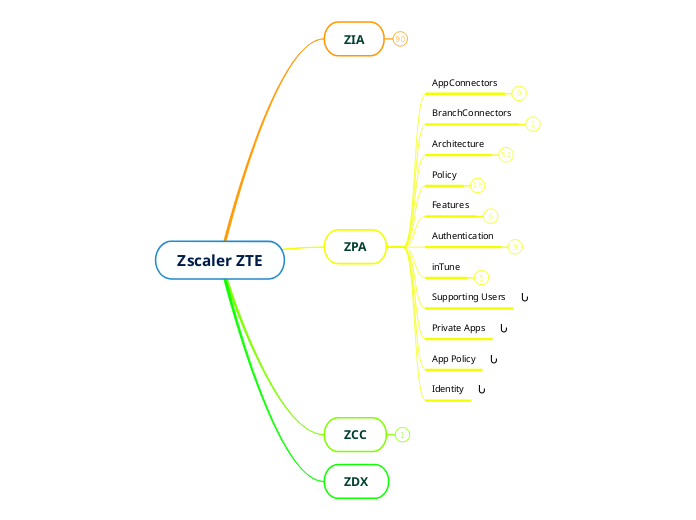
Zscaler ZTE
ZDX
Connect Users to ZTE
ZPA
Identity
App Policy
Private Apps
Supporting Users
inTune
InTune for IOS using SCEP
IOS v13 enabled SCEP with SSO (extension)
KDC discovery (location based) enables tighter scope
IOS v8 enabled SCEP with SSO
Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol
Admin SSO
Azure AD with SCIM
Okta
Azure AD
Test config, import attributes
3 Complete IdP setup in ZPA
2 Add ZPA Enterprise App in AAD
1 Add new IdP in ZPA for Use auth
Features
User Portal
Machine Tunnels
Browser Access
CNAME record
BA certificate
Best Practice & Troubleshooting
Principles & Evolution
Access Policy Building blocks
Operands
ZCC / BA
Select SAML / SCIM attribute values
Select App Segments
Select Segment Groups
Select ZCC posture profiles
Conditions
SAML / SCIM attributes
Segment Groups
App Segments
Client Connector Posture profiles
Client Connector Trusted Networks
Machine Groups
Client Types
Architecture
Public Service Edge
Private Service Edge
Configuration
Recommendation
create a subordinate CA for the Private Service Edges
use the same root CA as the one used for the Client Connector users
Requirements
Private to Public
Multiple trusted networks
Failover
Relay
Hybrid
External Users/Branch Office
Internal Users
Activation
Common use cases
Branch
Local SE
Hybrid workforce
On-prem
2
1
Why?
BYOE
Process
4 Upload signed CSRs to ZPA
upload signed CSR for ZCC
upload signed CSR for AppConnector
3 submit CSRs to root CA for signing
each CSR (ZCC, App) to be signed by CA
2 generate CSRs for client and App connectors (each)
1 upload root CA certificate
upload the cert into ZPA instance
export root CA cert from enterprise private CA
Double Encryption
Useful if legacy apps do not encrypt data transport (ie telnet, http)
used when traffic is encrypted as it transits ZPA enfrastructure
use enterprise CA to establish trust for ZPA connections
Subordinate CAs created in ZPA (signed by Enterprise private root CA)
The private keys never leave the ZPA CAs
create subsidiary CA for App Connectors
create subsidiary CA for Client Connectors
Bring Your Own Encryption
Best Practices
Privacy
BranchConnectors
Server to Server/Client
AppConnectors
Installation (Azure)
Deployment
ZIA tunnels
IPSEC / GRE
DMZ with split DNS
DMZ
Explicit Proxy
Concentrates and terminates the ZCC tunnels in the DC
ZCC Client to Server via the AppConnector
ZIA
Security
Monitoring
Issues
Policy
Troubleshooting
User Auth
Internet
Network
3 Authentication
Location
User
Upon sucessful authentication, appropriate policy is enforced
User is challenged for authentication
2 Policy Configuration
Policies
Administrator creates policy for groups or users
1 Provisioning
Users, groups and departments are provisioned on the cloud
Administrator configures authentication profile
departments
used for policies and reporting
users can only belong to one department
no limit to users in a department
groups
users can belong to <128 groups
no limit to users in a group
Methods
manual
Zscaler hosted DB
CSV import
SAML auto-provisioning
LDAP bind
Zscaler Authentication Bridge (ZAB)
Fundamentals
Access Control
File Type
URL & Cloud App
Web Security
Cloud Sandbox
Cloud Firewall
ATP
Malware Protection
Data Protection
CASB
DLP
HA
Traffic Forwarding
Explicit Proxy / Mobile
PAC
ZCC
Transparent Proxy / Fixed
Surrogate IP
dynamic address
Dedicated Proxy port
IPSEC
Dead Peer Detection (DPD)
CIA
Authentication
PSK
Integrity
Confidentiality
IKE
Phase 2
set up SAs
PFS
renewal of SA keys
negotiate parameters
Phase 1
setup secure channel for Phase 2
authenticate peers
< 400 Mbps
static address
GRE
Technicals
GRE MSS = GRE MTU(1476) - IP(20) - TCP(20) = 1436
GRE MTU = WAN link MTU(1500) - IP(20) - GRE(4) = 1476
WAN link MSS = WAN link MTU - IP(20) - TCP(20) = 1460
WAN link MTU = 1500
no mechanism for tunnel failures
ensure no NAT, otherwise < 250 Mbps
<1 Gbps
Recommended
enable User authentication
enable Surrogate IP
tunnel web traffic via GRE without NAT
implement monitoring and automated tunnel failover
two GRE tunnels to two different DC in active/standby