par Caterina Calabretta Il y a 8 années
361
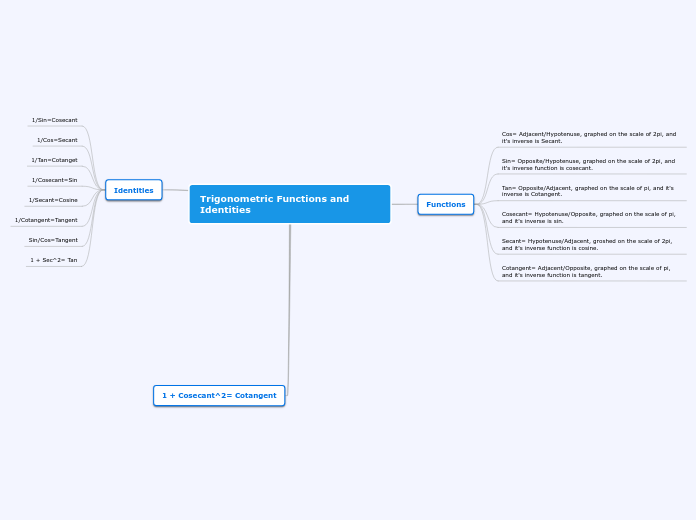
Trigonometric Functions and Identities
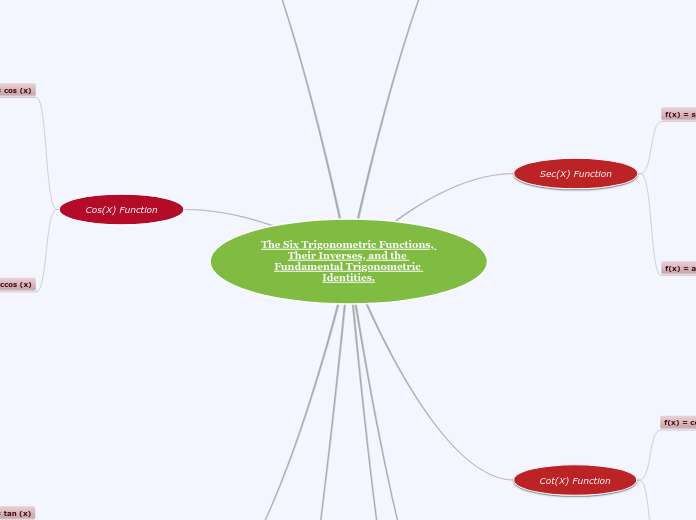
Trigonometric functions and identities are fundamental concepts in mathematics, often used to relate the angles of a triangle to its side lengths. These functions include sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, and cosecant, each with specific relationships and properties.