The social and physical causes of climate change
Future of Climate Change
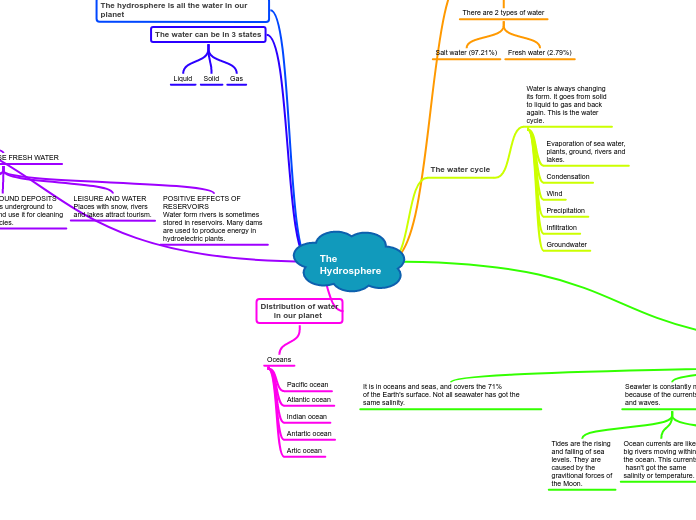
The result of the current climate change is global warming. If global warming continues at its current rate, there will be worldwide implications.
Impact on animal activity
In a similar fashion to the impact on human activities, animal habitats worldwide will be destroyed as a result of the rising sea levels. Flooding will occur on the coasts of most continents in the world, therefore destroying natural habitats of many terrestrial species.
The melting of the ice caps will result in the destruction of the habitats of the animals living in polar regions (polar bears, penguins, walruses, seals etc.)
Impacht on plant activity
Increased carbon dioxide levels will increase rates of plant growth and perhaps development (bud burst, flowering and leaf fall)
Changes in temperatures are expected to bring an earlier onset of growth in spring and a longer growing season
Mild winters may reduce the yield of fruit trees, because colder temperatures are needed to break the buds
Increased temperatures will aid the growth of more plants from warmer parts of the world
Higher temperatures and decreased summer rainfall will cause stress, especially in plants with extensive, shallow, fibrous root systems
Annual moisture content of soils is likely to decrease by 10-20% across the UK by the 2080s, with substantial reductions (of 20-50%) in soil moisture possible in the summer by the 2080s
Fungal diseases will thrive with the wet winter conditions.
Impact on human activity
Agricultural yields are expected to decrease for all major cereal crops in all major regions of production.
The availability of water will be affected by melting of glaciers, particularly in areas such as the Indus basin and western China, where much of the river flow comes from melt water.
Population increases, combined with changes in river run-off as a result of changes in rainfall patterns and increased temperatures, could mean that by 2080 significantly less water is available to approximately one billion people already living under water stress.
For many areas of the world sea-level rise, combined with the effect of storms, will threaten low-lying coastal communities. There are often very dense populations living along coasts, as well as important infrastructure and high-value agricultural land, which makes the impact of coastal flooding particularly severe. The intrusion of salt water on farming land, and the risk to lives of flooding events could affect millions of people worldwide every year.
How has our climate changed?
Climate can change through natural occurences and through man-made occurences.
Man-Made Changes
Humans cause the release of about 26,000 million tonnes of CO2 per year through several activities.
Deforestation
Deforstation has also indirectly affected climate change, since it prevents trees from intaking CO2 for photosynthesis. The less trees there are, the less CO2 is consumed by plants, and therefore the more CO2 left in the atmosphere to contribute to global warming.
Gas Emissions
Our climate has changed as a result of the increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. These gases include water vapour, CO2, methane and others. Recent climate change is a result of increased CO2 emissions around the world as a result of technological developments. Vehicles, factories etc. have contributed massively to the thickening of the atmosphere as a result of greenhouse gas emissions.
Naturally
CO2 and other greenhouse gases are released in the atmosphere through natural occurences. However, these releases of gases are usually balanced out through other natural occurences of the Earth's ecosystem. For example through plant consumption of CO2.
Volcanoes
Volcanoes release CO2 into the atmosphere through eruptions. In an average year, volcanoes put out an estimated 100—130 million tonnes of CO2 globally.
What causes climate change?
Two major factors affect climate: The sun and the atmosphere
The Atmosphere
The atmosphere has changed and has the strongest effect on climate change. The change has occured with the increase in greenhouse gases that trap heat waves from the Sun and prevents them from leaving the Earth.
The Sun
The sun provides a constant amount of heat to the Earth, therefore cannot be considered a major force in climate change.
What is climete change?
Climate change is the change of the temperature of the Earth over a certain period of time. Current climate change over the past century is through the increase of the temperature of the Earth. This has been called 'global warming'.
What are prople doing that is causing climate change?
using technologies that exhale certain gases that have an effect on the ozone layer
Air conditioners
Exploiting natural resources
Tomorrow we will be more organized and prioritize every task.
Pollution
Vehicles, factories, logging, deforestation,burning excess material.
What are people doing to prevent climate change?
Against Logging and deforestation
Eco-Friendly technologies
Solar Energy Vehicles
Natural gas nehicles
Saving non-renuable resources
Not everyone is aware of the Climate change problem and its long term effects.
Valuable mind maps
People who were previously by a climate change disaster
they become eco friendly after their experience.
people who experienced the effects of climate change start living eco friendly by altering some of their habits. such as, recycling paper, stop wasting electricity, find alternatives to vehicle such as bicycles.
Live their lives planet friendly; attempt to stop global warming and spread awarness
start planting trees and spread awarness of the dangers ahead of us.
Recycling
How do people get effected by climate change
After such occurences people have to begin from scratch and rehabilitate psychologically in order to move on with their lives.
The long term effect of climate change occurs causing an aftermath such as floods, tsunamis, earthquakes and blizards.
People need to adapt with their losses after any occurence (houses,cars, death)
Countries with weak resources and financial back up are the ones being effected substantially as oppose to wealthy counries
Subtopic