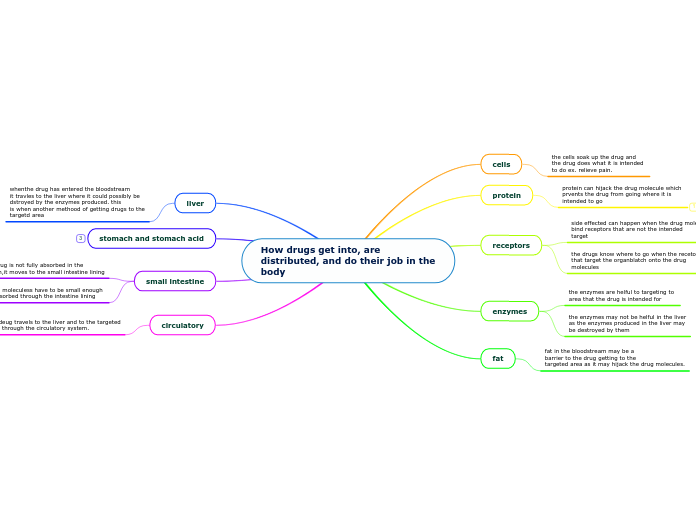
viruses
Types of viral infection
viruses and cancer
metastasis
anaplasia
neoplasia
tumor
infection in eukaryotic cells
transformation to malignant cell
infection in bacteria and Archeae
Archeae Viruses
lysogenic conversion
virion structure
virion genome
circular
Segmented
RNA
DNA
virion enzymes
viral envelopes
viral envelope protein
Subtopic
animal virus envelope
flexible, membranous layer
capsid
complex symmetry
icosahedral
helical
structure
Envelopes
contain nucleocapsid (DNA and RNA)
Prions
Neural loss
Proteinaceous Infectious Particle
viroids and satellites
encode one or more gene products
infectious nucleic acids (DNA / RNA)
requires host cell
do not encode gene
infectious agents of closed, circular ssRNAs
Cultivation and Enumeration of viruses
hosts for
plant viruses
plant protoplast cultures
plant tissue cultures
animal viruses
embryonated eggs
cytopathic effects
tissue cultures
bacterial and Archaea
agar cultures
requires inoculation of appropriate living host
Viral multiplication
virion release
assembly
synthesis stages
viral entry and uncoating
Attachment (Adsorption)
mechanism
Accelular Agents
prions
satellites
viroids
eukaryotic viruses
bacteriophages
virion
nucleocapsid (DNA and RNA)
size: 10-400nm