إعداد : معاذ بن سعد العساف
Organic Compounds
Nucleic Acid
Complementary, each a predictable counterpart of the other.
The two DNA chains are held together by Hydrogen bonds.
between their paired bases.
DNA usually consists of two polynucleotide strand warp around each other called Double Helix.
RNA usually consists of a single polynucleotide strand.
Note that: the nitrogenous bases are not part of the backbone.
Polynucleotide is built from its monomers (nucleotide) by dehydration reaction.
A sugar-phosphate backbone is formed by covalent bonding between
The sugar of the next nucleotide
The phosphate of one nucleotide
A nucleotide is composed of (3) parts:
Nitrogenous bases
*Nitrogenous bases extend from sugar-phosphate backbone
Uracil
Adenine
Thyamine
Guanine
Cytosine
Phosphate group
5-Carbon sugar ( pentose sugar )
Deoxyribose in DNA
Ribose is RNA
Genes consist of DNA.
Nucleic acids (DNA or RNA)are composed of nucleotides .
The two types of nucleic acid:-
RNA ( Ribonucleic acid )
DNA ( Deoxyribonucleic acid ).
DNA programs cell activities by directing synthesis of protein.
A gene direct the synthesis of an RNA molecule.
The genetic material that humans and other organisms inherit from their parents consist of DNA.
The amino acid sequence of polypeptide is programmed by a directing unit of inheritance known as a genes.
Proteins
Hydrophilic
Protein's Shape
Quaternary structure :-
Prions: are infectious misshapen proteins.
it may cause degenerative brain.
Hemoglobin has four polypeptides of two distinct types.
Collagen has three helical polypeptides.
Example : Collagen - Hemoglobin - Transthyretin.
Resulting from the association of two ore more polypeptide chains ( subunits ).
Tertiary structure :-
The hydrophilic R-groups are on the outside of the molecule.
The hydrophobic R-groups are on the inside of the molecule.
Disulfide bridges are covalent bonds that further strengthen the protein’s shape
Tertiary structure generally result from interactions between the R-groups of the various amino acids.
The term tertiary structure refers to the overall three dimensional shape of a polypeptide.
Secondary structure :-
Transthyretin (protein) has only one alpha helix region.
The R-groups of the amino acids are not involved in forming these secondary structures.
Folding of a polypeptide chain result a Secondary structure called beta pleated sheet.
Coiling of a polypeptide chain result a Secondary structure called alpha helix.
Parts of the polypeptide coil or fold into local patterns called Secondary structure.
Primary structure :-
Determined by inherited genetic information.
The primary structure of a protein is its unique sequence of amino acids.
Proteins Function
Proteins are involved in the following processes :-
5- communication in cells.
4- transport.
3- defense.
2- movement.
1- cellular structure.
* A protein loses its specific function when its polypeptides unravel, this process call ( Denaturation ).
* Nearly all proteins must recognized and bind to some other molecule to function.
* The functions of all these different types of proteins depend on their specific shape.
Storage proteins.
plant seeds.
Milk protein.
ovalbumin ( egg white ).
Transport proteins.
such as hemoglobin in red blood cells.
Receptor proteins.
Transmit signals into cells.
Signal proteins.
such as hormones.
Defensive proteins.
such as antibodies of he immune system.
Contractile proteins.
Muscle cells are packed with it.
Structural Proteins.
Proteins in fibers that make tendons and ligaments.
found in hair too.
Proteins Structure
A Functioning protein is one or more polypeptide chains precisely coiled, twisted, and folded into a unique three-dimensional shape.
A long polypeptide chain of specific sequence is not a protein.
Example of amino acids
2- Hydrophobic, Leucine (Leu)
1- Hydrophilic, Serine (Ser) and Aspartic acid (Asp)
Most polypeptides are at least 100 amino acids in length.
Polypeptide, chain of amino acids.
Dipeptide, made from two amino acids.
The bonds between amino acid monomers are called peptide bond.
The resulting covalent linkage is called a peptide bond.
Cells join amino acids together in a dehydration reaction.
The composition and structure of R-group determine
the properties of each 20 amino acids.
The simplest amino acid is ( glycine ). R= H atom.
Amino acid fundamental design composed of :-
* Carboxyl group and amino group covalently bonded to alpha carbon.
4- R-group ( unique side chain ) : differs with each amino acid.
3- Amino group ( NH2 ).
2- Carboxyl group (-COOH) makes it an acid.
1- Central carbon ( alpha carbon ).
The characteristic that distinguishes one amino acid from another is (R group).
There are 20 different amino acids that make up all proteins.
Structural proteins are long and thin called Fibrous proteins.
e.g. Collagen.
Most enzymes and other proteins are globular.
e.g. Transthyretin, Lysozyme.
You have tens of thousands of different proteins in your body.
Lysozyme's general shape is called Globular.
lysozyme, an enzyme found in sweat, tears, and saliva.
The most important are Enzymes that speed up all reactions in cells. e.g. Lactase.
Nearly every dynamic function in your body depends on proteins.
Protein is a polymer of amino acids.
Lipids
hydrophobic
Steroids
Too much cholesterol in the blood may contribute to atherosclerosis.
Different steroids vary in chemical groups attached to the rings.
Example:-
Sex hormones :-
Testosterone in Male.
Estradiol in Female.
Cholesterol :
is an essential structural component of animal cell membranes.
The carbon skeleton contains four fused rings.
Phospholipids
Hydrophilic heads : Phosphate group + Glycerol.
Hydrophobic tails : Fatty acids.
* negatively charged phosphate group.
Composed of: Phosphate group + Glycerol + 2 Fatty acids.
The major component of cell membrane.
cell could never exist without phospholipids
Fats large lipids made from glycerol and fatty acids.
Fatty acids
Omega-3 : Unsaturated fatty acids are found in certain nuts, plant oils, and fatty fish and appear to protect against cardiovascular disease.
* Hydrogenated vegetable oil: means that unsaturated fats have been converted to saturated fats by adding hydrogen.
2- Unsaturated
e.g. Corn oil - olive oil.
Occur in most plant cells.
Low melting point.
Liquid at room temperature.
The hydrocarbon chain contain one or more double bonds.
1- Saturated
e.g. Butter - Beef.
Occur in most animals fats.
High melting point.
Solid at room temperature.
the hydrocarbon chain without double bond(=)
The nonpolar hydrocarbon chains are the reason fats are hydrophobic.
Dehydration reaction linking glycerol molecule and fatty acids molecule.
Example: Triglycerides ( 1 glycerol linked to 3 fatty acids )
Main function: energy storage.
Fats consist Twice the energy as a polysaccharide has.
Fats Composed of
Fatty acid: consist of a carboxyl group ( make it an acid ).
and a hydrocarbon chain ( 16-18 atoms on length ) ( make it hydrophobic )
Glycerol: is an alcohol with three carbons,
each bearing a hydroxyl group.
Lipids differ from carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids in :
Not polymers built from similar monomers.
Not huge macromolecule.
Lipids consist mainly of Carbon and Hydrogen atoms.
Linked by nonpolar covalent bonds.
Lipids grouped together because they share one trait
They do not mix mell with water
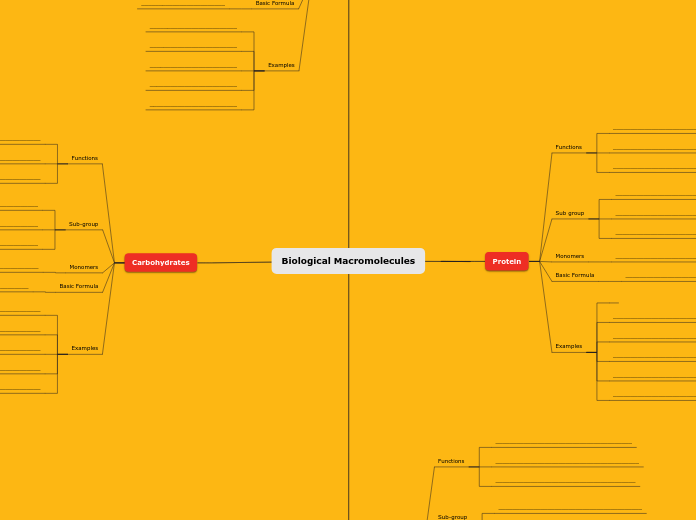
Carbohydrates
hydrophilic
Isomers: They contain the same atoms but in different arrangements.
e.g. Glucose and Fructose .. ( 6 carbon ).
An aqueous solution of glucose called Dextrose.
These molecules typically have a formula that is a multiple of ( CH2O).
Each molecule contain Hydroxyl groups and a Carbonyl group.
Polysaccharide
Chitin, 1- form insect exoskeleton.
2- cell walls of fungi.
Cellulose, form plant cell walls.
(abundant organic compound on Earth)
Cellulose molecules are joined together by
hydrogen bond ( arranged parallel )
Glycogen, energy storage in animals. ( Branched )
Most of your glycogen is stored as
granules in your liver and muscle cells.
Starch, energy storage in plants. ( Unbranched )
e.g Potatoes and Grains.
monomer = glucose
Disaccharide
lactose = glucose + glactose
Sugar in milk.
sucrose = glucose + fructose
The most common. ( table sugar, plant sap )
maltose = glucose + glucose
which is common in germinating seed and milk candy.
Disaccharide = two monosaccharides link by dehydration.
Monosaccharide
Monosaccharides, particularly Glucose, are the main fuel molecules for cellular work.
Honey consist of monosaccharides (glucose + fructose )
glucose - fructose - glactose - Ribose - Deoxyribose
Many monosaccharides form rings.
Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates.
Making and Breaking Polymers
Dehydration and Hydrolysis
Breaking Polymers ( Hydrolysis )
Hydrolysis mean to break with water.
Digestion process for a polymer call Hydrolysis.
Making Polymers ( Dehydration )
Dehydration form a covalent bond linking two monomers.
Dehydration, reaction that removes a molecule of water.
Cells link monomers together to form polymers by Dehydration reaction.
The building blocks of polymers are called Monomers.
Joining smaller molecules into chains called Polymers.
Carbohydrates, Proteins, Nucleic Acids are Macromolecules.
Introduction to organic compounds
Functional Groups
Hydrophilic
6- Methyl Group = Carbon bonded to three hydrogens. ( Nonpolar = hydrophobic )
Compounds with methyl group are call Methylated compounds.
5- Phosphate Group = phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms.
Often involved in energy transfers.
Compounds with phosphate group are called Organic Phosphates.
4- Amino Group = Nitrogen bonded to two hydrogen and carbon skeleton.
Amino Acids = amino group and carboxyl group.
is the building blocks of proteins.
Organic compounds with an amino group called amiens.
3- Carboxyl Group = hydroxyl group bonded to a carbonyl group.
Compounds with carboxyl groups are called Carboxylic Acids.
act as an acid.
2- Carbonyl Group = carbon atom linked by double bond to an oxygen atom.
If the carbonyl group at the middle of the carbon skeleton the compound called Ketone.
If the carbonyl group at the end of the carbon skeleton the compound called Aldehyde.
1- Hydroxyl Group = hydrogen atom bonded to an oxygen atom.
e.g. Ethanol.
Organic compounds containing hydroxyl groups are called alcohols.
Functional groups are Polar and Soluble in water. (except Methyl group)
Functional groups: is group of atoms.
e.g. Hydroxyl, Carbonyl, Carboxylm and amino group.
2- Determine the properties of organic compounds.
1- Participate in chemical reactions.
Carbon skeleton : the chain of carbon atoms in an organic molecule.
Isomers is the compounds which have same formula but different arrangement.
e.g. Butane and Isobutane.
Compounds composed of only carbon and hydrogen are called Hydrocarbon.
e.g. Methane and Propane.
Carbon-based molecules are called Organic compounds
e.g. Methane (CH4) is the simplest organic molecule.