a Louis van Rooyen 10 hónapja
60
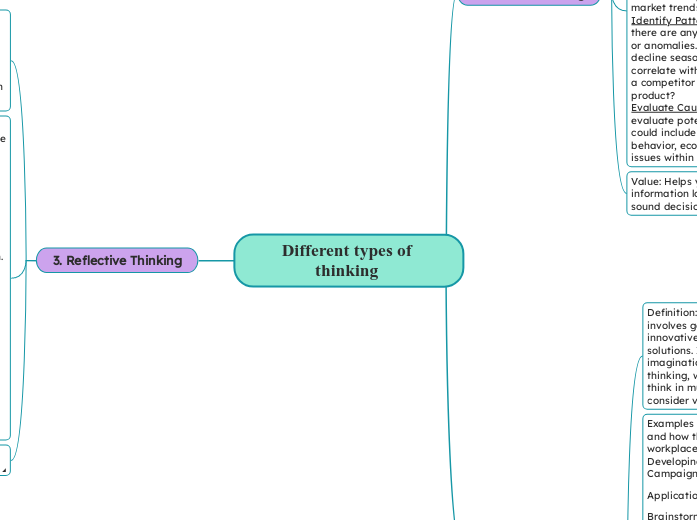
Different types of thinking
Reflective thinking involves looking back on one’s decisions and experiences to learn and improve continuously. In a workplace setting, it can be applied through techniques such as brainstorming, mind mapping, and prototyping.