RESOURCES
2. Readability
There are two methods to access readability.
Qualitative meassure
1.Read through the Resources text while trying to see it through the eyes of the pupils.
2. Conceptual qualities
3. Vocabulary: how reader-friendly is the choice of words?
4. Sentence construction
5. Genre conventions and discourse structure
Quantitative measure
Long words tend to be harder to read than short ones
(b) long sentences tend to be harder to read than short ones.
Calculate the average number of(a) syllables per word, (b) words per sentence and (c) syllables per sentence.
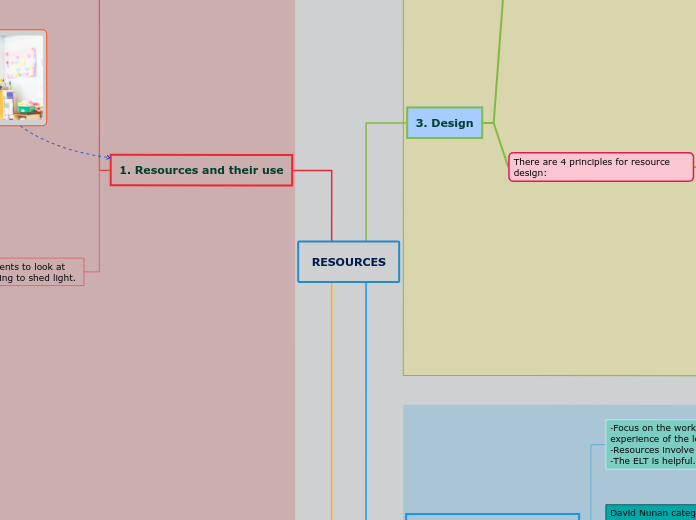
1. Resources and their use
Resources allow students to look at the world, while helping to shed light.
Comparation
Teacher-made resources
Legibility, spelling mistakes, punctuation errors and shaky grammar.
Poor in quality and even error-ridden.
Difficult to preserve, store and retrieve.
Precisely because they are bespoke, they may be difficult to transfer between context.
They are created for use by particular classes in specific settings.
They also often cost little to produce.
Ready-made resources
Disadvantages
The quality of resources varies and so the resources still need to be evaluated.
They’re unlikely to suit to any specific context perfectly.
Advantages
Their production values are often high.
They are often tailored to particular courses
Designed, edited and tested by professionals.
Resources in the classroom
c) Teacher-produced resources
Worksheets, assignments posted on the school intranet, PowerPoint presentations and so on.
b) Ready-made resources
Textbooks, educational software, gymnastic and laboratory equipment and so on.
a) Teacher
Teachers here have a dual role: they are both resources in themselves and users of resources.
The resources play a supportive role.
Teachers sometimes adopt a passive, uncritical role
Ian McGrath identifies four ‘evaluative processes’
4. Changing material
3. Adding material
Supplementation
Introduce some fresh material to be used in addition to the original resource.
Adaptation
‘Add’ to the material by extending it
2. Rejection
1.Selection
4. Bringing it all together
The main point is to consider what each resource requires from each student. This will help to know whether the resources are varied and ambitious enough.
David Nunan categorizes resources according to thetype of response required of the student:
Interact
Productive work.
He identifies two main types of response:
One is repetition
The other is the practice
Process
-Focus on the work of the teacher and experience of the learner.
-Resources involve the learner.
-The ELT is helpful.
3. Design
There are 4 principles for resource design:
PROXIMITY
• When two elements are not related, they can be placed far apart.
• Group together the items that are related. Physical closeness implies relationship When two pieces of information are related to each other.
ALIGNMENT
• Nothing should be arbitrarily placed on the screen.
• Every element must have at least one edge connected to another element.
REPETITION
• Repeat certain design elements such as colors, symbols, words or texts to create a sense of coherence.
CONTRAST
• Contrast can be achieved with size, shape, color, position.
• The use of strong contrast helps to generate interest.
• The title should contrast clearly with the body text
DESIGNER
Robyn Williams