a Karilinn Sommers 7 éve
271
Origins of the US Constitution
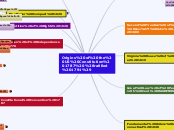
Origins of the US Constitution 1787 (ratified 1791)
Constitutional Convention 1787
Connecticut Compromise Plan July 1787
2 houses
House of Repr.
Senate
ONE Repr. per state
Proportional Gov't
Roger Sherman
New Jersey Plan June 1787
ONE house = ONE repr. from EACH state
William Patterson
Based on population
Each state to have 1 vote in Congress
Virginia Plan May 1787
3 Branches
Proposed strong central gov't
James Madison
Declaration of Independence 1776
People have right to replace bad gov't
Gov't gets power from people
Unalienable Rights
Petition of Rights 1628
Rights of commoners to have a voice in gov't
Mayflower Compact 1626
Gov't organized for good of people
Contract to self gov't
English Bill of Rights 1689
Right to trial
Right to petition gov't
No excess bails
Freedom of speech & debate
Fundamental Orders of Connecticut 1636
Framework for their government needed to be written and approved by representatives of the people
Powers & Limits of gov't
First written Constitution in Colonies that outlined how gov't worked
Great Law of Peace 12th Cent. HAUDENOSAUNEE
Benjamin Franklin + Albany Congress 1754
Women's Counsel = to Supreme Court
Separation of Powers
2 houses & Grand Counsel
Included: Freedom of speech, religion,
Oldest, highly evolved participatory democracy
Developed by Iroquois Nation
Virginia House of Burgesses 1619
Elected from each county in Virginia with each county sending two representatives
First elected representative assembly in America
Second Treatise of Civil Gov't John Locke 1689
If gov't fails to protect citizens, they have a right to overthrow gov't
Life, Liberty & Property
Protect natural rights of people
Ruler gains authority through consent of governed
Basis of legitimate gov't
Magna Carta 1215
Govt' must have peoples approval to levy taxes
Right to fair & speedy trial by peers
No cruel & unusual punishment

