par Ahmad Hakim Il y a 4 années
268
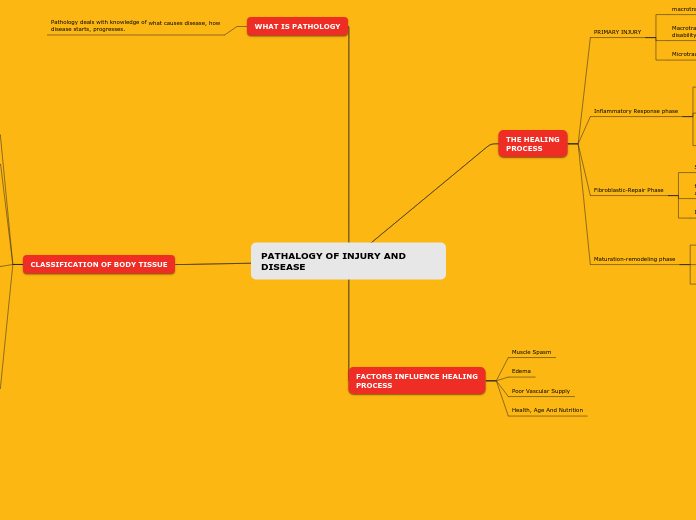
PATHALOGY OF INJURY AND DISEASE
Pathology is a field focused on understanding the causes, initiation, and progression of diseases. It classifies body tissues into categories such as nerve tissue, muscle tissue, epithelial tissue, and connective tissue.