Disease Prevention
Needlestick safety act
- 600,000-800,000 needlesticks occur each year
- Identify, use effective, safer medical devices
- Bring in changes in annual update, exposure control plan
- solicit in put from nonmangerial
- employees who are responsible for direct patient care
- Corporate changes, annual update, exposure control plan
Bloodborne pathogens standard
Regulations that require all health care facility employers to follow:
- Need a plan to make sure exposure to bloodborne pathogens
- Identify employees that have occupational exposure to body fluids
- Enforce rules, areas that can potentially contaminated by body fluids.
- Should be confidential medical evaluation and follow-up
- Should be training about regulations and all potential biohazards
Maintaining Transmission-based Isolation precautions
Meaning:
- Isolation precautions vary from one facility to another
- Depends, the type of units provided for the isolated patients
- Most facilities convert a regular patient room into an isolation room
- some facilities use special room isolation units (two)
- Basic principles maintaining transmission, isolation are the same regardless of the facility
Contact precaution
Before care: Private room.
Droplet precaution
Before care: Private room, maintaining 3 feet of space between patients/residents and the visitors.
During care: Limit transport of patients/resident, essential purpose only, patients residents must wear mask appropriate for disease.
After care: Bag linen to prevent contamination of self, the environment, or outside.
Airborne precaution
Before care: Private room and closed room, monitored negative air pressure, frequent air exchanges, high-efficiency filtration.
During care: Limit transport of patients/resident, essential purposes only, patients residents must wear mask appropriate for disease.
After care: Bag linen to prevent contamination of self, the environment, or outside bag.
Standard precaution- Wash hands, Wear gloves, Wear gown, etc.
Stopping transmission of infections
Standard precautions
Transmission-based precautions (also called isolation precautions)
- Contact precautions
- Droplet precautions
- Airborne preactions
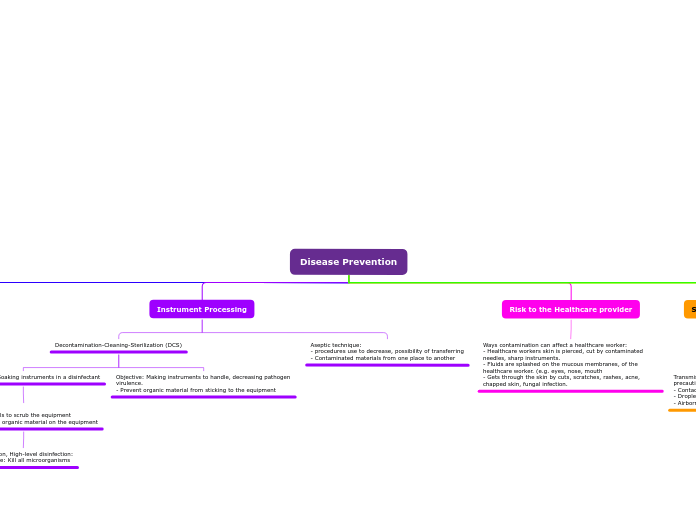
Risk to the Healthcare provider
Ways contamination can affect a healthcare worker:
- Healthcare workers skin is pierced, cut by contaminated needles, sharp instruments.
- Fluids are splashed on the mucous membranes, of the healthcare worker. (e.g. eyes, nose, mouth
- Gets through the skin by cuts, scratches, rashes, acne, chapped skin, fungal infection.
Instrument Processing
Aseptic technique:
- procedures use to decrease, possibility of transferring
- Contaminated materials from one place to another
Decontamination-Cleaning-Sterilization (DCS)
Objective: Making instruments to handle, decreasing pathogen virulence.
- Prevent organic material from sticking to the equipment
Decontamination: Soaking instruments in a disinfectant
Cleaning:
- Use the right tools to scrub the equipment
Objective: remove organic material on the equipment
Sterilization, High-level disinfection:
- Objective: Kill all microorganisms
Aseptic Control
Surgical Asepsis (Sterile technique)
- Actions that keep equipment and supplies free of all microorganisms
- Uses all procedures including sterilization areas of the body
- Also minor operations or injections
- Object is either sterile or not
- If you are unsure, then it is not
- Only touch sterile to sterile
Medical Asepsis
- Practices reduce the number of pathogens
- Prevents their spread
- Called clean technique
- Objects are known as clean or dirty (Contaminated)
Includes:
- Hand hygiene
- Barrier techniques
- Maintaining a clean environment
Asepsis information
Antiseptics: chemicals that kill microorganisms on living skin or mucous membranes.
Disinfectants: Chemical that kill microorganisms on inanimate objects
Asepsis: is the freedom from disease causing microorganisms
Asepsis: absence of disease-producing microorganisms, pathogens
Sterile:
- free from all organisms
- pathogens and nonpathogenic
- aswell as spores, viruses
Contaminated: Organisms and pathogens are present
Antisepsis: Prevents or inhibits growth of pathogenic organisms.
- not effective attacking spores, viruses.
Disinfection: Destroys or kills pathogenic organisms
- Not always effective attacking spores, viruses.
Sterilization: Destroy all microorganism
- Both pathogenic and nonpathogenic
Modes of Transmission
Airborne transmission
- Microorganisms are carried by the air
- Remains in the air
- Dispersed over long periods
Droplet transmission
- a form of contact transmission
- Involves transfer of small droplets
- Released when an infected person: Coughs, sneeze, talk's during some medical procedures
Contact transmission: Most common mode of infection transmission
Indirect transmission:
- an object or person
- transfers microorganism from infected person to new host
Direct transmission:
- transfer of microorganisms
- directly from an infected person too someone else.