par Nikolina Nasirudin-Hosein Il y a 2 années
343
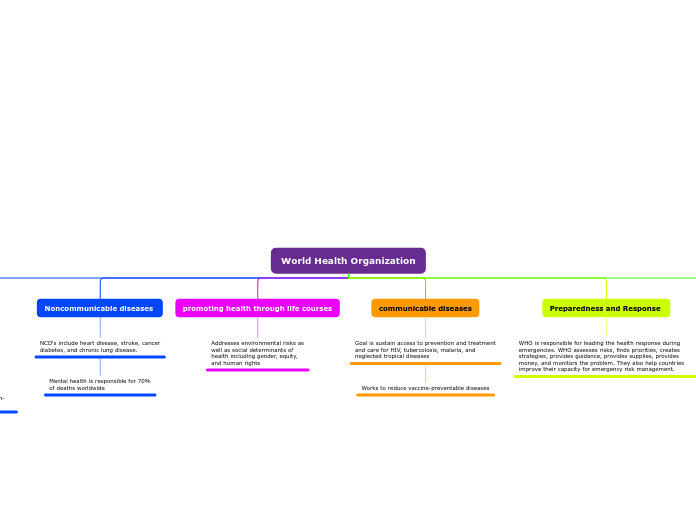
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) plays a vital role in ensuring the efficacy of global health systems and programs. It is tasked with gathering reliable data on global health situations, which is crucial for decision-making, resource allocation, and monitoring.