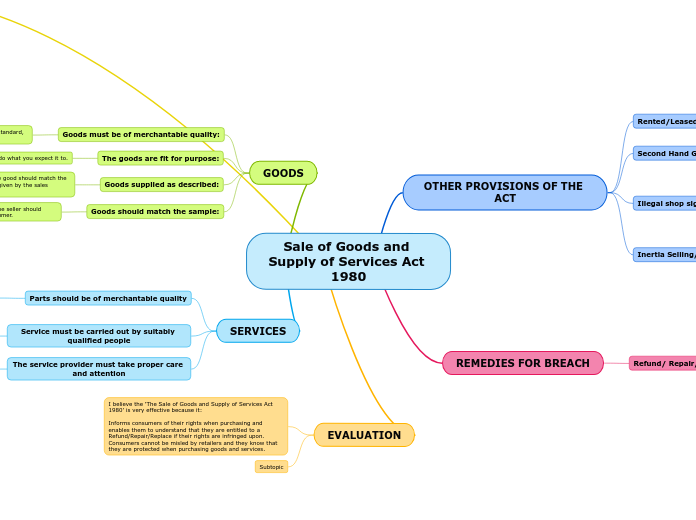
Sale of Goods and Supply of Services Act 1980
EVALUATION
I believe the ‘The Sale of Goods and Supply of Services Act 1980’ is very effective because it:
Informs consumers of their rights when purchasing and enables them to understand that they are entitled to a Refund/Repair/Replace if their rights are infringed upon. Consumers cannot be misled by retailers and they know that they are protected when purchasing goods and services.
SERVICES
The service provider must take proper care and attention
When carrying out the work, a surgeon for example must take proper care when doing the procedure. If they do not, they would be legally liable. They cannot be watching Netflix while performing the procedure.
Service must be carried out by suitably qualified people
This means that you have the right to assume that a person doing the work for you is qualified at their job
Example: Mechanic fixing your car, not your Business teacher.
Parts should be of merchantable quality
This means that the parts supplied during a service are of merchantable quality.
Example: would be a door handle should open a door. This is a part of the overall good.
GOODS
Goods should match the sample:
This means the sample shown to you by the seller should match the product purchased by the consumer.
Example: A sample of curtains selected must match the sample delivered to the consumer.
Goods supplied as described:
This means that the description of the good should match the packaging, catalogue, or description given by the sales person.
Example: A silver I-phone X must be silver if selected by the consumer.
The goods are fit for purpose:
This means that the good must do what you expect it to.
Example: A freezer should freeze food
Goods must be of merchantable quality:
This means that the good must be of an acceptable standard, taking into account price and durability
Example: If you buy a watch it should not stop working after using it once
Main topic
REMEDIES FOR BREACH
Refund/ Repair/ Replacement
REPLACEMENT
If a consumer buys a faulty good they can ask for a working replacement. This form of redress is common, especially when the good cannot be easily repaired.
Example: You buy an iPad which stops working for no apparent reason. When you bring it to the Apple Store they say it cannot be repaired. You are entitled to a replacement iPad.
REPAIR
If a consumer buys a faulty good in need of repair through no fault of their own they can ask for a repair.
Example: A dress with a faulty zip is returned to the seller and repaired for the consumer.
REFUND
If a consumer buys a good that does not meet the standards set out by the Sales of Goods and Supply of Services Act they are entitle to a complete refund. This is one form of redress that is used to solve consumer conflicts.
Example: You pay for a guided tour of Rome through English. The guide cannot speak English and gives the tour in Italian. You are entitled to a refund.
OTHER PROVISIONS OF THE ACT
Inertia Selling/Unsolicited Goods:
This is where goods are sent to a person who hasn’t ordered them and the seller later demands payment for them. This law makes this practice illegal.
The Act outlaws this practice and allows the consumer to keep the good free of charge after 30 days provided they have written to the seller asking them to collect the goods, or after six months, as long as the consumer has not prevented the seller from accessing them
Illegal shop signs:
It is an offence for the retailer to display signs that give the consumer the impression that they have no legal rights. These signs are illegal and do not affect your statutory consumer rights
E.g. ‘No Refunds on Sale Items’ Consumers’ rights under the act cannot be taken away or limited by signs such as ‘Credit Notes Only’, ‘No exchange on items’ etc.
Second Hand Goods
They must be fit for the purpose they are sold but not fair for us to assume they should be brand new either. It is important to note if you buy from a private seller you are not covered
Subtopic
example a second hand video game from a friend.
Rented/Leased/ Hire Purchased Goods:
You are entitled to return such goods if they do not work
example rent a lawnmower from the local hardware store that doesn’t work