par RAUL LOPEZ Il y a 4 années
138
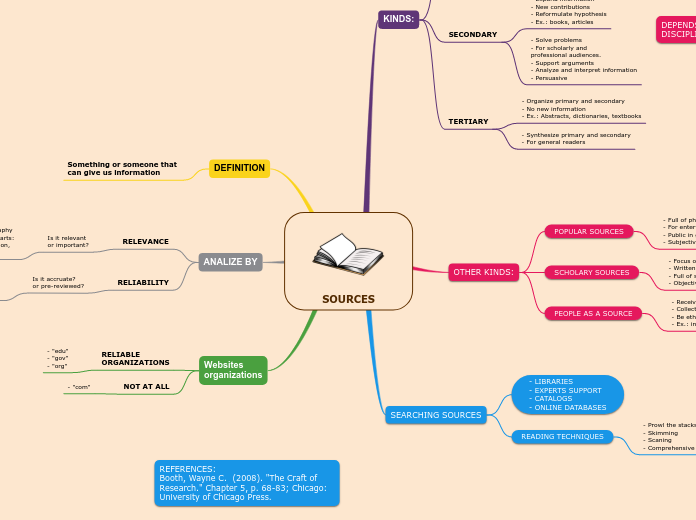
SOURCES
Effective research hinges on the ability to source information from a variety of outlets, each serving specific purposes. Scholarly sources, characterized by their objectivity and scientific rigor, are pivotal for academic work.