Subject and object questions
To name your story, you have to think about the overall message and what you want your audience to understand from the story. Also, make it relevant and easy to remember.
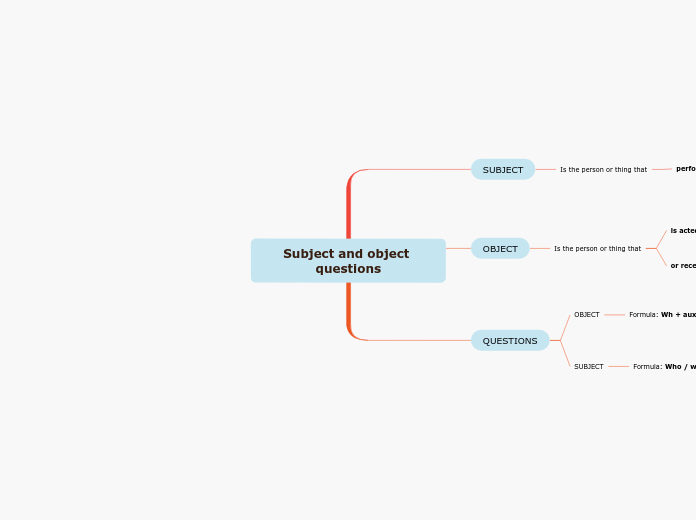
QUESTIONS
The ending of a story is essential. We all know that if the ending is weak, what happened before loses its importance. So make it unpredictable, but fair. A resolved ending answers all the questions and ties up any loose threads from the plot.
This is the closure section of the story.
See examples of possible outcomes below:
- all problems have been solved
- it's clear how each one of your characters ends up
- your main character is transformed by the challenge
Formula: Who / what + Verb + object + ?
Try answering these questions to come up with a closure:
- Have all the problems been solved?
- Is there a clear picture of what happens with each character in the story?
- Has the challenge transformed your main character?
- How do the characters feel in the end?
we want to ask about the subject.
Who likes George?
Angie likes George.
Who wants some fruit juice?
We want some fruit juice.
This is the moment when the main character surpasses the last obstacle and finally faces their greatest challenge.
The climax usually follows one of these patterns:
- realization
- resolution
- choice
Type in your answer.
Formula: Wh + aux + S + V + C + ?
we want to know about the receiver of the action.
What does smoking cause?
Smoking causes cancer.
What do you want to drink?
We want some fruit juice.
OBJECT
The middle of the story is where you add layers of complications that will lead to the end. Reveal more about the character's journey. Did their personality go through changes? How did they overcome the challenges? And as you build up the story’s central conflict, make it more personal to that character. Also, from the middle act, you have to lead into the final act.
Your character(s) need(s) motivation in order to solve the challenge(s).
or receives the action
Secondary characters might also have motives that lead them to cross paths with the main character or which might trigger them to help the main character.
is acted upon
Why does your character need to confront this challenge? What does he/she expect to accomplish by solving it?
See a few examples:
- will marry in 3 days
- can fix the mistakes of the past
SUBJECT
In the beginning of the story (or the exposition), you will need to introduce the setting and characters. You might also want to introduce the main conflict. This part of the story is important because it gives the reader necessary background information and maybe even a first insight into a character’s personality.
Is the person or thing that
Characters are essential to a good story. Usually, the protagonist(s) is/are the most affected by the plot. Introduce a character by focusing on their actions, interests, and occupation, as the physical appearance doesn't make a difference in most cases.
performs the action
Type in the name of your character.
Mikaela is a woman really beautifull
Angie likes George.
Add other qualities/attributes of the character.
Smoking causes cancer.
What is your character's main goal?
fight Evilfind lovedefeat his/her enemyrule the worldmake friendstime travelmake an awesome discoveryOther
Winston is a good student.
Which traits best describe the character's personality? Choose more if necessary:
introvertedloyalkindindependentquick-thinkingadventuresomeidealisticsweet-naturedcalmrisk-takercreativewittystrictfussyweirdclumsyharshaggressivecarelessclingingcowardlycrueldeceitfulimpulsiveOther
We want some fruit juice.
Choose the type of your chacter:
Protagonist (main character)Antagonist (main character's opponent)Flat (stereotypical character)Round (his/ her personality develops throughout the story)Static (doesn't evolve as a person throughout the story)Dynamic (dramatical change in personality)Confidant (the main character trusts him/ her)Foil (contrasting character who enhances the personality of another character)Other