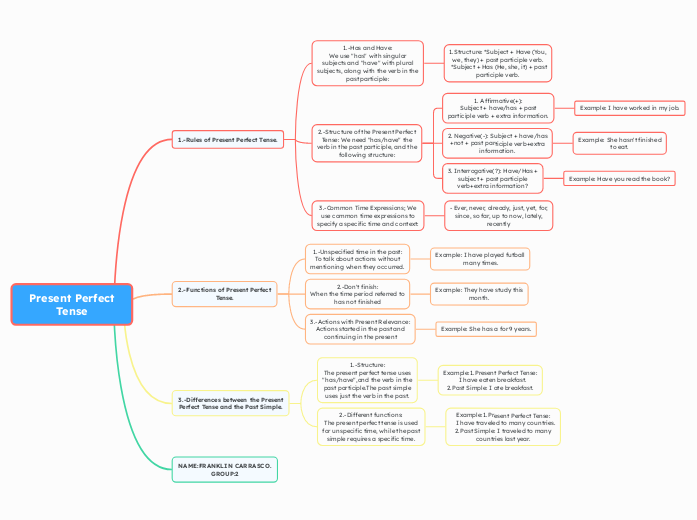
Present Perfect
Tense
NAME:FRANKLIN CARRASCO.
GROUP:2
3.-Differences between the Present
Perfect Tense and the Past Simple.
2.-Different functions:
The present perfect tense is used
for unspecific time, while the past
simple requires a specific time.
Example:1.Present Perfect Tense:
I have traveled to many countries.
2.Past Simple: I traveled to many
countries last year.
1.-Structure:
The present perfect tense uses
"has/have",and the verb in the
past participle.The past simple
uses just the verb in the past.
Example:1.Present Perfect Tense:
I have eaten breakfast.
2.Past Simple: I ate breakfast.
2.-Functions of Present Perfect
Tense.
3.-Actions with Present Relevance:
Actions started in the past and
continuing in the present
Example: She has a for 9 years.
2.-Don't finish:
When the time period referred to
has not finished
Example: They have study this
month.
1.-Unspecified time in the past:
To talk about actions without
mentioning when they occurred.
Example: I have played futball
many times.
1.-Rules of Present Perfect Tense.
3.-Common Time Expressions; We
use common time expressions to
specify a specific time and context:
- Ever, never, already, just, yet, for,
since, so far, up to now, lately,
recently
2.-Structure of the Present Perfect
Tense: We need "has/have" the
verb in the past participle, and the
following structure:
3. Interrogative(?): Have/Has +
subject + past participle
verb+extra information?
Example: Have you read the book?
2. Negative(-): Subject + have/has
+not + past participle verb+extra
information.
Example: She hasn't finished
to eat.
1. Affirmative(+):
Subject + have/has + past
participle verb + extra information.
Example: I have worked in my job.
1.-Has and Have:
We use "has" with singular
subjects and "have" with plural
subjects, along with the verb in the
past participle:
1.Structure: *Subject + Have (You,
we, they) + past participle verb.
*Subject + Has (He, she, it) + past
participle verb.