S&C Refurb
Output Review
Notes recorded here and apologies for the vagueness but these were just general comments that were recorded whilst the SME's were discussing.
Have you got what you paid for?
Options for managing success criteria
How do you manage?
Conduct an Output review
Analyse the pre and post works documentation management process as stated in NR/L2/MTC/089
A desktop assessment is completed as a minimum
As a minimum, the following items shall be reviewed:
a) Acknowledgement that the work has been completed as per the requirements of the specification
b) Acknowledgement that the site has been handed back to maintenance and documentation received
c) That the construction tolerances specified have been achieved
d) That no unplanned no-compliances are present
e) That the Success Criteria to be achieved have been addressed by the work carried out
f) Details of any further work required, e.g. shortfalls.
Ross and Andy to feedback the references here and are they appropriate?
Task = comments from Ross
- Agree to a decision or reject a shortfall
- Identify what it is, yes or no?
- Identify what's the shortfall
- Does it present a performance or safety risk?
- Needs a high level overview
A discussion around risk mitigation to insert into content road map, add shortfalls
Reference the standard
Record the Output review
Complete TEF3255 Part C or regional variation.
Identify a review of the work against the specification and success criteria is undertaken by the Asset Manager or nominated delegate.
Identify the actions to take if the success criteria are not met.
Identify alternative options and analyse the benefits and drawbacks of each.
Construction
A shorter session is needed here, use examples in slides. Further training will be included at a later stage separate from this course.
Outline the Construction Methodology process
Define the deliver of works phase
Define the design phase
Define the roles involved in a survey
Define the purpose stage
Recognise the construction methodology used for S&C as outlined in NR/L2/TRK/3415
Refer to standards where required:
NR/L2/TRK/018
NR/L2/TRK/3100
NR/L2/TRK/2500
NR/L2/TRK/018
NR/L2/OHS/0047
NR/L2/MTC/089
NR/L3/TRK/3406
NR/L3/TRK/7012
NR/L2/RSE/02009
NR/L2/TRK/001
NR/L2/TRK/3419
NR/L2/INI/CP1030
NR/L3/TRK/2049
NR/L2/TRK/6100
NR/L2/OHS/019
NR/L2/TRK/2102 (where specified)
NR/L2/SIG/19809
NR/L3/SIG/19810
NR/GN/TRK/7001
Need NR/L2/TRK/018
Specification
This section potentially needs more time on the course agenda, more than 30 mins for the group exercise defined the content map. One of the SME's suggested a whole morning for this section.
Tolerance Requirements
Identify how the tolerances of the work will be based.
Identify the appropriate tolerances agreed in the success criteria should meet the requirements of NR/L2/TRK/001 and NR/L2/TRK/2102 (where specified)
Need NR/L2/TRK/2102
Identify the roles responsible for agreeing tolerances for all aspects of the work.
Determine if re-use and recycling of S&C assets is possible as referenced in NR/L2/TRK/063
Need to see standard NR/L2/TRK/063 for information on reuse and recycling of S&C assets
Identify the guidance for ordering replacement track components as stated in the Track Work Information sheets listed in standard NR/GN/TRK/7001.
Need NR/GN/TRK/7001.
Identify the items to be included in the specification
List the possible track refurbishment activities as defined in section B.2. in the standard NR/L2/TRK/3415
Identify the purpose of assessing the suitability of the condition of components and fastenings for the re-ballasting method.
The purpose of this is to control the risk of the track system collapsing whilst being supported, as stated in standard NR/L2/TRK/3415 Appendix C.2
Reballasting 0 - 25%
Reballasting 25% - 50%
Reballasting 50% - 75%
Reballasting 75% - 100%
Bearer changing 0 - 25%
Bearer changing 25% - 50%
Bearer changing 50% - 75%
Bearer changing 75% - 100%
Replace crossing unit
Stressing
S&T Disconnect and reconnection
Switch toe alignment
Replace S&C unit
Replace 1/2 switch
Replace full switch
Replace IBJs
OTM Tamping
OTM Stoneblower
Removal of existing scrap
Upgrade access point
Upgrade stretcher bars to tubular
Replace sideworn rails
Replace foot gall rail
Replace gall baseplates
Replace all pads, clips, nylons and screws 0 - 25%
Replace all pads, clips, nylons and screws 25% - 50%
Replace all pads, clips, nylons and screws 50% - 75%
Replace all pads, clips, nylons and screws 75% - 100%
Replace shroud plates, screws and associated pads
Housing repairs on concrete bearers
Resin repairs on cracked concrete bearers
Survey and design costs
Treat timber bearers with resin repair.
Define the work outlined in the specification
Clarify further issues identified during the scoping
Identify all assets impacted but the S&C refurbishment
Identify the role responsible for the specification andcompleting TEF3255 (Part B)
Scoping.
Outline all the scoping activity options
Identify the purpose of the ground condition assessment in assessing the ballast conditions to determine the correct treatment.
Explain why the position and condition of any drainage should be established for a worksite.
Identify drainage on a worksite
Explain how structures with foundations that could be undermined during re-ballasting
Identify and record risks associated with undermining structure foundations
Identify what should be recorded when re-ballasting is being considered.
Explain why recording the presence of these items is important.
The presence of:
Geotextiles
Geocells
Grids
Geocomposites.
Outline the conditions for S&C trial holes
Identify S&C trial hole information on a TEF3106.
Explain the impact of re-ballasting work on sites with formation issues on the designed life extension.
Outline the conditions for conducting a Track Bed Investigation (TBI) may be appropriate to be completed.
Determine the additional Inspections that may be completed to provide additional up to date information on the asset condition.
a) TEF3068 - Management of gauge: periodic switches and crossings inspection
b) TEF3239 - Management of gauge: field face to field face
c) TEF3074 - SM[T] points gauge FWC and RSO measurements
d) TEF3029 - Switch inspection form
e) TEF3031 - Crossing inspection report.
List the components of a site assessment
Reference made to NR/SIN/150 re: cracked bearers in RT60 layout. Do we need sight of this for the curriculum design work?
Reference made to NR/L2 TRK/001 modules 03-05. Do we need this for the curriculum design?
Copies of TEFs required for curriculum design:
TEF3068
TEF 3239
TEF 3074
TEF3029
TEF3031
Reference made to NR/L2/TRK/001 mod14 for ball and claw settings. Do we need this for the curriculum design?
The detailed site assessment may consider:
a) correlation of maintenance records and operational failure history with on-site conditions
b) Inspection of the existing S&C assets to check that the correct components and geometry as per the manufacturer's drawing are in place
c) Missing components, e.g. screws, clips
d) A visual assessment of the condition of track/components e.g. for wear or damage
e) The condition of:
i) bearers
ii) baseplates including signs of baseplate shuffle
iii) fastening systems, and
iv) welds and joints
f) Any fastening systems that are damaged which should be scoped for replacement and fastening systems should be considered for renewal if re-ballasting is planned
g) The presence of obsolete fastenings
h) The presence of cracked bearers in RT60 layout (see NR/SIN/150)
i) The presence if damage to the underside of bearers from mechanical works e.g. tamper tine damage
j) Any bowed long bearers
k) The presence of dipped joints and wide gaps
l) Headwear where new rails might be specified for renewal
m) The presence of pre-1978 rail
n) S&C supplementary equipment (e.g. legacy POE)
o) Any component which does not meet the requirements of NR/L2/TRK/001
p) Track geometry including track gauge which should be checked throughout the layout for compliance to NR/L2/TRK/001 with any non-compliances recorded
q) Whether ball and claw settings are in accordance with NR/L2/TRK/001/Mod14
r) Switch toe squareness and crossing nose to toe measurements
s) The identification of two levelling baseplates
t) All E&P, S&T, Building and Civil assets present within the area if proposed works (where re-ballasting works are being considered the relevant asset owners should be consulted)
AND
u) The presence of Remote Condition Monitoring.
Taken from Appendix A Scoping and Guidance Sec A.3 Detailed Sire Scoping Assessment A.3.1 Component Assessment and A.3.1.1 Additional Inspections
NOTES:
i) Where track or signalling drawing is missing, this should be identified to the Network Technical Head of S&C.
ii) Damaged or missing components might cause issues during the re-ballasting process.
List the data sources used in a desktop assessment
I have a note regarding this section but not sure of its relevance
Include 'Undertake and State', ???
Data sources to consider:
a) Ellipse/INM data for the asset type and component age
b) Track geometry data to check rates of deterioration
c) Maintenance records to identify existing or repeat geometry faults and existing reliability issues
d) Forward-facing video camera data
e) GeoRINM Viewer data
f) Where sites have repeated faults, the root cause should be established, e.g. the presence of bearers damaged by mechanical maintenance
g) The presence of:
i) existing rail defects
ii) any registered eighths
iii) Inherent design alignment faults
h) Ground penetrating radar (GPR) data to establish the condition of the ballast at the site )and run in/run out)
i) Stressing records for the S&C unit
j) S&C supplementary equipment ( e.g. legacy POE)
k) the presence of remote condition monitoring (and any usable data)
l) any record drawing (e.g. permanent way/signalling design plans and/or long sections)
m) Assets present in the National Gauging Database
and
n) Historical track bed investigation data.
Taken from Appendix A Scoping Guidance Sec A.2 Desktop Scoping Assessment.
Identify the differences, benefits and drawbacks of desktop assessment and site assessment.
Identify the role responsible for undertaking scoping and how the resulting scope is documented.
Complete TEF3255 (Part A) or regional variation to record the scope.
Removed Refer and Inserted Complete
Examine the project documentation and determine the the required level of scoping.
Identify what the scoping should include as a minimum, as stated in standard.
Identify the role of the Asset Manager or nominated deputy.
Define the purpose of scoping.
Examine the development of options to eliminate the identified root cause as stated in standard NR/L2/TRK/6001.
Explain how scoping supports moving from a problem statement to a specification.
Success Criteria.
Define the success criteria
Define the purpose of the success criteria.
There should be a focus on linking the success criteria to the problem statement, explain the process and that facts checks are required.
It was emphasised on numerous occasions, the need for linking all sections together.
Alott weighting to each success criteria
Address the track asset risk
Explain how the success criteria demonstrates the drivers for refurbishment
Identify the role responsible for defining success criteria.
Target Asset Life Extension / Value for Money
Explain the link between a problem statement and Target Asset Life Extension/Value for Money
This will need checking to see if this flows and is relevant. We agreed that this session will include the presentation of the problem statements and case studies as part of day 1 homework.
This is similar to the tasks listed in 5. Problem Statement but it was discussed that there needs an understanding of the link between a problem statement and the Target Asset Life Extension/Value for Money, the content map will need to highlight this and describe the correlation between the two.
There was also a discussion that the flow chart maybe needed an extra stand alone box for the problem statement?
Present a detailed problem statement
Present an outline problem statement
Define a detailed problem statement
Define an outline problem statement
Analyse the value for money
Calculate Value for Money
Gather data to measure cost
List all cost considerations
Gather data to measure standard adherence
List standard adherence benchmarks
Gather data to measure safety
List safety data points
List safety benchmarks
Gather data to measure performance
Add text
List sources of performance measures
List performance benchmarks
List the considerations of Value for Money
cost
standards
safety
performance
Define 'Delivering Value for Money'
Determine plan refurbishments based on maintenance and renewal timelines.
List the types of Refurbishment Strategies
Identify target asset life extensions in project documentation
Refer to [XXX] to find asset life expectancy
List all S&C Asset types
Explain Asset Life Extension
Problem Statement
List information is required to make an informed decision
Produce a problem statement
- There was a lot of discussion around this task, it was still unclear of who actually attends the course and was decided it would be passed onto CDG for final decision.
- There was a request for the problem statement to outline the differences between an outline and detailed problem statement, so to create two separate boxes.
- There should be a focus on identifying the difference between the two and the process for creating each of these.
- The learners should create both on the course.
- There was also discussion around who actually creates the problem statement and awareness of the roles and responsibilities and how it moves forward ( as highlighted above). A comment was made that the people closest to the problem, creates it.
- It was decided that currently, this course is needed 2 to 3 times a year depending on demand.
- We will need to add a S&C problem statement to the resources.
Develop and outline a problem statement following standards to identify root causes, reduce asset-related risks, and improve asset reliability and availability
Complete a case study using a proposer to outline and asset manager to complete the problem statement as examples
This will need clarifying by the SME's the nature and purpose of this exercise
Prepare a case study example of a problem statement for presentation on day 2
Identify a root cause of an issue
Adhere to NR/L2/TRK/6001 requirements
identify the failure mode
Collate all data to determin root cause analysis
Create a Track Problem Statement using TEF3305 (or a regional equivalent),
To be complete by a SME using the provided 'data points'
Write a detailed problem statement
Write an outline problem statement
Case Study 4 - Not maintainable Asset
Differentiate between an outline and a detailed problem statement
Definitions
Define briefly the definitions in section 4 of standards document NR/L2/TRK/3415
Define components of a POE
Explain how points operating equipment (POE), controlling track switches
List the function of each POE component
Define failure modes
Roles and Responsibilities
Apply the process of creating a RACI
Create a RACI Model for a Given project
Demonstrate the ability to problem solve and build a RACI Model using case studies
Identify the region of the learner and use an example for the RACI exercise
Identify and Assign Roles for Tasks
Apply the RACI model Framework
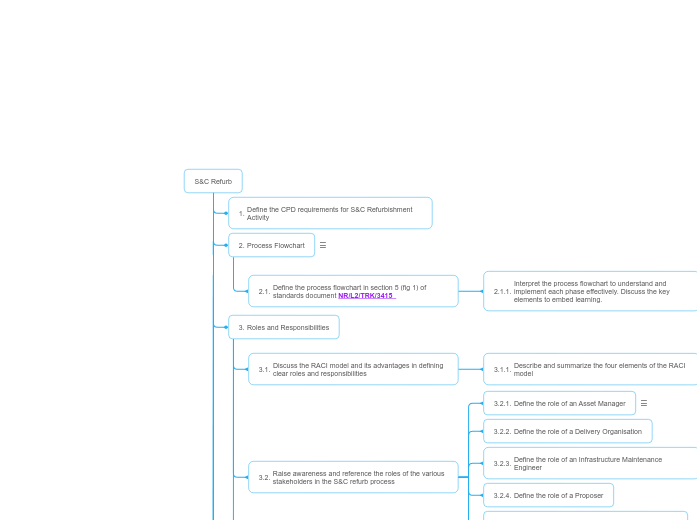
Raise awareness and reference the roles of the various stakeholders in the S&C refurb process
Define the role of a Track Maintenance Engineer
Define the role of a Signalling Maintenance Engineer
Define the role of a Proposer
Define the role of an Infrastructure Maintenance Engineer
Define the role of a Delivery Organisation
Define the role of an Asset Manager
0.1 General
A specification shall be prepared and recorded in project documentation by the Asset Manager or nominated delegate. The work outlined in the specification shall be aligned to the target asset life extension and success criteria. The specification shall include the following items as a minimum: a) general information (point number, location, ELR, track ID, mileage, target and delivery year); b) layout information (type, profile, speed, turnout direction); c) switch information (type, rail depth, steel grade, toe opening, out of square measurement); d) crossing information where scoped for refurbishment (angle, fabrication, steel grade, check rail type); e) description of work, including tolerance requirements and any impact on POE; f) ballast treatment where scoped for refurbishment (extent, crossfall grade and direction); g) handback and follow up requirements ; h) success criteria ; i) non-compliances/derogations (standard, clause, reason for non-compliance, acceptance criteria, supported by); and j) author/reviewer/approver/accepted by. TEF3255 (Part B) or regional variation may be used to record the specification. A list of potential refurbishment activities is provided in B.2. Consideration should be given to the re-use and recycling of S&C assets (see NR/L2/TRK/063). Where existing non-compliant conditions have been identified, or the planned work will result in non-compliant conditions, the Delivery Organisation shall agree these with the Asset Manager or nominated delegate as part of the development process, supported with a track temporary variation or derogation. Other discipline Asset Managers should review their plans to identify opportunities to update their assets. These opportunities should be evaluated and exploited as part of the refurbishment works where appropriate to maximise efficiency. Page 14 of 32 NR/L2/TRK/3415 Ref: Issue: Date: 3 04 March 2023 Compliance date: Refer to NR/L2/TRK/6100/Mod03 for the installation requirements for tubular stretcher bars and subsequent actions.
Discuss the RACI model and its advantages in defining clear roles and responsibilities
Describe and summarize the four elements of the RACI model
Process Flowchart
Move to section 2 to sit above Roles and Responsibilities
Define the process flowchart in section 5 (fig 1) of standards document NR/L2/TRK/3415
Interpret the process flowchart to understand and implement each phase effectively. Discuss the key elements to embed learning.
Evaluate the learners knowledge of the process flow.
Define the CPD requirements for S&C Refurbishment Activity