par LARRENZO GATLIN Il y a 1 année
89
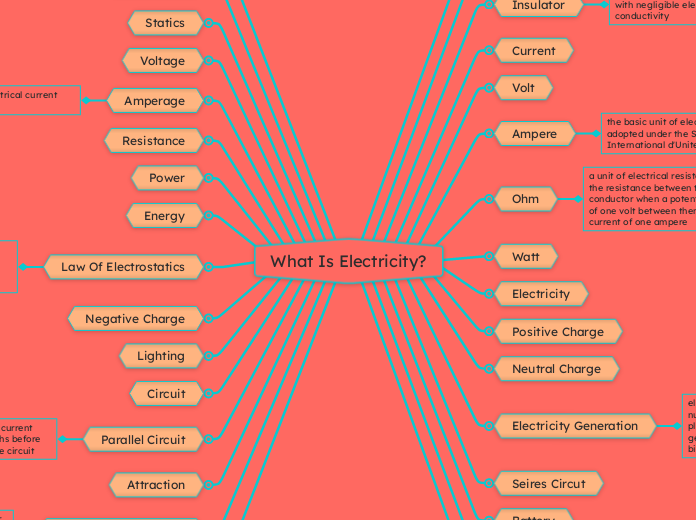
What Is Electricity?
Electricity is a fundamental force that powers countless aspects of modern life. It involves various concepts such as voltage, which measures the potential difference between two points, and current, which is the flow of electric charge.