a Garrett Sieger 5 éve
279
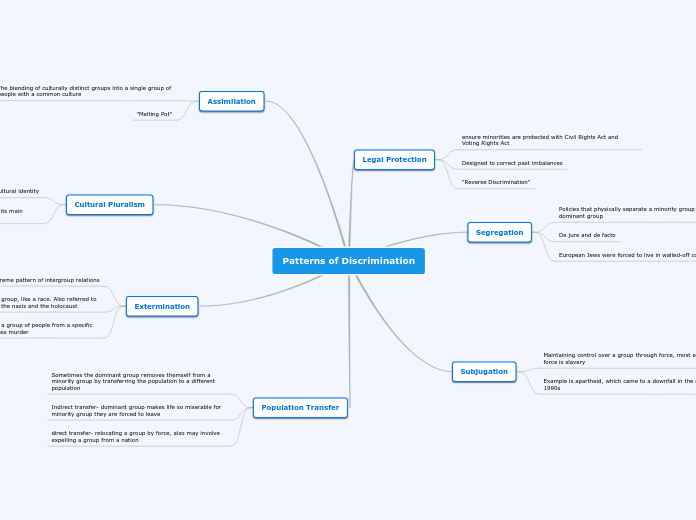
Patterns of Discrimination
Different forms of social and political policies shape the interactions between dominant and minority groups. Discrimination and protection frameworks, like the Civil Rights Act and Voting Rights Act, aim to address past inequities and ensure minority rights.
Megnyitás
Patterns of Discrimination Population Transfer direct transfer- relocating a group by force, also may involve expelling a group from a nation Indirect transfer- dominant group makes life so miserable for minority group they are forced to leave Sometimes the dominant group removes themself from a minority group by transferring the population to a different population Extermination Ethnic cleansing: removing a group of people from a specific area through terror and mass murder Goal is the destruction of a group, like a race. Also referred to as a genocide, for example the nazis and the holocaust Most extreme pattern of intergroup relations Cultural Pluralism Switzerland has 3 national languages for each of its main ethnic groups Allows each group to keep its cultural identity Assimilation "Melting Pot" The blending of culturally distinct groups into a single group of people with a common culture Subjugation Example is apartheid, which came to a downfall in the mid 1990s Maintaining control over a group through force, most extreme force is slavery Segregation European Jews were forced to live in walled-off communities De jure and de facto Policies that physically separate a minority group from the dominant group Legal Protection "Reverse Discrimination" Designed to correct past imbalances ensure minorities are protected with Civil Rights Act and Voting Rights Act