National Unity
Canada's Role In The World
The Treaty of Versailles
Vimy Ridge
Outcome
It was celebrated as
a new coming of age
for the Canadians
First allied victory since the
beginning of the war
Four Victoria Crosses were given out
at the end of this battle
Nearly 10,000 casualties
in total in this battle
3,598 Canadians were killed
Ridge was conquered
Canadians won the battle
Background of the battle
Battle was led by Sir Arthur Currie
Each soldier was given a
map of the ridge
'Soldiers knew the battle
field like the back of their hands'
Made his soldiers train over
and over for this specific battle
Implemented tactics learnt
in different battles into his own
Never lost a single battle
His tactics were what led
to ultimate success
Organized the troops in into
waves of attacks
Ridge was important because it
was a good strategic position.
It was great for both offensive
and defensive strategies.
Battle was fought through blinding
sleet and snow.
The British and French had already failed
to conquer this territory previously
The ridge was finally
captured from the Germans
All four of the Canadian divisions
fought together for the first time.
Took place on the western front in France
Battle
Often called the, 'Birth of Canadian
national pride and awareness.'
Happened in April, 1917
League Of Nations
The fall of the League Of Nations
Later countries began to come together
to make an organization that would be
far more successful than the League.
This new organization was named the
United Nations or the UN.
The league of nations failed to stop
WWII from occurring and as a result
was dissolved in 1946
Canada
Made Canada seem more important
as only the most powerful countries
were in the league.
Important because it gave Canada
a say in global issues
Had 3 seats in the league
Responsibilities
Deal with global welfare problems
Settle problems between countries
Prevent war
To maintain world peace
Founded after the Paris Peace Conference
Founded in 1919
Created after WWI
Minorities In Canada
Enemy Aliens
Sent into internment camps because they
were from the enemy countries. Canadians
believed that they would attack Canada
and so were sent into interment camps where
they were forced to do labour work.
Russians
From Enemy Side
Polish
From enemy side
Germans
From an enemy country
French Canadians
Didn't consider themselves
Canadians
Didn't want to be apart of Canada
WWI
Conscription
Lots of riots and marches were taken out
by the French
Raised lots of tensions in
Canada
French Canadians were ultimately forced
to got to war
Refused to go and fight
or be apart of the war
effort
Believed it to be a English war
didn't believe they should be
apart of the war
Chinese
Coming into Canada
Racially profiled
very regularly
Shops, stores and belongings
damaged on purpose by the
white living in their
neighborhoods
Made to work labour
jobs in Canada
Washing Dishes
Packing Fish
Hauling coal
Charged a head tax
Chinese Immigration Act
$50 upon arrival
Japanese
The Japanese that did come to Canada
belongings, homes, stores, companies
were destroyed or vandalized by the
white people already living there
Treated with lots of racism
An agreement passed in Canada
in the 1920's
Restricted immigration from Japan
to a 150 people each year
Many restrictions on Japanese
immigration in Canada
They had to pass many specifications
to even get here
Black Canadians
After WWI
Treated very cruelly
Many were lynched in the U.S
after the war
Their efforts in the war weren't
recognized back in Canada
During WWI
Were oppressed and racially
marginalized by the whites
at the time
Made artillery in factories
Built trenches
Would carry the dead
Few made it to the front lines
and got to fight
No.2 Construction Battalion
Not allowed in the battalions
that fought on the front
Put in battalions that
would build roads, and bridges
After the war
Treated very badly
Lost all of the freedom that
they had gained during the
war
Faced with lots of racism
Pushed away from
cities and other people
No rights to vote
During the war
Felt included for once
Lots of freedom
Given many rights
Allowed to fight in the war
Economy/Labour Relations
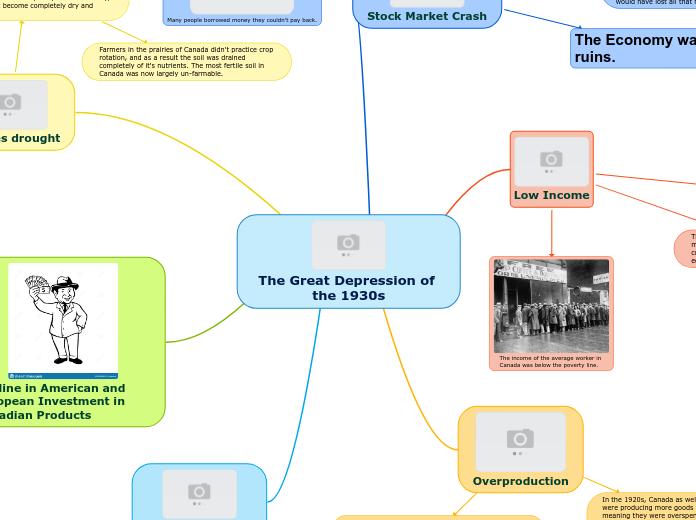
Stock Market Crash
Black Thursday
Stock market began to plunge
October 24, 1929
Prices of stocks and
companies began to drop
Black Tuesday
When the stock
market literally crashed
When the prices of stocks
were absolute zero
October 29, 1929
Happened because of how people
were misusing the stock market
The Great Depression
People at the time
Poor
Belongings had been
taken by the banks
No money
Were bankrupt
Had no food
Malnourished
Homeless
Living on the streets
also meant that diseases
were running rampid.
Happened as a result of
the stock market crash
Winnipeg General Strike
Strike
After the strike
Positive Effects
Worker equality eventually became very important
Lots of the workers' rights were later granted
Social and economic problems of the worker's
finally seen by government
Brought awareness to worker's rights
Forced to sign contracts saying
they would never join a union
Many had no jobs to return to
Became illegal to join a union
Federal Government
Governments actions towards the strike
Government broadens the definition
of sedition. (speech or action taken
to set people up against the
government.
Acts as a threat to other strike leaders
allows strike leaders to be arrested
Federal Immigration Act
Made to deport
British-born
immigrants
Federal employees forced
to come back to work or
face being laid off
to come back to work
or face being laid off.
Sets up meetings with the employers
and the Citizen's Committee of One Thousand
Government supports
the employers
Refuses to meet with the
strike committee though
Comes in to Winnipeg to help with the building
tensions between employers and employee's.
Strike committee
Formed to recognize the needs
of the worker's
Formed to organize the tactics of the strike
One Big Union (OBU)
Was all across Canada
Supported workers and their rights
Citizen's Committee of One Thousand was formed in response to the strike
Made up of the richest people in the city
Were against the strike and convinced
people against it.
ignored all workers' basic needs
Named all striker's 'aliens'
Actual strike
Bloody Saturday
2 strikers killed and 30 injured
Strike leaders put an end to the
strike to avoid further conflict
Saturday, June 21
Thousands of strikers had come out
to protest imprisonment of strike leaders
Special Police
2 strikers killed 30 injured
Attacked the strikers
Carried clubs and bats with spokes
Called in by the government
When the strike ended
The strike lasted 6 weeks.
25,000 to 35,000 workers walked out on strike
Happened Thursday, May 15, 1919
WTLC (Winnipeg Trades & Labour Council)
Had a poll on whether or not to actually strike
11,000 voted yes, while only less than 600 were
against it
Worker's Needs
A union
Wanted the right to bargain collectively
More rights at the workplace
More jobs
Most jobs had been taken over by women
Women had been kicked
out to make space for the
men entering the workplace
Higher wages
People were outraged that war profiteering individuals had a lot of money so they want money as well.
Workers wanted higher wages since the cost of living inflated. To keep up with the prices, they needed higher wages to support themselves and their families.
8 hour workday
They previously worked 12 hours a day.
Better working conditions
Unions
Protected worker's rights at the workplace
All unions for workers banned
Technology/Entertainment
Golf
Glenna Collett
American Hall of Fame
golfing champion
Claimed her first of six U.S.
championships in 1922
Bobby Jones
Most successful
amateur golfer ever to
compete on a national
and international level
Tennis
Helen Wills
Won 19 single championships
Won 2 Olympic gold medals
Won the Wimbleton
William Tilden
First American to win Wimbleton
Football
Red Grange
Made 2 famous touchdowns
Played in the NFL
Boxing
Jack Dempsey
He fought 83 bouts, won 66 (with 51
KO’s), lost 6 (with 1 KO), and drew 11
Baseball
Babe Ruth
Played for
Boston Red Sox
New York Yankees
Hit a total of 60 homeruns in 1927
Baseball, Hockey and Football
Lionel Conacher
'The Big Train'
Basketball
Invented by: Dr. James Naismith
Track and Field
The Matchless Six
Jane Bell
Ethel Catherwood
Myrtle Cook
Ethel Smith
Jean Thompson
Fanny Rosenfield
Percy Williams
Set record for 100 m in the Olympics
at 10.6 seconds
Sailboat Racing
The Bluenose
Undefeated champion of the International
Fisherman's Trophy
Hockey
Howie Morenz
Won the Stanley Cup twice
Scored 51 points from 1927 to 1928
Presented with the Hart Trophy
Airplane
Connected Canada because people
could now travel to different parts
of Canada more easily and quickly
Could bring supplies and needed
resources to isolated areas such
as the territories
Created travel across
further distances easier
Created jobs
'Bush Pilots'
Mainly people who flew jets
in WWI were pilots of these
planes
Commercial airplanes created after WWI
Telephone
Created
There was 1 telephone per four families
in the 1920's. By 1929 there were 3
telephones per four families
Invented by Alexander Graham Bell
Easier to contact people living
in more isolated areas
Brought Canadians together
The Edmonton Grads
502 wins and only 20 losses
Easier to contact family
Could contact people living
very far away
Model T
Car created by Henry Ford:
Also called the 'Tin Lizzie'
Uniting Canada
The car also increased mobile culture
which also meant that people traveled
more.
Made travel easier which meant that
people traveled more. This united Canada
because since travel was easier and cheaper
people started to travel more.
Cars meant building of roads,
motels, gas stations and such
things to accommodate these
cars
Created jobs for lots of people
Ended isolation of people living
in remote areas
Advantages
Didn't cost much to make
especially through the assembly
line system
Workers could be paid less
Fewer workers were needed
Was easy to manufacture
Only one colour and engine
were available
It was an incredibly popular way
to travel
Affordable for all people
Film
Famous Actors
Gloria Swanson
Douglas Fairbanks
Greta Garbo
Clara Bow
Mary Pickford
Rudolph Valentino
Charlie Chaplin
What they were like
Were blurry and had spots
Live music played in the background
Near the end of the 20's these films were
replaced by 'talkies,' films with sound.
Actors would wear a lot of make up
and had to exaggerate all of their actions
so that it was easier to understand what
was happening in the film.
Text was used in the background of
the movie so that audience would
understand what was going on.
Films were originally silent movies, no sound
Black and white
Popularity
It was amusing for people to watch
Helped people to have some leisure time
Radio
Brought families together because
they come together to listen to
games, news, music and drama's.
Drama
Sports
Foster Hewitt's: Hockey Night
News
Music
Jazz music
Jazz dances also popular at the
time
Changing Role Of Women
Flapper
Personality
Dancing/singing at clubs
Going to clubs
Smoking in public
Drinking a lot
dress
hair cut in a short bob
wore lots of makeup
lots of feathers on clothing
revealing clothing
heels
knee high socks
knee high skirts
Women of the roaring 20's were called flappers
These women put themselves
out there more than ever
Work
Women took on these jobs during the war.
When the men came back they had no jobs.
So they decided upon kicking the women out
of the workforce.
Women worked as
Bus Drivers
Factory workers
Tailors
Teachers
Nurses
Secretaries
Gaining Suffrage:
The right to vote
Military Voter's Act
Made so that the government would
get people to vote pro conscription
Women who had relatives
in the army could vote
Person's Case
Considered women as people
Decided that women were
eligible to sit in the senate
Rallies
Many women were beaten at
these rallies and jailed for voicing
thier concerns.
November, 1917 women rallying
outside the White House were
beaten and tortured by guards.
Women rallying for suffrage came
from all different parts of Canada.
All there for the same cause.
Women rallied a lot for their rights
specifically for suffrage
Rejection
The women's suffrage pleas
were rejected many times;
However this didn't stop
women from continuing to
fight. These women fought
no matter the circumstances.
Granted
Each province gave women
the right to vote in different years
Women gained the right to vote in 1928
People who fought for the right
The Famous Five:
A group of five women
who got together and fought
for the right to vote. They
made really big impacts
back then.
Irene Parlby
Women's activist
Canadian women's farm leader
Louise Crummy McKinney
First woman elected to a
legislature in the British Empire
First woman sworn into the
Legislative Assembly of Alberta
Women's rights activist
Canadian politician
Nellie McClung
Suffragette
Social activist
Politician
Canadian author
Henrietta Muir Edwards
Women's rights activist
and reformer
Emily Murphy
Leader of the Famous Five
Judge
FNMI
Treaties
Indian Act
Prohibited sale of alcohol to FN"s
FN's not allowed to speak their language
Prohibited sale of arms to FN's
Only FN's going to university with rights
Could move an entire reserve
Could take reserve property away
Created reserves
Could lease out parts of reserve to other people whenever needed
FN's not allowed to make political organizations
Renamed people on these reserves with European names
FN's not allowed to leave reserves without permission
Introduced residential schools
Denied any woman status
Banned traditional dances
Reserves
Location
Land couldn't be farmed
Camp couldn't be easily set up there
Camp land was muddy and uneven
Could be kicked off of reserves
whenever the government felt it was necessary
Far from any resources
Far from water any clean water
reserves and reserves in general
Far from other people
and essentially civilization
Life
No clean water
Sometimes no water at all
No resources for food to hunt
Couldn't practice culture
Totally controlled
Residential Schools
Many never made it out of these schools
many died in these schools
Experience
Education
American/European Way Of Life
Laundry work
Field Work
Cleaning
Cooking
Farmwork
Religion
Christianity
Halloween
Easter
Thanksgiving
Christmas
Jesus
Language
French
English
Trauma
Pushed out of culture
Not allowed to speak their language
Only allowed to speak English or French
Their long traditional hair was cutoff
All were kids had the same hair cut
Change of clothes
Made to wear European clothes
Taught new ways of life
'Killing the Indian in the child"
Savage
Abuse
Emotional
Cultural
Culture made to look bad
Forced out of culture
Identity
Made to forget who they were
Loose cultural ties
Assimilation
Cannot speak native language
No more cultural clothes
Family made to look bad
Verbal
Spoken to in a demeaning way
Yelled at
Psychological
Isolated
Physical
Given labour jobs
Beaten
Sexual
Raped
Molested
Intergenerational Trauma
Parents of children who had been taken
Children dead
Jailed for trying to get their kids back
Drugs
Substance abuse
Lost children: can't find their children
Committed suicide
Fell into depression
Graduates coming out of these schools
Some former students families didn't recognise
their children because of all the changes their
children had gone through.
Children didn't recognise their families either
Graduates didn't remember their family
Some already had children due to the rape
The survivors children grew up in
the same environments as their
parents and so they also grew up
homeless, addicted to drugs and
essentially bad people
Were left homeless