a Sierra Simioni 1 éve
70
Nuclear Energy
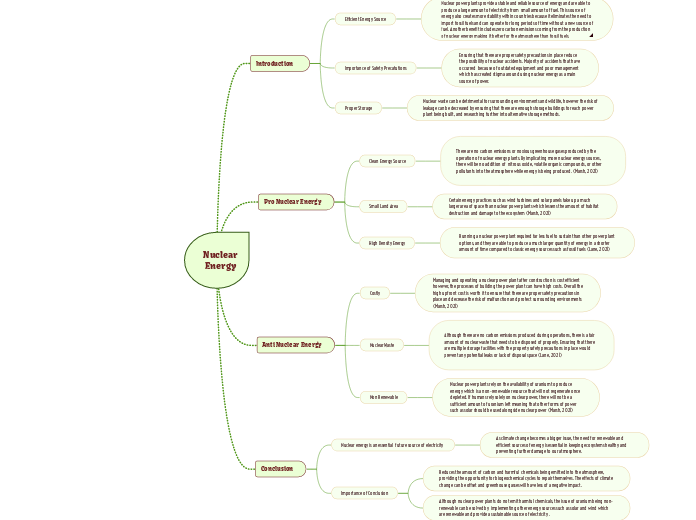
Nuclear energy presents a compelling option for future electricity needs, largely due to its high energy density and minimal land usage when compared to renewable sources like wind and solar.
a Sierra Simioni 1 éve
70

Még több ilyen