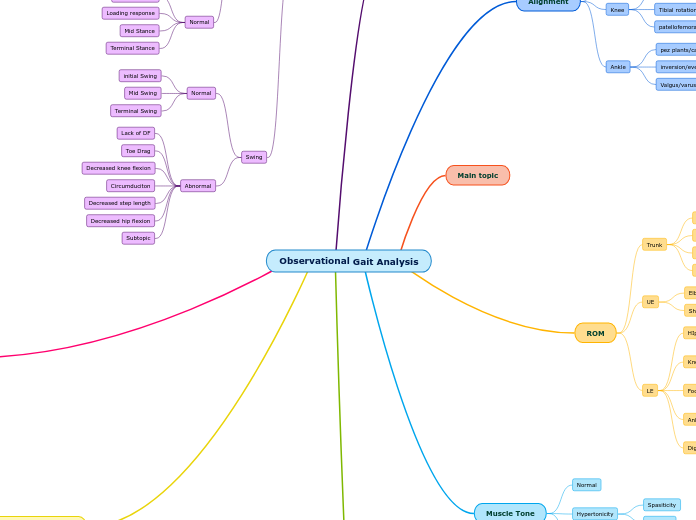
Observational Gait Analysis
Strength
Functional Strength Measures
Burg
6 Minute Walk Test
TUG
Knee Musculature
Ankle Musculature
In/evertors
Hip musculature
Internal/external rotators
Abductors/Adductors
Flexors
Extensors
Temporal Parameters
Velocity
Cadence
Step Length
Stride Length
Pre-Requsite of Gait
Energy conservation
Clearance in swing
Forward progression in Stance
Stance Stability
Pre Positioning of Gait
Phases Of Gait
Swing
Abnormal
Subtopic
Decreased hip flexion
Decreased step length
Circumduciton
Decreased knee flexion
Toe Drag
Lack of DF
Terminal Swing
Mid Swing
initial Swing
Stance
Loading response
Initial Contact
Abnormality
Lack of one of the above
Pre Swing
Terminal Stance
Early Toe off/No toe off
Mid Stance
Trandelenburg
Lack of Trunk Extension/Control
Early Heel Rise
Decreased Mid Stance Time
Crouched Gait
Loading Response
Excessive In/Eversion
Crouched Gait Posture
Foot Slap
initial Contact
Medial Heel Strike
Lateral Heel Strike
Toe strike
Flat foot IC
Muscle Tone
Hypotonicity
Flaccidity
Hypertonicity
Ridgidity
Spasiticity
ROM
LE
Digital
DF/PF
Inversion/Eversion
Foot
Pez Plants/Cavus
HIp
Add/ABduction
IR/ER
Flexion/Extension
UE
Shoulder
Elbow
Trunk
Flexion
Sidebend
Rotation
Extension
Main topic
Alignment
Ankle
Valgus/varus deformity
inversion/eversion angle
pez plants/cavus
Knee
patellofemoral
Tibial rotation
varus/valgus
Hip
rotation
Anteversion/retroversion
Coxa Valga/vara
Normal