a JOSELYN CRISTINA MU�OZ ALBUJA 4 éve
226
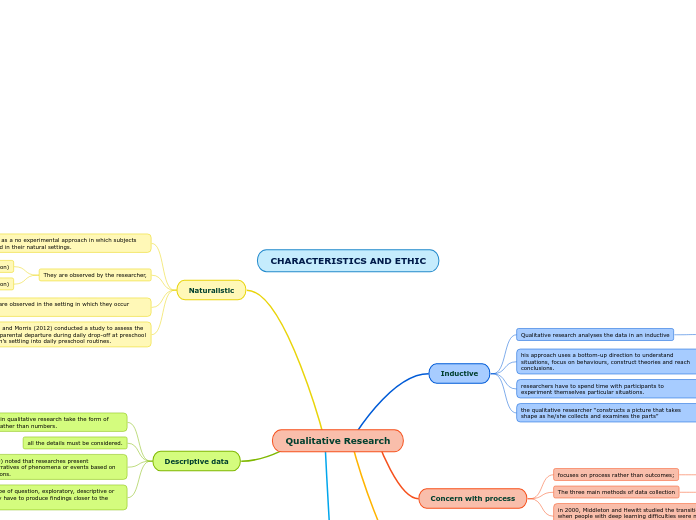
CHARACTERISTICS AND ETHIC
Qualitative research is a method that places a strong emphasis on understanding processes rather than merely focusing on outcomes. It employs an inductive approach, meaning that it builds theories and concepts from the ground up based on gathered data.