a james cosmai 13 éve
878
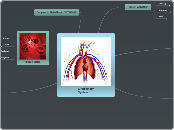
Circular System
The circulatory system is a complex network responsible for absorbing and distributing essential nutrients and gases throughout the body. It comprises the heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic system.
a james cosmai 13 éve
878

Még több ilyen
consists of water and disolved minerals such as glucose
oxygen poor blood enters heart from body
largest vein
Blood goes from heart to lungs
takes blood from heart to all parts of body
largest artery in the body
Mostly water mixed with some nutrients
Liquid part of blood
thrombocytes
Help form blood clots
luekocytes
figh infection
Erthrocytes
contain Hemoglobin