367nine to baseten
4(96)+1(95)+2(94)+0(93)+3(92)+6(91)+7(90)=2,198,239
Base Systems
Using Manipulatives and Models
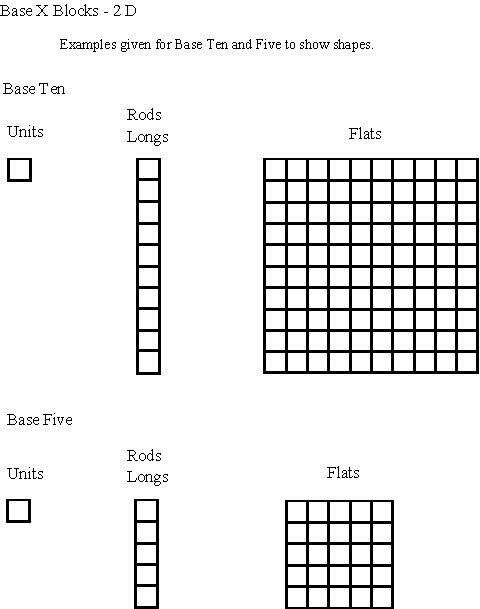
Place Values
Base Ten
- Ones, tens, hundreds
- Ones=100
- Tens=101
- Hundreds=102
Other Bases
- Units, long, flats
- Units=x0
- Longs=x1
- Flats=x2
- x=base number
Other Bases
- Base is specified as subscript
- Counting in basefour: 1, 2, 3, 10
- Counting in basethirteen: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, T, E, W, 10
Base Ten
- Standard system of counting
- Created because humans have 10 fingers
- Assume base ten if no base is specified
- Counting in Baseten: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10
Types of Logical Reasoning
Inductive Reasoning
Figuring something out based on a pattern
Deductive Reasoning
Figuring something out based on or using prior knowledge
Standards of Mathematics Practice
Problem Solving Strategies
- Look for the pattern
- Do an easier problem
- Modify the problem (get rid of the hard part)
- Draw a diagram
- Guess and check
- Write an equation
Common Core Standards
- Make sense of the problem
- Use abstract/quantitative reasoning
- Use logical arguments
- Use tools
- Understand structure
- Look for patterns of reasoning
- Model
- Use precision
4 Step Problem Solving Process
- Understand the problem
- Develop a plan to solve the problem
- Carry out the plan
- Look back- does the answer make sense?
Weeks 11-15
Percents
- Find 10%
- Multiply to get desired percentage
- Add 5% if needed
- Subtract from 100 first for discount problems
Example:
40% of 70
10% = 7
x4 x4
40% = 28
Decimals
Show:
- Draw out box, divide into ten
- Draw first number
- Divide box into ten the opposite way
- Draw second number
- Count how many boxes are shaded twice
Solve:
- Estimate answer by multiplying the whole numbers
- Write out multiplication problem without the decimals
- Multiply like normal
- Compare answer to estimate and add decimal where the answer is closest to the estimate
Show:
- Flat = unit
- Longc= tenth
- Unit = hundredth
- Draw out like fractions
- Addition: draw out box divided into ten, fill in decimals
- Subtraction: draw out box divided into ten, fill in first decimal, take away (cross out) second decimal
Solve:
- Line up the whole numbers and add normally
Multiplication Table
Order to teach multiplication table:
- Ones, twos
- Tens, fives
- Threes, Nines
- Doubles
Order of Operations
- GEMDAS
- Make groups
- Use EMDAS to simplify groups
Divisibility Rules
A number is divisible by x if...
2: Ones place is even
3: Sum of all digits is divisible by 3
4: Last two digits is divisible by 4
5: Ones place is 5 or 0
6: Divisible by 2 and 3
8: Last 3 digits is divisible by 8
9: Sum of all digits is divisible by 9
10: Ones place is 0
Division Algorithms
Repeated Subtraction
- Students don't need to know many multiplication facts
- Takes longer
Example:
52/3
3|52
-30| 10
22
-15| 5
7
-6|
1
=17 1/3
Upwards Division
- Write division problem as a fraction
- Divide denominator into each digit left-to-right
Example:
474=59 2/8
8
47/8
8*5=40
47-40=7
74/8
8*9=72
74-72=2
Weeks 6-10
Fractions
What is a fraction?
- Parts of a whole
- Numerator (top number): how many pieces you have
- Denominator (bottom number): what size the pieces are
Comparing Fractions
- Determine if fraction is >, <, or = to another fraction
- > greater than
- < less than
- = equal than
- Methods:
- Anchor fractions: simple fractions to compare each fraction to (1/2, 1, etc.)
- Whole numbers: whichever number has the larger whole number is greater
- Same denominator: whichever fraction has the same numerator is greater
- Same numerator: whichever number has the smaller denominator is greater (because they have the same number of pieces, but a smaller denominator means bigger pieces)
Show:
- When # of groups = fraction:
- Draw a full group and fill in with the number inside the group
- Draw a box around how much of the group you want
- Example: 1/2(4)
- Draw a group with 4 dots inside
- Draw a box around 1/2 of the group
- Answer = 2 because 2 dots are boxed
- When number inside the group = fraction:
- Draw number of groups
- Inside each group, draw a box to represent the fraction
- Add the fractions together
- When both numbers are fractions:
- Draw a box
- Divide box vertically by first denominator and divide box horizontally by second denominator
- Shade in vertically based on first numerator and shade in horizontally by second numerator
- Answer: numerator = number of boxes that are double shaded, denominator = numbers of boxes total
Solve:
- Multiply numerator by numerator and multiply denominator by denominator
- Example: (2/3)(1/4) = (2/12)
Addition/Subtraction
Show:
- Draw two same-sized boxes
- Divide first box vertically based on the first fraction's denominator
- Divide second box horizontally based on the second fraction's denominator
- Shade in each box based on its respective numerator
- Copy the dividing lines from one box onto the other and vice versa
- Draw a third box with the vertical and horizontal dividing lines
- Shade in the third box by counting the number of small sections in the first and second boxes
Solve:
- Two fractions must have common denominators to be added or subtracted
- If denominators are the same, add or subtract the numerators and keep the denominator
- If denominators are different, find a common denominator:
- Factor each denominator using one common factor
- Whatever is missing from each denominator, multiply by it as a fraction equal to one (x/x=1)
- Denominators are the same, add or subtract numerators and keep the denominator
Factoring
Least Common Multiple
- The smallest multiple that two numbers have in common
- List out all factors of each number
- Add the biggest exponent on each number
Example: 20 and 18
20 = 2*32
18 = 22*5
LCM = 22*32*5
Greatest Common Factor
- The largest factor that is common for two different numbers
- Using each number's prime factorization, the GCF is all of the factors the two have in common, with the lowest exponent present for each
Example: 20 and 18
20 = 2*32
18 = 22*5
GCF = 2
Prime Factorization
- Factors: numbers multiplied together to get an answer
- Prime: a number with exactly 2 factors
- Composite: a number with more than 2 factors
- Prime factorization: factoring a number using only prime numbers
Downwards Division
- Use downwards division, but the number on the left must be prime
Example:
3 L24
2 L8
2 L4
2
24 = 23*3
Factor Trees
- Draw any two factors coming down from number
- Keep drawing two factors for each next number until left with only prime numbers
24
^
12*2
^
6*2
^
3*2
24 = 2*2*2*3 = 23*3
Integers
Absolute Value
- Value of a number without its sign
Example: Abs. value of -12 is 12. Abs. value of -53 is 53.
Division
Solve:
- Divide numbers like normal
- If signs are the same, answer is positive
- If signs are different, answer is negative
Multiplication
- First number is # of groups, second is what's in each group
- 2(3) is 2 groups of 3
- -2(3) is like 0-2(3)
Show:
- Draw circles to represent groups, fill in groups with + or - to represent what's in each group
- For problems where the first number is negative:
- Create zero banks first
- Circle and arrow what is being taken away
Solve:
- Multiply numbers like normal
- If the signs are the same, answer is positive
- If the signs are different, answer is negative
- Example:
- -2(3)=-6
- -2(-3)=6
- 2(3)=6
- 2(-3)=-6
Subtraction
- Say "take away" instead of "minus" or "subtract"
- Difference between take away and negative:
- Take away is an action
- Negative is a description
Show:
- Draw out + and - for what you have
- Circle what you are taking away and draw arrow
- Answer is whatever is left after taking away
Solve:
- Use "Keep, change, change"
- Keep the first number's sign, change the subtraction to addition, change the second number's sign
Addition
Show:
- Draw out + and - for what you have (the first number)
- Draw out + and - for what is added
- Circle zero pairs (pairs of one + and one -, which add up to zero)
- Answer is what is left without zero pairs
Solve:
- Draw two + or - under whichever number is larger (absolute value)
- Draw one + or - under whichever number is smaller (absolute value)
- Circle one sign under one number and one sign under the other number
- If the signs circled are the same, add
- If the signs circled are different, subtract
- The sign left out of the circle is the sign the answer will have