a Torotane Ramandeep 1 éve
101
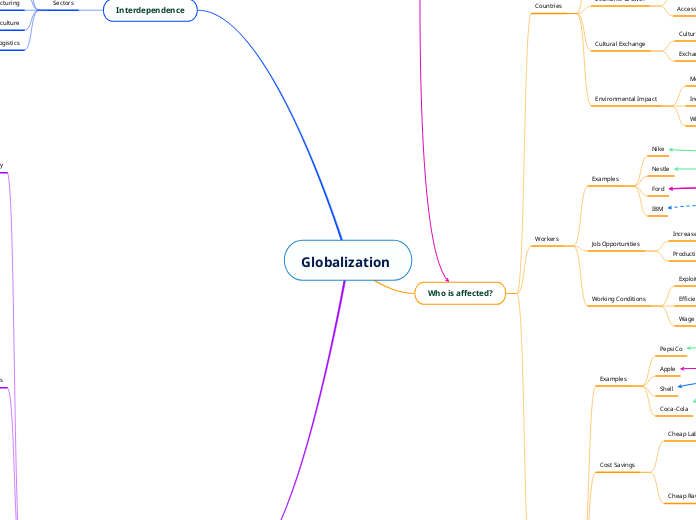
Globalization
The interconnectedness of workers, companies, countries, and consumers underpins the global economy, driving productivity and functioning across multiple sectors. Globalization plays a significant role in shaping job opportunities and employment rates, influencing the conditions under which workers operate.