suspension
settling
avoid formation of "cake"
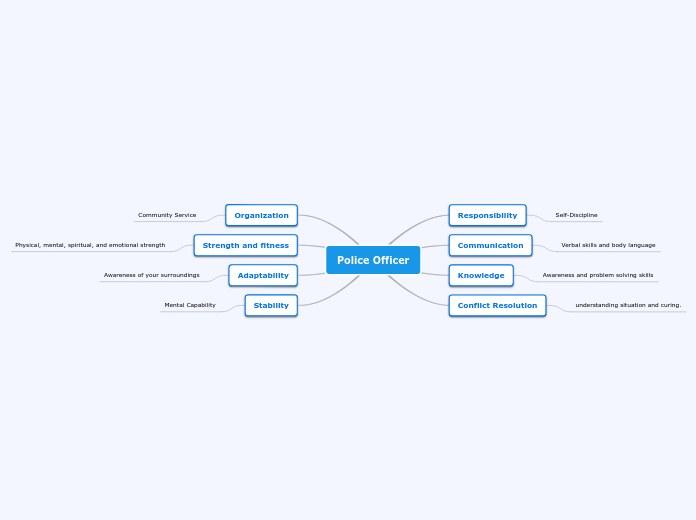
I-clicker
A flocculated system settles very rapidly not allowing enough time for accurate dosing. what would you try first to fix
d) add a wetting agent
wetting agent is used to make a flocculated system
C) use homogenizer to better breakdown the drug particle
RUIN the flocculated suspension??
B) increase viscosity
flocculated solution is a very loose suspension thus increasing viscosity will allow the drug to settle in a slower rate. giving more time for accurate dosing
A)reduce particle size of disperse phase
we already have a flocculated system! change is particle size can affect the flocculated systemm
disadvantage
lack drug stability data
cause clumps floating around
promote loose settling
fast settling but "fluffy" ( loose structure) = Floc
easily redistributed
we cannot prevent settling
might as well control it
process to form "floc", a loose structure
due to particle settling very fast
weak particle particle forces
artificially form when
particle settle to re disperse
made by additive
adjusting pH and electrolytes
most sophisticated
promote int interactions for particle
to repple and prevent from clumping forming cake
Suractants
done by wetting
prevents particle from sticking
clays
cons: add volume
interfere with other particle creating barrier
thus help support the floc structure once it forms
all suspension particle
WILL eventually settle
once particles settle can form a
hard cake that does not re-distribute
easily and is to be avoided
preparing
process
add remaining vehicles in parts while mixing
dispersed particle are wetted---> paste
Extemporaneous
compound
less stable
from solid--> suspension
Wetting to create barrier
too much
dissolution of drug
bad tase
used to reduce interfacial tension
prevent particles from
sticking to each other
creating a barrier to avoid "caking"
surfactants
amphiphilic
cover particles and form a bridge
between the lipophilic particle and
the hydrophilic medium
classification
coarse
always a suspension
settle under gravity
over 1 micron
Colloidal
may look like solution
suspension/solution
typically do not settle under gravity b/c so
small that particle remain suspended
< 1micron
nanometer range
3 main type
parenteral
fastes growing
suspension limitation in the blood
is the particle size of the drug.
must be low particle size == looks like solution
particle size can be determined by
light transmission through the suspension
large particle size = light does not passes through
small particle size = light passes through
liposomal doxorubicin
most common insulin zinc suspension
externally applied
lotion
oral
most common
oral suspensionn better flexibility in
dosing than oral tablet
definition
drug
suspensiod
internal phase
the dispered phase
external liquid phase
dispensing medium
cant see through
will not dissolve
WILL eventually settle over time
finely divided particles distributed somewhat uniformly throughout a vehicle in which the drug exhibits minimum solubility
drug molecule surrounded by drug molecule
Particles( clubs) surrounded by water molecule
Why
slower dissolution and absorption than tablets
better dissolution and absorption than tabelts
mask the tase
dose flexibility
when. liquid is required but
drug is not dissolve in liquid or
unstable in solution
suspension can improve the stability
of undissolved drug
common use
antiimicrobial- unstable in solutions
Antiacid - are inorganic particle that are insoluble in water
good suspension
flocculation
loose structure when settle
thus easily redistributed
FLOC
vehicle
thixotropy is a good vehicle
overtime viscosity increases
under high stress become less viscous
not heavily adjusted to
achieve good suspension
easy consistent pour
vehicle viscosity
thixotropy is a
good vehicle
over time viscosity increases
high stress --> less viscous
easy to disperse
adjusted via addition
thickening agent
suspending agent
adjusted in accordance
to particle size and density
to minimize sedimentation
rate
the stokes equation cannot determine
if particle will readily re-disperse
slow sedimentation rate
slow to settle
slow sedimentation rate for stability**
Sedimentation rate
particle density
WANT particle density to be a
little but lower than medium
Density of particle a
>> than medium
Density of particle less
than medium (water)
float
WANT the particle size to
be as narrow as possible
10 x increase in particle size
results in 100x increase in
sedimentation rate
too large
easy to re-disperse
fast to settle
too small
will form cake
slow to settle
particle size
differentiating factor in suspension
stable
particle with the samilar density
as medium can afford having
more particle because the
sedimentation rate is slower
uniform=narrow particle size distribution