order
class
phylum
superclass
sub phylum
groups
kingdom
species
domain
Three domains of life
Eukaryotic
- Eukaryote
- Resistant to antibiotics
animalia
- multicellular
- heterotrophic
- no cell wall
- have ability to move
- diploid
- digest food
- sexual reproduction
echinodermata
- Habitat: fresh and salt water; terrestrial
- Body Plan: The body of a roundworm is long, smooth and unsegmented. Three tissue layers; ecto, endo and mesoderm.
- Digestive System: Roundworms have a complete digestive system which means their digestive tract has 2 openings; a mouth to ingest food and an anus to egest waste.
- symmetry: Bilateral symmetry with an anterior end and a posterior end.
enoplea
platyhelminthes
- bilateral symmetry
- three tissue layer
- no coelom
- centralized nervous system and digestive system too.
turbellaria
New Zealand flatworm
monogenea
monogenetic flukes
cestoda
tapeworms
trematoda
liver fluke
mollusca
- Habitat: marine and fresh water; terrestrial
- Body Plan: Mollusks have a soft, unsegmented body and often move with a strong muscular foot on its ventral surface.
- The radula: Mollusks are well known for their tongue-like organ called the radula which has many rows of teeth and is used to scrape food from the surface of plants and rocks.
- Symmetry: bilateral
monoplacophora
neopilina galatheae
aplacophora
chaetodermia
cephalod
squid
bivalves
snails
gastropod
clams
chordata
- Habitat: marine, freshwater, or terrestrial
- Symmetry: bilateral
- Dorsal nerve cord.
- Chordates have a flexible, supporting rod or notochord on their dorsal side. In the invertebrates the notochord remains stiff and flexible. In the vertebrates, cartilage or bone replaces the notochord to form a supporting backbone
cephalochordates
amphioxus
urochordata
tunicates
ascidians
vertebrates
with a backbone
gnathostomata
have jaw
tetrapoda
fish
salmon
mammals
- warm blooded
- have hair and fur on their body
- feed milk to their babies
- do not lay eggs
- internal fertilization
lagomorpha
All lagomorphs are herbivores, which has shaped features of skull and dentition.
rabbits
artiodactyla
deer
carnivora
- All teeth are rooted and diphyodont
- A simple stomach “consisting of a single dilation of the alimentary canal”
- four or more toes
- molars are blade like, suited for cutting and grinding
bears
reptiles
- dry skin covered with scales
- two pairs of legs
- cold blooded
- lay eggs
- three chambered heart
- ectothermic
turtle
aves
- endothermic
- forelimbs modified into limbs
- heart four chambered
parrot
amphibia
frog
pisces
osteichthyes
eel
chondrichthyes
shark
agnathans
lacks jaw
cyclostomata
arthropod
- Habitat: arthropods are found in all environments.
- Body Plan: Arthropods have a segmented body with paired jointed appendages that provide excellent movement for walking, swimming, flying, grabbing, fighting, digging and biting just to name a few. In most arthropods the body is divided into a head, abdomen and thorax.
- Exoskeleton: The outside skeleton of arthropods is made of chitin which protects the soft body of this animal and prevents water loss allowing them to live successfully on land.
- Symmetry: Bilateral
chelicerates
pycnogonida
nymphon
merostomata
horseshoe crab
arachnida
scorpion
hexapod
entognatha
springtail
insecta
ant
crustacea
brachiopoda
composita
maxillopoda
copepod
ostracoda
podocopida
malacostra
crab
annelids
- digestive tract
- body segmentation
- coelom inside the body to surround or contain the organs of the body like digestive tract.
- closed circulatory system like humans
hirudinea
leech
oligochaeta
earthworm
polychaeta
lugworm
cnidaria
- radical symmetry
- 2 tissue layers
- muscle tissues and nervous tissues
- gastrovascular cavity help in digestion and circulation.
- nematocysts( no jaws)
cubozoa
sea wasps
hydrozoa
hydra
anthozoa
coral
scyphozoa
jelly fish
porifera
- asymmetrical
- no tissues
- organized as an assemblage of different kinds of specialized cells.
- skeletol lacking
- asexual or sexual reproduction
- no organs
- consist of only two layers
demosponge
plants
- Multicellular
- Photosynthetic
- alternation of generations
- develop from embryos
- product of sexual fusion
- arise from multicellular structures in the maternal tissues
nonvascular
- plants appear leafy but lack true stems, roots or leaves.
- lack vascular tissues
- found in moist habitats
- small
hepaticpphyta
liverworts
porella
anthocerophyta
hornworts
Hornworts are a group of non-vascular plants constituting the division Anthocerotophyta. The common name refers to the elongated horn-like structure.
bryophyta
mosses
Mosses are small flowerless plants that typically grow in dense green clumps or mats, often in damp or shady locations.
sphagnales
vascular
- vascular tissues
- have leaves called fronds
- moist habitats
- can be almost any size
- transports food and water
seeded
- zygote is protected in a seed
- pollination replaces the sperm cell swimming to the egg
- gametophytes is much reduced and are not free living
gymnosperms
- naked seeds
- sporophytes produce both male and female cones
gingkophyta
ginkgoales
gnetophyta
gnetum
cycadophyta
cycadales
coniferophyta
pinales
angiosperm
- reproduction takes place within the the flower
- gametophytes are microscopic
- sporophyte is the dominant part of the life cycle
flowering plants
magnolids
seedless
- do not produce seeds
- leaves are called fronds
- strong cell walls provide strength and stability
- grow in moist places
- sporophyte is the important part of life cycles
pterophyta
ferns
ostrich fern
lycophyta
club mosses
lycopodiopsida
fungi
- usually not motile
- reproduce through spores
- eukaryotic
- bot sexual and asexual
- have cell walls composed of chitin
Basidiomycota
Sexual reproduction in Basidiomycota takes place in the fruiting body, in specialized structures called basidia. The basidia is itself formed by plasmogamy between mycelia from two different spores.
mushrooms
ascomycota
Sexual reproduction in the Ascomycota leads to the formation of the ascus, the structure that defines this fungal group and distinguishes it from other fungal phyla
yeast
zygomycota
Zygomycota, a small group in the fungi kingdom, can reproduce asexually orsexually, in a process called conjugation. The identifying characteristics of the Zygomycota are the formation of a zygospore during sexual reproduction and the lack of hyphalcell walls except in reproductive structures.
Rhizopus stolonifer
deuteromycotes
Only their asexual form of reproduction is known, meaning that this group of fungi produce their spores asexually, in the process called sporogenesis
aspergillus
aspergilus niger
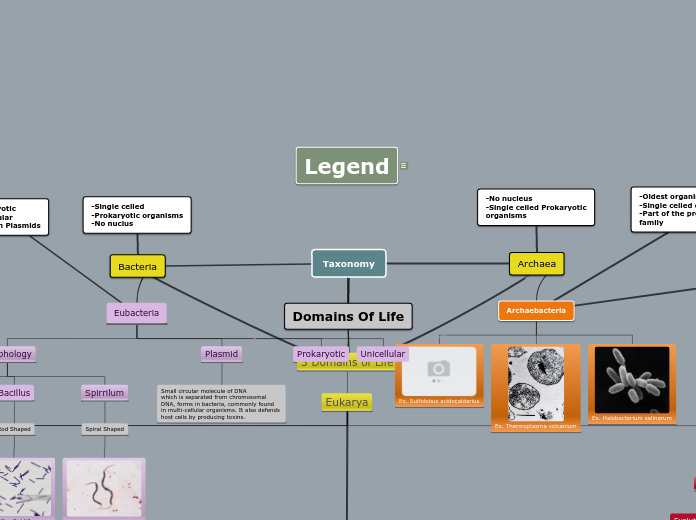
Archae
- Prokaryote
- Sensitive to traditional bacteria.
- Unicellular
- Reproduce asexually
- lack nuclei
- multiple by binary fission
protista
- most diverse kingdom
- all are aquatic
- motile
- unicellular (some are multicellular)
- Large,complex cells
- can reproduce asexually or sexually
- move using cilia, pseudopods or flagella
plant like
algae
Autotrophic and carry out photosynthesis
Rhodophyta
non motile
red algae
animal like
protozoa
- heterotrophic
- lack cell wall
sacordinians
pseudopods,flagella or cillia help to move
Amoeba
move using pseudopods
fungus like
molds
slime molds
when food is short supply, they start moving as a single body.
red raspberry slime mold
archaeabacteria
- unicellular
- autotroph or heterotroph
- have cell walls
- most can't move
halobacteria
euryarchaeota
crenarcheota
Subtopic
Bacteria
- Prokaryote
- lives in more extreme environment than bacteria such as hot springs, near sea floors, alkaline, waters. Some of them live in saline environment such as dead sea. they live without oxygen. .
- not sensitive to antibiotics that effect bacteria.
- multiple by binary fission
- lack nuclei
- Autotroph or heterotroph
eubacteria
- Unicellular
- Prokaryote
- Autotroph or heterotroph
- Most are beneficial or some are harmful
rod shaped
spirillum
spiral
bacillus
spherical
coccus