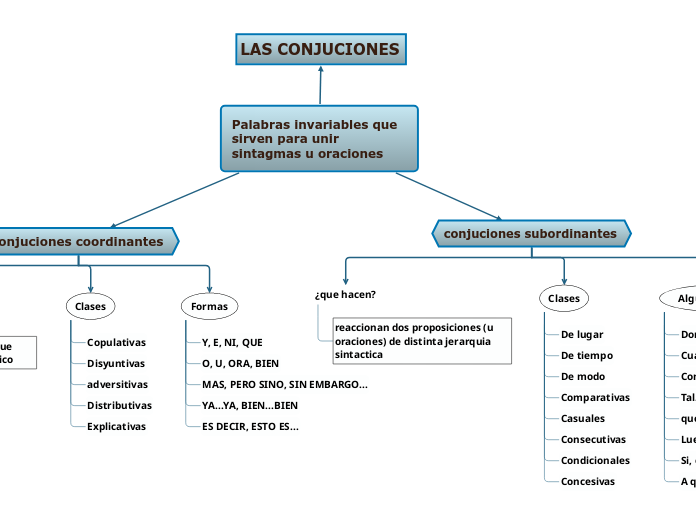
Palabras invariables que sirven para unir sintagmas u oraciones
Name the character
Type in the name of the character whose change throughout the story you are going to analyze.
Example: Nick Carraway.
conjuciones subordinantes
Character's behavior
Think of the character's behavior at the beginning of the story and look for the way it changed throughout the story.
Algunas formas
A que, para que,para...
Si, en el caso de que, como...
Luego, con que, por lo tanto...
que, porque, puesto que, pues..
Tal...cual,tan...como, igual..que
Como, segun, segun que...
Cuando, apenas, en cuanto...
Donde
Concesivas
Condicionales
Consecutivas
Casuales
Comparativas
De modo
De tiempo
Change in behavior
In what way did the character change the other behavior(s) you mentioned? Type in a relevant quote.
Example:
'You said a bad driver was only safe until she met another bad driver? Well, I met another bad driver, didn't I? [...]
I thought you were rather an honest, straightforward person. I thought it was your secret pride.'
De lugar
Change in behavior
How did the character change the first behavior you mentioned? Type in a quote to prove your statement.
Example: Nick assumes the whole responsibility for Gatsby's funeral arrangements, 'with that intense personal interest to which every one has some vague right at the end.'
¿que hacen?
reaccionan dos proposiciones (u oraciones) de distinta jerarquia sintactica
Initial behavior
What is the character's behavior at the beginning of the story? Type in a relevant quote for your statement.
Example: Nick seems to be an honest person, calling himself 'one of the few honest people that I have ever known'.
Conjuciones coordinantes
Character's feelings
Focus on the way the character's feelings are presented at the beginning and at the end of the story, while explaining why they have changed.
Formas
ES DECIR, ESTO ES...
YA...YA, BIEN...BIEN
MAS, PERO SINO, SIN EMBARGO...
O, U, ORA, BIEN
Change of feelings
How did the character change the belief you mentioned?
Type in a relevant quote for his change.
Example: 'Winter night and the real snow, our snow(...)We drew in deep breaths of it . . . unutterably aware of our identity with this country for one strange hour before we melted indistinguishably into it again. That's my middle-west.' - Nick on the purity and integrity of Midwest.
Y, E, NI, QUE
Change of feelings
In what way did the character change the feeling you mentioned?
Type in a quote to support your statement.
Example: 'They are a rotten crowd. You're worth the whole damn bunch put together.' - Nick criticizing the Buchanans.
Clases
Explicativas
Distributivas
adversitivas
Disyuntivas
Initial feelings
What was the character's initial belief? Type in a relevant quote.
Example: 'seems like the ragged edge of the universe' - Nick talking about Midwest, the place where he grew up.
Copulativas
Initial feelings
How does the character feel about a certain subject at the beginning of the story? Type in a relevant quote to support your statement.
Example: "Reserving judgements is a matter of infinite hope."
¿Que hacen?
unen palabras u oraciones que estan al mismo nivel sintactico
LAS CONJUCIONES
Title
Type in the title and author of the literary work that introduces the character.
Example: The Great Gatsby, by F. Scott Fitzgerald.