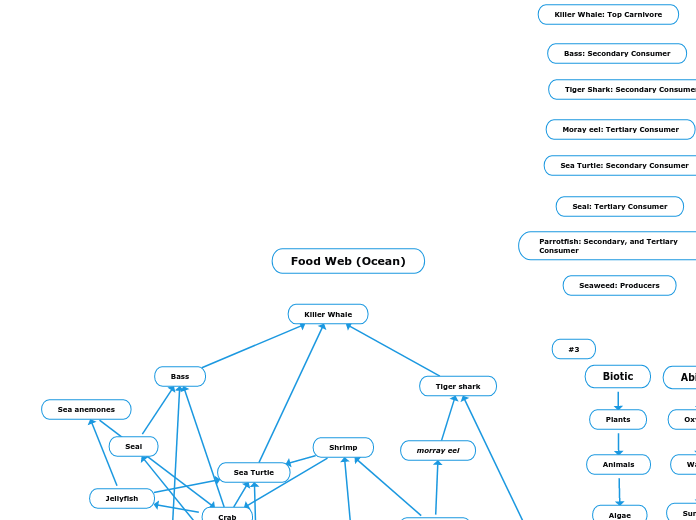
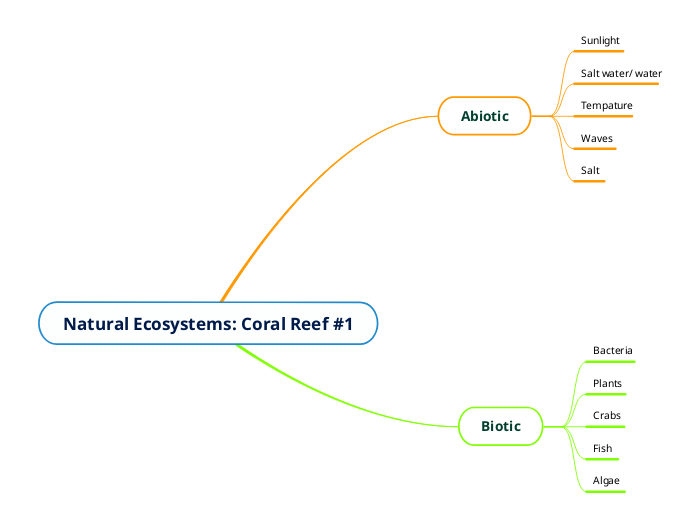
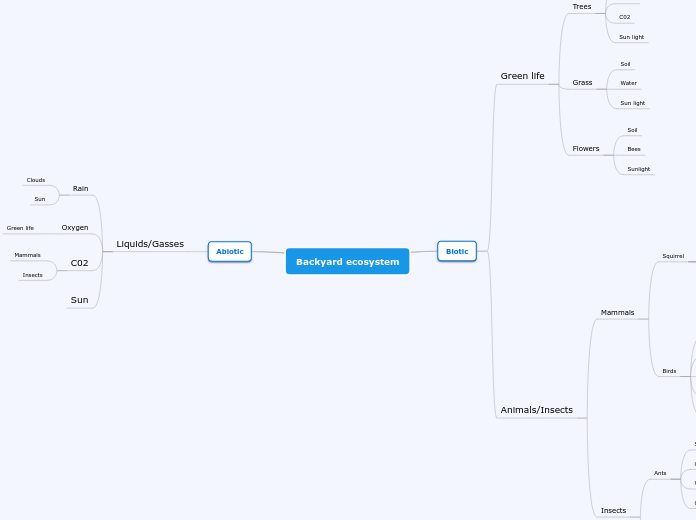
Boreal Forests/Taiga
Can be found in Canada, Alaska, and parts of the northern contiguous United States. Sweden, Finland, much of Russia from Karelia in the west to the Pacific Ocean (including much of Siberia), much of Norway and Estonia, some of the Scottish Highlands, some lowland/coastal areas of Iceland, and areas of northern Kazakhstan, northern Mongolia, and northern Japan.
Biotic factors: Many conifer trees (evergreens with needles) grow in the taiga, eg: Evergreen spruce, fir, pine, and deciduous larch, or tamarack. Some broadleaf deciduous trees and shrubs also grow in Taiga, most common are alder, birch, and aspen.
Abiotic factors:
ECOREGIONS
West Siberian taiga
Urals montane forest and taiga
Trans-Baikal conifer forests
Scandinavian and Russian taiga
Nordic Forest
Sakhalin Island taiga
Okhotsk-Manchurian taiga
Northeast Siberian taiga
Iceland boreal birch forests and alpine tundra
Iceland clifs
Kamchatka
Kamchatka taiga
Kamchatka-Kurile taiga
Kamchatka-Kurile meadows and sparse forests
East Siberian taiga
Watson Highlands taiga
Southern Hudson Bay taiga
Northwest Territories taiga
Northern Cordillera forests
Northern Canadian Shield taiga
Muskwa-Slave Lake taiga
Mid-Canada Boreal Plains forests
Interior Alaska-Yukon lowland taiga
Midwest Canadian Shield forests
Eastern Canadian forests
Copper Plateau taiga
Cook Inlet taiga
Alaska Peninsula montane taiga
ESSENTIAL
ECOREGION ESSENTIAL
Subclimaxes
Larch forests
Larch forests claim the thin, waterlogged substrate in level areas underlain with permafrost. These forests are open with understories of shrubs, mosses and lichens. In Alaska stands of Larix larichina are localized phenomena, but in Siberia east of the Yenesei River the extreme continentality and nearly continuous permafrost give rise to vast areas dominated by Larix dihurica.
Pine forests
Pine forests, in North America dominated by the jack pine (Pinus banksiana), occur on sandy outwash plains and former dune areas. These are low nutrient, droughty substrates not tolerated by spruce and fir.
SCANDINAVIAN AND RUSSIAN TAIGA
FUNGI
MUSHROOMS
False Morel
(Gyromitra esculenta)
Chantarelle
(Cantharellus cibarius)
Pine cep
(Boletus pinophilus)
Cep
(Boletus edulis)
SHELF FUNGI
Antrodiella faginea
Antrodiella Citrinella
Haploporus odorus
Fomitopsis rosea
Phellinus viticola
Phellinus ferrugineofuscus
Phellinus lundellii
Phellinus chrysoloma
LICHENS
Horsehair Lichen
(Bryoria fremontii)
Witch's Hair Lichen
(Alectoria sarmentosa)
Reindeer Lichen
(Cladonia rangiferina)
Snow Lichen
(Stereocaulon)
Wolf Lichen
(Letharia vulpina)
Alectoria sarmentosa
Horsehair Lichen
(Bryoria)
Old Man's Beard
(Usnea)
Iceland Moss
(Cetraria Islandica)
Tree Lungwort
(Lobaria pulmonaria)
MOSSES
Peat Moss
(Sphagnum Angustifolium)
Peat Moss
(Sphagnum warnstorfii)
Long-Leaved Fork Moss
(Paraleucobryum longifolium)
PLANTS
CARNIVOROUS PLANTS (BOG)
Common Sundew
(Drosera rotundifolia)
English Sundew
(Drosera anglica)
FERNS
Ostrich Fern
(Matteuccia struthiopteris)
Poa glauca
Rusty Woodsia
(Woodsia Ilvensis)
Maidenhair Spleenwort
(Asplenium trichomanes)
(Asplenium septentrionale)
Common Lady-Fern
Worm Fern
(Dryopteris filix-mas)
HERBACEOUS / FLOWERS
Lapland Lousewort
(Pedicularis lapponica)
Liverwort
(Anemone hepatica)
Cudweed
(Galium triflorum)
Red Alpine Catchfly
(Silene suecica)
Sticky Catchfly
(Lychnis viscaria)
Yellow Coralroot
(Corallorhiza trifida)
Bog Star
(Parnassia palustris)
Great-spurred Violet
(Viola selkirkii)
Bog-Rosemary
(Andromeda Polifolia)
Lapland Buttercup
(Ranunculus lapponicus)
Alpine Sow-thistle
(Cicerbita alpinaA)
Small Cow-wheat
(Melampyrum Sylvaticum)
Fireweed
(Chamaenerion angustifolium)
Labrador Tea
(Rhododendron tomentosum)
Twinflower
(Linnaea borealis)
ORCHIDS
Lady's Slipper
(Cypripedium guttatum)
Lady's Slipper
(Cypripedium calceolus)
Frog Orchid
(Coeloglossum)
Fairy Slipper
(Calypso bulbosa)
Bottled Sedge
(Carex rostrata)
Black Sedge
(Carex Nigra)
Velvet Bent
(Agrostis canina)
Common Bent
(Agrostis capillaris)
Wood Bluegrass
(Poa nemoralis)
Calamagrostis phragmitoides
Lappland Reedgrass
(Calamagrostis Lapponica)
Cotton Deergrass
(Trichophorum alpinum )
Deergrass
(Trichophorum cespitosum )
Tussock Cottongrass
(Eriophorum Vaginatum)
Cottongrass
(Eriophorum angustifolium)
Sweet Grass
(Hierochloe Odorata)
Low Shrubs
Raspberry
(Rubus idaeus)
Crowberry
(Empetrum nigrum)
Cloudberry
(Rubus chamaemorus)
European Blueberry
(Vaccinium myrtillus)
Dwarf Cornel
(Cornus suecica L.)
Red Baneberry
(Actaea erythrocarpa)
Cranberry
(Vaccinium oxycoccos)
Small cranberry
(Vaccinium microcarpum)
Bearberry
Lingonberry
(Vaccinium vitis-idaea)
Betula humilis Dwarf Birch
(Betula Nana)
Common Heather
(Calluna vulgaris)
High Shrubs
Grey Willow
(Salix cinerea)
Dark-leaved Willow
(Salix Myrsinifolia)
Found in Sweden (Muddus/Muttos national park)
DWARF TREES
Common Juniper
(Juniperus communis)
Pussy/Grey Willow
(Salix Cinerea)
Silver Birch
(Betula Pendula)
White Birch
(Betula Pubescens)
Found in Sweden (Skuleskogen)
Grey Alder
(Alnus Incana)
Siberian Fir
(Abies sibirica)
Siberian larch
(Larix sibirica)
Mostly found in Siberia but there are some instances in Scandinavia
Siberian spruce
(Picea obovata)
Norway Spruce
(Picea Abies)
Scots pine
(Pinus Sylvestris)
TERRAIN TYPES
FIRES
MEADOWS
FORESTS
WINTER
FALL
SPRING
MOUNTAIN SLOPES
PEAT BOGS
BOREAL ZONES
SOUTHERN BOREAL
HIGH BOREAL
Permafrost
Eastern Canadian Shield taiga
mixed with
Rhododendron
Laurel
Larix laricina
Black spruce, Picea
Central Canadian Shield forests
south-facing areas
Balsam poplar
Fir, Abies
Aspen populus
dominant
Paper birch
Black spruce
BIOME ESSENTIAL
COMPONENTS
For this biome
most typical and representative species of:
trees
shrubs
grass
mosses
lichens
soil
rocks
other
source
https://php.radford.edu/~swoodwar/biomes/?page_id=92
https://www.activewild.com/taiga-plants/
SOIL
Bogs (muskeg)
MOSS
Lichens
Sphagnum
FLOWERS
Genus Drosera
Labrador Tea
Twinflower
Fireweed
Grass of Parnassus
GRASS
Eriophorum gracile
Cotton grass
Cyperaceae
SHRUBS
Berries
Blueberries
Bearberries
Lingonberries
Heath shrubs
Juniperus communis
Betula nana
distrib.map
TREES
Needleleaf, coniferous (gymnosperm) trees are the dominant plants of the taiga biome. A very few species in four main genera are found: the evergreen spruce (Picea), fir (Abies), and pine (Pinus), and the deciduous larch or tamarack (Larix). In North America, one or two species of fir and one or two species of spruce are dominant. Across Scandanavia and western Russia the Scots pine is a common component of the taiga.
Soil: Podzolization occurs as a result of the acid soil solution produced under needleleaf trees. The main soil order associated with the taiga is spodosol.
DECIDUOUS
Larix sibirica
Willow
Larix decidua
Although they are conifers, larches are deciduous trees that lose their needles in the autumn.
Aspen
Eastern Cottonwood
(Populus deltoides)
Balsam Poplar
(Populus balsamifera)
Trembling Poplar
(Populus tremuloides)
Birch
Paper birch
(Betula papyrifera
)
Betula pendula
Betula pubescens
Alder Alnus
CONIFEROUS
Siberian Cedar
Tamarack, Red Larch
(Larix laricina)
Spruce
Picea obovata
Norway Spruce
(Picea abies)
Black Spruce
(Picea mariana)
White spruce
Pine
Lodgepole Pine
(Pinus contorta)
Subtopic
Jack pine
Scots pine
pine
Fir
Balsam Fir
(Abies balsamea)
Fir
(Abies Balsamea)
Siberian fir
(Abies sibirica)
GENERAL LOOK
PALEARCTIC
NEARCTIC