a HECTOR MARTIN GARCIA 2 éve
162
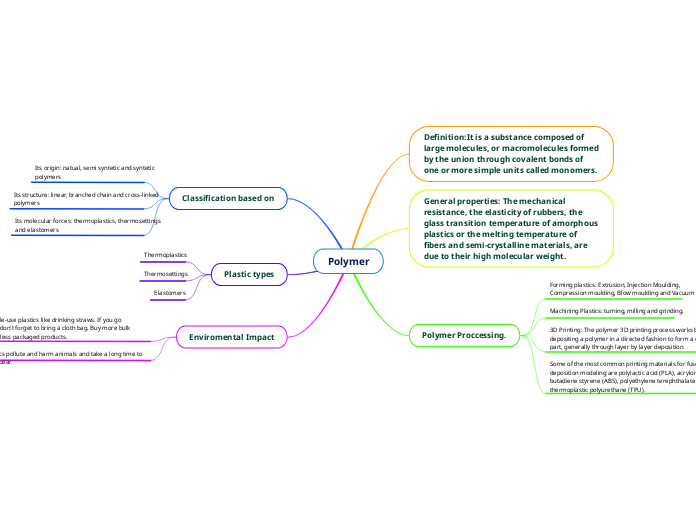
Polymer
Polymers are large molecules formed by the union of monomers through covalent bonds. These materials can be classified based on their origin, molecular forces, and structure into natural, semi-synthetic, and synthetic polymers; thermoplastics, thermosettings, and elastomers; and linear, branched chain, and cross-linked polymers, respectively.