a Emily Sanders 3 éve
151
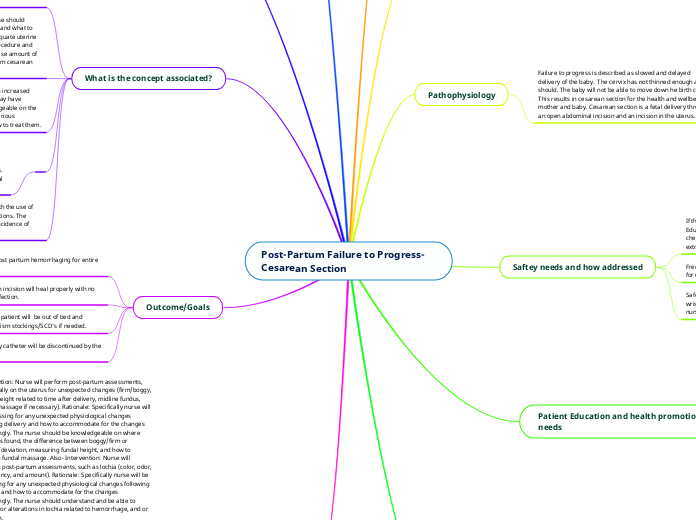
Post-Partum Failure to Progress- Cesarean Section
After a cesarean section, it is crucial for nurses to manage various aspects of post-partum care to ensure the well-being of the patient. Nurses should assist patients gradually out of bed to prevent orthostatic hypotension, using a gait belt to reduce fall risks.