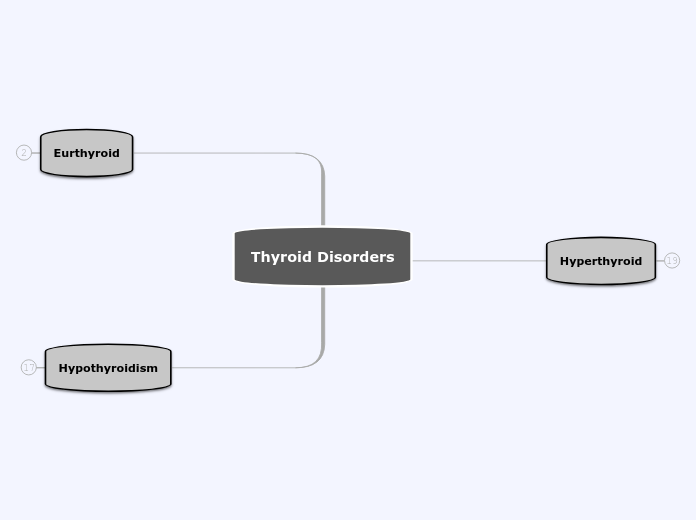
Thyroid Disorders
Hypothyroidism
Pituitary Insufficiency
Iatrogenic
Medications
Amiodarone
- antiarrhymthic drug decreases T4 to T3 conversion and can casue inflammatory thyroiditis
Lithium
- drug for bipolar disorder inhibits thyroid hormone synthesis and release
Aspirin and Sulfonamide can induce thyroiditis
Radioactive Iodine Ablation
- treatment for hyperthyroidism or thyroid cancer
Congenital
- cretinism
- protruding umbilicus
- pale skin
- puffy face
- pot belly
- protruding tongue
- poor neuro development
Iodine Deficiency
most common congenital cause in developing countries
Autoimmune maternal hypothyroidism
Fetal thyroid agenesis
- most common congenital cause in US
Riedel Thyroiditis
- rare
- rock hard goiter, no pain
- develops as response to chronic inflammation
- normal thyroid parenchyma replaced by dense fibrous tissue with an inflammatory infiltrate
- associated with IgG4-related diseases
- may lead to compressive symptoms
- impinge on trachea
- interfere with breathing
- hoarseness
-painless goiter
-often as asymptomatic as Hashimoto
-anti-TPO and TGB antibodies
-50% transient with full recovery; 50% develop permanent hypothyroidism
Postpartum
Subacute granulomatous (de Quervain)
-painful goiter
-self limited with recovery after few weeks
-precipitated by viral infection
-symptoms of hyperthyroidism
-pain managed with NSAIDs or corticosteroids
-inflammation of thyroid and sudden release of thyroglobulin
Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
- 2% of US
- most common
- Autoimmune disease
- Anti-TPO, anithyroglobulin, antimicrosomal immunoglobulin G (IgG)
- personal/family history
- more common in women
- HLA subtypes DR3 and DR5
- Lymphocitic infiltration with Hurthle cells
- smooth, nontender, goiter
- firm, nonpitting edema in legs (pretibial myxedema)
- risk of pernicious anemia
Eurthyroid
Single Nodule (thyroid neoplasm)
Multicellular Goiter
Hyperthyroid
Subclinical
-Low TSH
-Normal FT4
-at risk for hypothyroidism
Secondary
-High TSH
-High FT4
Pituitary Adenoma
-overproduction of TSH secretion by pituitary gland
-stimulates thyroid to produce T3/T4
Primary
-Low TSH
-High FT4
Diffuse Uptake Scan
Grave's Disease
- 80% of cases
- family history, autoimmune condition
- smooth diffuse goiter
- Type 2 hypersensitivity reaction
- HLA subtypes B8 and DR3
- Anti-TSH receptor antibodies (IgG)
- thyroid biopsy
- diffuse hypertrophy and hyperplasia
- more crowded
- vascular congestion
- pretibial myxedema
- Exophthalmos positive
Hot Nodules/Nodular Scan
Toxic multinodular goiter
- uncommon
- Plummer's Disease
- seperate nodules develop throughout gland
- follicular cells distended with colloid in uneven or patchy manner
Toxic Follicular Adenomas
uncommon
Reduced Scan
Exogenous
Nonthyroid Secretion of Thyroid Hormone
- rare ovarian tumor struma ovarri
- monodermal teratoma
- mature thyroid tissue
Factitious Thyrotoxicity
-drugs used to treat hypothyroidism for weight loss
-also suppress TSH
-Low TSH, elevated T3/T4
Thyroiditis
Autoimmune
Silent lymphocytic
-painless goiter
-often as asymptomatic as Hashimoto
-50% transient with full recovery; 50% develop permanent hypothyroidism
Pospartum
-transient, self-limited variant of hashimoto
Infectious
Subacute Granulomatous (de Quervain) thyroiditis
-painful goiter
-self limited with recovery after few weeks
-precipitated by viral infection
-symptoms of hyperthyroidism
-pain managed with NSAIDs or corticosteroids
-inflammation of thyroid and sudden release of thyroglobulin
-second most common type