par PABLO FERNANDO RODRIGUEZ CARDENAS Il y a 1 année
119
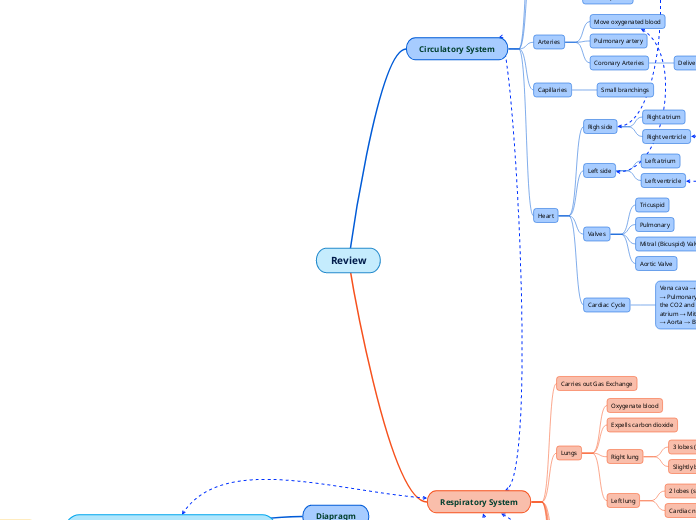
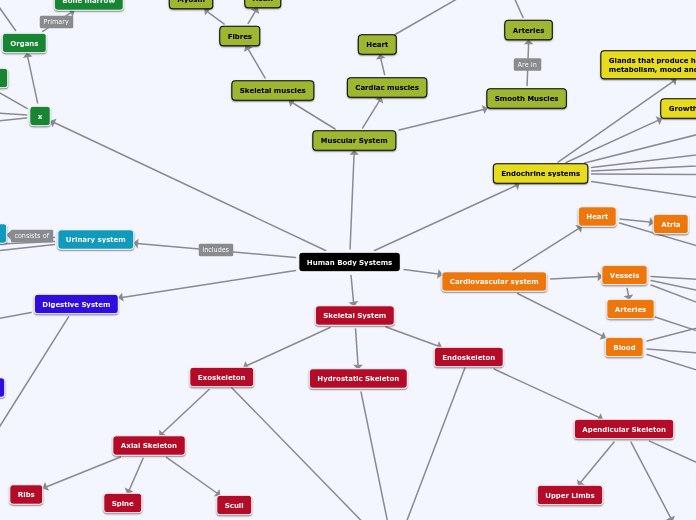
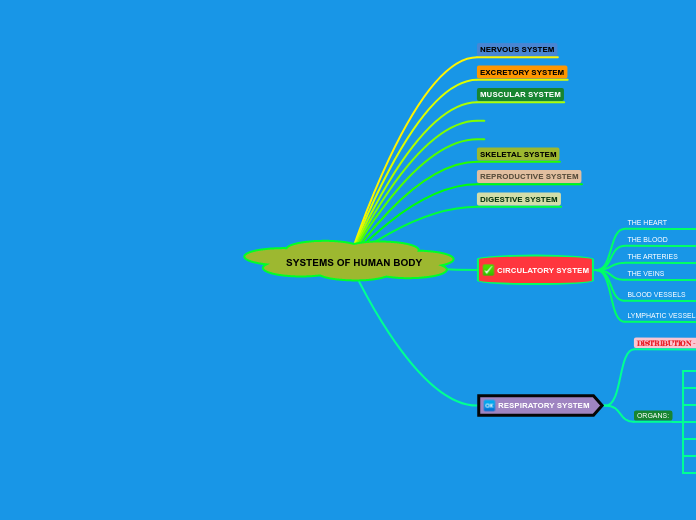
Review
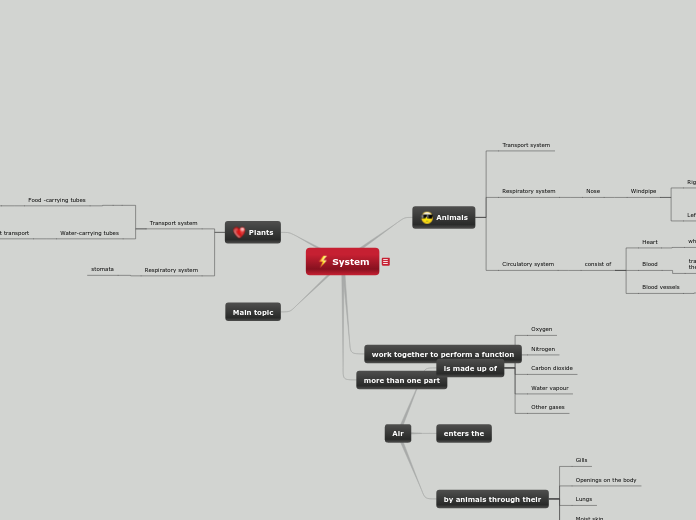
The human body relies on various interconnected systems to maintain homeostasis and ensure survival. The respiratory system is responsible for oxygenating blood and expelling carbon dioxide, featuring structures such as the lungs, trachea, and alveoli.