Lipids and Cardiovascular Risk
Treatment
Pharmacological Therapy
Sitostanol
Antioxidants
Fish Oils
Nicotinic Acid (niacin)
Bile acid-binding resins
E.g. colestyramine
Cholesterol Absorption Inhibitors (Ezetemibe)
Inhibits absorption of exogenous biliary cholesterol in the GI tract, reducing total cholesterol and LDL. Often used as an additive to statin instead of increasing the statin dose when side effects aren't tolerated.
Fibrates
Use reduces cardiovascular events but not overall mortality, therefore not routinely recommended in primary or secondary care
Mechanism of Action: Activate peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha, leading to alterations in lipoprotein metabolism, therefore stimulating peripheral lipoprotein lipases which breakdown very low density lipoproteins (VLDLs) and some LDLs, whilst increasing levels of HDLs. It also leads to a reduction in triglycerides. However, increased biliary excretion of cholesterol can lead to gallstones
Gemofibrozil
Fenofibrate
Ciprofibrate
Bezafibrate
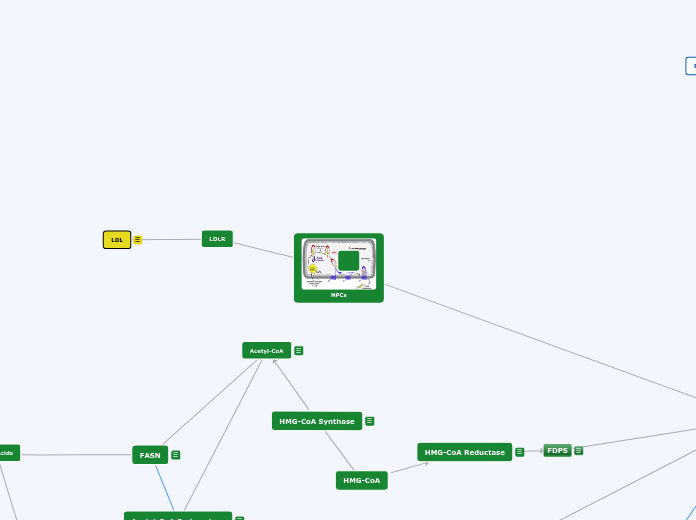
Statins (HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors)
Examples
Simvastatin
Rosuvastatin
Pravastatin
Fluvastatin
Atorvastatin
Mechanism of Action
Extensive first pass metabolism
Inhibit hepatic hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase (HMG-CoA reductase) which would otherwise catalyse the first step of cholesterol synthesis in the liver
Lifestyle and Diet Modification
Goals
Regression of atherosclerotic lesions
Reduce risk of MI and Stroke
Clinical Features
Coronary artery disease, presenting as angina or myocardial infarction
Xanthomas
Lab test date indicative of hyperlipidaemia
Total cholesterol > 5mmol/L
LDL:HDL > 3
Contributing Factors Towards the Development of Hyperlipidaemia
Modifiable Risk Factors
Infection associated with chronic inflammatory response
Reduced physical activity
Hyperglycaemia
Excess alcohol consumption
High-fat diet
Obesity
Smoking
Secondary to disease
Poorly Controlled Diabetes Mellitus
Renal Disease
Liver disease
Genetics
Drug-Induced
Oral Contraceptives containing levenorgestrel
Retinoids
Anabolic Steroids
Thiazide Diuretics
Corticosteroids
Beta blockers
Interactions
Co-morbidities
Peptic ulcer
Caution: Nicotinic Acid
Postmenopausal Osteoporosis
Statins may reduce bone turnover
Pregnancy
Contraception required whilst using and 3 months after
Statins, nicotinic acid and fibrates are contra-indicated in pregnancy and breastfeeding
Hypothyroidism
The condition itself may have adverse effects on a person's lipid profile
Increased risk of rhabdomyolysis with statins and fibrates
Gout
Use nicotinic acid in caution
Diabetes mellitus
Fibrates can improve glucose tolerance in combination with other hypoglycaemic agents. A reduction in the dose of hypoglycaemic agent may be necessary, particularly with clofibrate. Nicotinic acid should be used with caution
Renal impairment
May require dose reductions due to increased risk of rhabdomyolysis. Avoid MR benzofibrate.
Recent Heart Attack
Patients taking a statin before an MI are at an increased risk of further cardiac events for the following week if the statin is abruptly withdrawn at the time of the initial event.
Hypertension
Statins may lower blood pressure when used with antihypertensives
Thiazides raise cholesterole and triglycerides. Uncertainty over whether this is sustained
Gallstones
Can be caused by fibrates. Avoid in those who have gallbladder disease
Liver Disease
If severe avoid fibrates
Avoid statins
Medicine Interactions
Warfarin + Fish oil
Increased anticoagulation, additional monitoring
Macrolides e.g. erythromycin + simvastatin
Increased level of simvastatin, increased risk of rhabdomyolysis
Colesytramine + fluvastatin/pravastatin
Increased lipid lowering effect but reduced bioavailability of statin through colesytramine binding to it. Give several hours apart.
Grapefruit Juice + Simvastatin
High consumption can increase plasma concentration, advise patient to avoid. Smaller effect with atorvastatin, pravastatin appears unaffected
Orlistat + pravastatin
Possible increased levels of pravastatin
Ciclosporin + Fibrates/Statin
Increased levels of ciclosporin + increased risk of rhabdomyolysis (particularly with simvastatin/fibrates). Simvastatin is contra-indicated with ciclosporin and/or gemfibrozil. Pravastatin doesn't seem to interact.
Warfarin + fibrate/statin
Increased anti-coagulant effect with fibrate/SOME statins. Monitor INR
Simvastatin + CCBs e.g. amlodipine
Generally limit dose of simvastatin to 20mg in patients on amlodipine, verapamil or diltiazem. See: http://mm.wirral.nhs.uk/document_uploads/alerts/NWMICsummarysimvaamlodipineinteractionSep12.pdf
Fibrates + statins
Additional lipid lowering but increased risk of myopathy (rare). Caution.