UNIDAD 2 PROBLEMATICA AMBIENTAL
The part of speech is a category to which a word is assigned according to its syntactic functions. In English the main parts of speech are noun, pronoun, adjective, determiner, verb, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection.
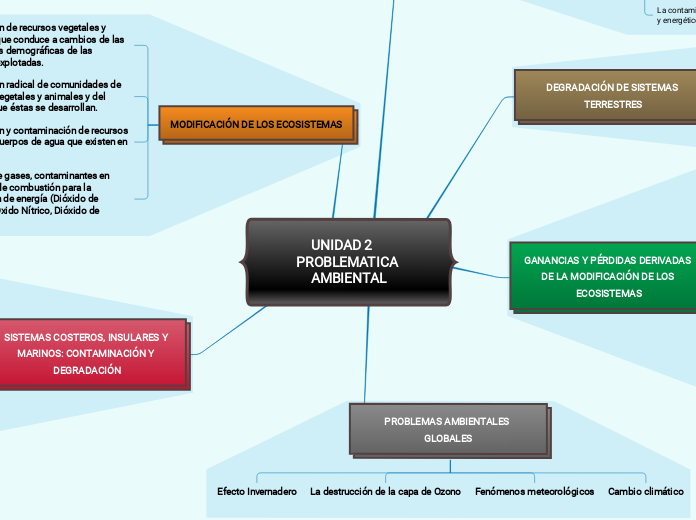
SISTEMAS COSTEROS, INSULARES Y MARINOS: CONTAMINACIÓN Y DEGRADACIÓN
An adverb is used to describe a verb, but it can also describe an adjective or another adverb.
Adverbs normally help paint a fuller picture by describing how something happens.
Los ecosistemas marinos se han visto afectados por distintas cosas, como:
La pérdida de manglares y arrecifes de coral.
La demanda mundial creciente de alimento para el consumo humano de las especies sometidas.
Materias primas extraidas del mar:
Minerales
Sales
Gas
Petróleo
MODIFICACIÓN DE LOS ECOSISTEMAS
A numeral is a word or phrase that describes a numerical quantity.
Some theories of grammar use the word 'numeral' to refer to cardinal numbers that act as a determiner to specify the quantity of a noun, for example the 'two' in 'two hats'.
Emisión de gases, contaminantes en procesos de combustión para la generación de energía (Dióxido de Carbono, Óxido Nítrico, Dióxido de Azufre)
Explotación y contaminación de recursos hídricos (cuerpos de agua que existen en el planeta)
Destrucción radical de comunidades de especies vegetales y animales y del suelo en que éstas se desarrollan.
One, two..
Explotación de recursos vegetales y animales que conduce a cambios de las densidades demográficas de las especies explotadas.
Create sentences
First, second..
PROBLEMAS AMBIENTALES GLOBALES
An interjection is used to express emotion in a sentence.
Think of other interjections!
Cambio climático
Fenómenos meteorológicos
La destrucción de la capa de Ozono
Efecto Invernadero
GANANCIAS Y PÉRDIDAS DERIVADAS DE LA MODIFICACIÓN DE LOS ECOSISTEMAS
An adjective is a word that's used to describe a specific noun and to provide more detail to the listener.
Daños
Superlative adjectives demonstrate a higher level of comparison between entities.
El aumento de desigualdades entre grupos de población
La agudización de la pobreza para ciertas personas
La pérdida de capital natural
El aumento del riesgo de cambios no lineales o abruptos en los ecosistemas.
Ganancias
Expresses a comparison between two entities or groups of entities in quality or degree.
Infraestructura en hogares rurales
Empleos de agricultura, pesca y cultivos
DEGRADACIÓN DE SISTEMAS TERRESTRES
A noun is defined as a person, place, thing or idea. Proper nouns always begin with a capital letter. Common nouns, which are general words, such as 'cars,' are not capitalized.
Desertificación
Compound nouns are words where two nouns have been stuck together to make a new noun. Compound nouns should be written as one word, without a hyphen.
Erosión del suelo
A noun which refers to a group of things/people.
Impactos por contaminación de sobreexplotación humana.
Countable nouns are nouns that can be counted, even if the number might be extraordinarily high.
Uncountable nouns are nouns that come in a state or quantity which is impossible to count; liquids are uncountable, as are things which act
like liquids.
Impacto por cambio de uso de suelo
Proper nouns are the names of specific people or places. They should always begin with a capital letter.
SISTEMA DE AGUA DULCE: INSUFICIENCIA Y EXTRACCIÓN
A verb is an action word or 'doing' word that signifies movement in some way.
Las principales causas del estrés hídricoa nivel global son:
A linking verb connects the subject with a word that gives information about the subject, such as a condition or relationship.
La contaminación por usos industriales, mineros y energéticos.
La falta de tratamiento de las aguas residuales
La demanda agrícola e industrial
Las principales causas del estrés hídricoa nivel global son
las zonas pobladas pueden padecer de situaciones de estrés hídrico
A verb with its own meaning: a verb that is not an auxiliary verb.