Sex Ed
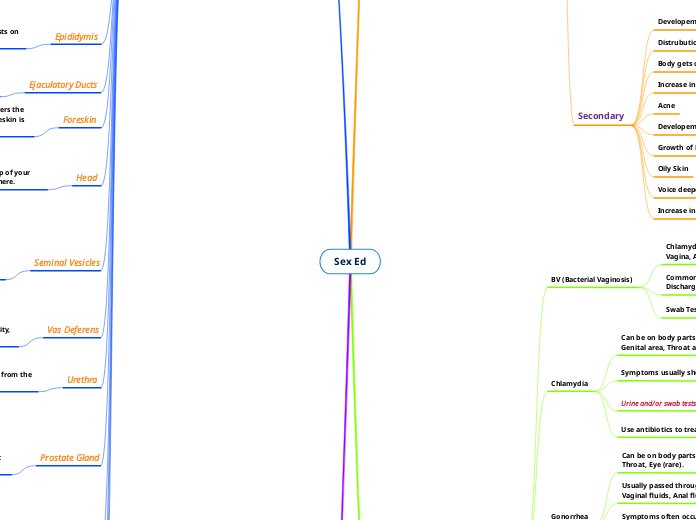
Birth Control
Abstinence
Free
!00% Effective.
No side effects.
Not having sex
Surgical
Tubal Ligation
Cutting and sealing the fallopian tubes.
Longer procedure, infection,
fallopian tube pregnancy.
99.9% No STD protection.
Vasectomy
Cutting and sealing the vas deerens.
30 minute procedure, some swelling
and pain.
99.9% No STD protection
Barrier
Phsyical Block
Spermicides
Foam cream, jelly that is inserted into the vagina 10 min. prior. Effective for 1 hour.
Rash if allergic messy?
74% No STD protection.
Sponge
Needs to be left in place for 6 hours after sex.
Cervical Cap
Disk shaped devices that covers the cervix.
Diaphragm
"Disk shaped devices that covers the cervix."
TSS (Toxic Shock Syndrome is a fatal infection if
these are left in for too long. ((24+ hours))
97% (improper use 75%) No STD protection.
Female Condom
Polyurethane sheath shaped like a male condom only bigger.
Can prevent STI's
Spermicide
Rash if allergcan (can be messy)
Jelly, cream, foam, is inserted to the vagina 10 minutes prior. (Effective for an hour)
$10 or less at stores usually.
No side effects
95% (actual 85%) STD protection.
Male Condom
A latex sheath placed over the penis before sexual contact.
Needs Lube
Can rip
Latex allergies (use lambskin)
97% (actual 85%) STD protection.
Natural
Basal Body Temperature
Count days or measure body temperature.
Calender Method
Don't have sex when ovulation is supposed to happen.
Sperm can live up to 7 days,
egg cell lasts for 3 to 5 days.
Low success rate, no STD protection.
Douching
Rinsing the vagina.
Withdrawal
Removing penis before ejaculation.
Douche can irritate the vaginal lining. Douching
may push sperm further up.
Less than 60% No STD protection.
Hormonal
Tricks the body.
IUD
No STD protection.
Pelvic imflammatory disease
Pregnancy in the fallopian tubes
Small device inserted into the uterus (1 - 10 years)
Available through doctors.
Not used by teenagers.
95 - 98% effectiveness against pregnancy.
Intrauterine Device
Small device inserted into the uterus for one to ten years.
Pelvic inflammatory disease, Pregnancy
in the fallopian tubes.
95% - 98% No STD protection.
Emergency Contraceptitive Pill
Morning after pill delays ovulation,
must be taken 24 - 48 hours after sex.
Nausea, vomiting.
75% No STD protection.
Norplant
Implanted Rods (3-5 years).
Depo Provera
Injections (every 3 months)
Birth Control Pill
21 - 28 mixed hormone pills.
Nausea, headache, weight gain.
breast tenderness.
97% - 99% No STD Protection.
Male Reproductive Organs
Holds urine . When urinating the urine will travel through your urethra to maintain correct hydration levels.
Located infront of rectum.
Erectile Tissue
This tissue contains thousands of large spaces that fill with blood when the man is sexually aroused.
Skin is loose and elastic, allowing it to change in size when having an erection.
As the penis fills with blood, it becomes rigid and erect, which allows for penetration during sexual intercourse.
Cowper's Gland
Peasized glands that will produce thick clear mucus prior to ejaculation.
Protects the sperm while ejactulating.
Bulbourethral Glands
The bulbourethral glands, or Cowper’s glands, are pea-sized structures located on the sides of the urethra just below the prostate gland.
This fluid serves to lubricate the urethra and to neutralize any acidity that may be present due to residual drops of urine in the urethra.
These glands produce a clear, slippery fluid that empties directly into the urethra.
Prostate Gland
The prostate gland is a walnut-sized structure that is located below the urinary bladder in front of the rectum.
The urethra, which carries the ejaculate to be expelled during orgasm, runs through the center of the prostate gland.
Prostate fluids also help to nourish the sperm.
The prostate gland contributes additional fluid to the ejaculate.
Urethra
The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to outside of the body.
In males, it has the additional function of expelling (ejaculating) semen when the man reaches orgasm.
When the penis is erect during sex, the flow of urine is blocked from the urethra, allowing only semen to be ejaculated at orgasm.
The vas deferens is a long, muscular tube that travels from the epididymis into the pelvic cavity, to just behind the bladder.
The vas deferens transports mature sperm to the urethra in preparation for ejaculation.
The seminal vesicles are sac-like pouches that attach to the vas deferens near the base of the bladder.
The fluid of the seminal vesicles makes up most of the volume of a man’s ejaculatory fluid, or ejaculate.
The seminal vesicles produce a sugar-rich fluid (fructose) that provides sperm with a source of energy and helps with the sperms’ motility (ability to move).
Head
Your glans is also called the head or tip of your penis. The opening of your urethra is here.
This is where pre-ejaculate (precum) and semen (cum) come out of, and it's where you pee out of. For many people, it's the most sensitive part of the penis.
(This skin is sometimes removed in a procedure called circumcision.)
The glans, which also is called the head of the penis, is covered with a loose layer of skin called foreskin.
Foreskin
The foreskin is the sheath of skin that covers the head (glans) of the penis. At birth, the foreskin is fully attached to the penis.
In time, the foreskin separates and can be retracted (pulled back). This can usually be done by the age of about two.
Ejaculatory Ducts
These are formed by the fusion of the vas deferens and the seminal vesicles.
The ejaculatory ducts empty into the urethra.
The epididymis is a long, coiled tube that rests on the backside of each testicle.
During sexual arousal, contractions force the sperm into the vas deferens.
It functions in the carrying and storage of the sperm cells that are produced in the testes.
The testes are oval organs about the size of very large olives that lie in the scrotum, secured at either end by a structure called the spermatic cord.
Within the testes are coiled masses of tubes called seminiferous tubules.
These tubules are responsible for producing the sperm cells through a process called spermatogenesis.
Most men have two testes
It is near the Vas Deferens
Produces Testosterone
Scrotum
The scrotum is the loose pouch-like sac of skin that hangs behind the penis.
For normal sperm development, the testes must be at a temperature slightly cooler than the body temperature.
The scrotum has a protective function and acts as a climate control system for the testes.
Shaft
The shaft of your penis extends from the tip to where it connects to your lower belly. It looks like a tube. Your urethra is inside the shaft. The foreskin is a patch of skin that covers and protects the head.
Cylindrical in shape and consists of three internal chambers.
Penis
Releases semen and other fluids
Sperm
When the penis is erect, the flow of urine is blocked from the urethra, allowing only semen to be ejaculated at orgasm.
The head is meant to protect the sperm / semen
Sperm can be made in alot of different locations on the body
Vas Deferens
Seminal Vesicles
Testes
Prostate
Epididymis
In the sperm that is made daily, one of those times make it to the egg
Lucky / Rare chance
Consists of a Tail and a Head
The tail is called an flagellum
Strongest part
The head is called an Acrosome
It has semen and also other kinds of fluids
Made by men in order to make babies
Spermatozoon
Sperm is made daily
The whole process is under the influence of the hormone testosterone.
Sperm is produced for the first time and the male will experience erections. This is due to engorgement of blood in the penis.
Penis enlarges
Covered with a loose layer of skin called foreskin.
Lots of muscle
Lots of nerves
Pudendal nerves
The perineal nerves
Illoinguinal nerves
Dorsal penile nerve
The penis is the male organ for sexual intercourse. It has three parts: the root, which attaches to the wall of the abdomen; the body, or shaft; and the glans, which is the cone-shaped end of the penis.
Body oder
Deep voice
Greater height than females
Broadening Shoulders
Libido
Pubic Hair
STI's
Fungus
Yeast
Swab tests.
Tests are accurate immediatly.
Common symptoms; Abnormal whitish, thick discharge, Genital area is itchy, red, sore and dry, Painful sex.
Anti-fungal medications, Symptoms may go away without treatment.
Not usually passed.
Can be on body parts such as; Penis, Vagina, Anus, and Genital area.
Parasite
Pubic Lice
Treat it with Topical medications.
Common symptoms; Genital itching, Visible lice in and around pubic hair.
Can take up to 2 - 21 days for symptoms to show.
Can be on your Genital and other body hairs.
Scabies
Treat with Topical medication.
Common symptoms; Itchiness (especially at night) Rash between fingers, on wrists, armpits, genitals, thighs.
Can take up to 1 - 21 days for symptoms to show.
Can be passed through; skin-to-skin contact, sharing clothes, bedding, towels.
Usually on your skin.
Trichomoniasis
Unknown test result accuracy.
Common symptoms; Abnormal vaginal discharge, Pain or trouble when urinating.
Can take up to 5 - 28 days for symptoms to show.
Can be passed through; Semen, Pre-ejaculate, Vaginal fluids.
Can be on your Penis or Vagina.
Virus
HPV
A way to treat it is Topical medications and treatments, although vaccines can prevent some strains of HPV. Theres also a chance symptoms will go away without treatment.
Visual exams.
A common symptom is painless bumps on the skin.
Sometimes it takes weeks to years for symptoms to show.
Can be on body parts such as; Penis, Vagina, Anus, Genital area, Throat (rare), and Mouth (rare).
HBV
Tests will take up to 4 - 12 weeks for them to be accurate.
Can take up to 6 - 22 weeks for symptoms to show.
Usually passed through Blood, Semen, Pre-ejaculate, and Vaginal fluids.
Treat it through Anti-viral medications, Symptoms may go away without treatment, Vaccines can prevent infection
HCV
Test results are accurate within 5- 10 weeks.
Can take up to 6-7 weeks for symptoms to show.
Common symptoms; Combination of nausea, loss of appetite, fever, stomach pain, and jaundice.
Usually passed through blood.
Treat it through; Anti-viral medications, Symptoms may go away without treatment.
Molluscum Contagiousum
Topical medications and treatments, Symptoms may go away without treatment.
Visual exam.
Common symptoms; Small, firm, painless pink or white bumps on the skin.
Symptoms can take 1 week - 6 months to show up.
Passed through skin-to-skin contact.
Can be on body parts such as, Genital area, and skin.
HAV
Can take up to 4 weeks for any tests to be accurate.
Symptoms show up within 2-7 weeks.
Symptoms can/usually will go away on their own, but vaccines can prevent infections.
Common symptoms are; Combination of nausea, loss of appetite, fever, stomach pain, jaundice, dark urine, and grey colored stool.
On your stool (body part).
Passed through fecal-oral contact.
HIV
Treat it with Anti-viral medications.
Blood tests.
Test results are accurate within 3-12 weeks.
Symptoms show within 2-4 weeks.
Common symptoms are; Flu-like illness, headache, muscle aches and joint pain, swollen glands (seroconversion illness)
Passed through, Blood, Semen, Pre-ejactulate, Vaginal fluids, Anal fluids, and Breast milk.
Can be in your blood.
Bacteria
Syphillis
Swab or Blood tests.
Tests can be accurate if to do a blood test every 3 months.
Common symptoms; A painless sore, and a non-itchy rash.
Can take up to 3 days - 3 months for symptoms to show.
Usually passed through skin-to-skin contact.
Can be on body parts such as; Penis, Vagina, Anus, Genital area, Throat, and Skin.
LGV
Tests are accurate within 2 - 6 weeks.
Common symptoms; Painless sores, Swollen lymph nodes, and Abscesses.
Symptoms can take 3 days - 6 weeks to show up.
Usually passed through Semen, Pre-ejaculate, Vaginal fluids, and Anal fluids.
Can be on body parts such as; Penis, Vagina, Anus, Genital Area, Throat, and Lymph-nodes.
Gonorrhea
Antibiotics for treatment.
Urine and/or swab test.
Test results can take up to 7 days to be accurate.
Symptoms often occur in the penis, but you can also have abnormal discharge aswell as pain or trouble urinating
Symptoms show up within 2 - 7 days.
Usually passed through; Semen, Pre-ejaculate, Vaginal fluids, Anal fluids.
Can be on body parts such as; Penis, Vagina, Anus, Throat, Eye (rare).
Chlamydia
Use antibiotics to treat.
Urine and/or swab tests.
Test results will / can take up to 2-6 weeks for it to be accurate.
Symptoms usually show up within 2-6 weeks.
Common symptoms are; Abnormal discharge, and Pain or trouble urinating.
Can be on body parts such as; Penis, Vagina, Anus, Genital area, Throat and Mouth (which is rare).
Passes usually through Semen, Pre-ejaculate, Vaginal fluids, Anal fluids.
BV (Bacterial Vaginosis)
Swab Tests.
Test results are accurate immediatly.
Common symptoms are Increased Vaginal Discharge, Fish-like smell, Vaginal Irritation.
A way to treat it is Antibiotics, but symptoms may go away on their own, without treatment.
Chlamydia can be on body parts such as, Penis, Vagina, Anus, Throat, and your eye but its rare.
Not usually passed
Female Reproductive Organs
Secondary
Increase in body oder.
Voice deepens
Oily Skin
Growth of Pubic Hair.
Developement of mammory glands.
Acne
Increase in height
Body gets curvier
Distrubution of fat to hips
Developement of Breasts
Primary
Bladder
Supported by front wall of the vagina
When filled it causes the urge to urinate
Located infront of the vagina and below the uterus.
Hollow organ in the pelvis
Stores urine.
urine travels from bladder and throughout the urethra.
Hymen
For some women, theres practically no tissues at all.
Membrane covering the vaginal opening.
Can be removed surgically.
Membrane can interfere with sex and/or tampon usage.
Has no "proven" medical or phsycological purpose.
Anus
Tough tissue called fascia surrounds the anus and attaches it to nearby structures
The anorectal line separates the anus from the rectum.
The anus starts at the bottom of the rectum, the last portion of the colon (large intestine).
The anus is the opening where the gastrointestinal tract ends and exits the body.
Colon
The colon removes water and some nutrients and electrolytes from partially digested food.
The longest part of the large intestine (a tube-like organ connected to the small intestine at one end and the anus at the other).
Cervix
The lower, narrow end of the uterus that forms a canal between the uterus and vagina.
Rectum
The rectum stores feces until a person is ready to have a bowel movement.
It receives waste from the colon and stores it until it passes out of the body through the anus.
The rectum is the lower part of the large intestine that connects to the sigmoid colon. It is about 15 cm (6 in) long.
Ovaries
The ovaries produce eggs and hormones.
The ovaries are small, oval-shaped glands that are located on either side of the uterus.
Produces hormones to start the
menstraul cycle.
Fallopian Tubes
The fertilized egg then moves to the uterus, where it implants to the uterine lining.
Fertilization of an egg by a sperm normally occurs in the fallopian tubes.
These are narrow tubes that are attached to the upper part of the uterus and serve as pathways for the ova (egg cells) to travel from the ovaries to the uterus.
Clitoris
The two labia minora meet at the clitoris, a small, sensitive protrusion that is comparable to the penis in males.
Like the penis, the clitoris is very sensitive to stimulation and can become erect.
The clitoris is covered by a fold of skin, called the prepuce, which is similar to the foreskin at the end of the penis.
Males are usually taller and heavier than females when hitting puberty.
The hormones estrogen and progesterone are responsible for the menstraul cycle of the female.
Enlargement of the labia of the vagina and a change in hormone production.
The menstraul cycle begins, indicting the release of fertile ovum.
Uterus
Labor
Allows fetus to move through the birth canal
Continous progessive contractions of the uterus
Helps the cervix dilate to open
Makes the efface thin
Starts two weeks before estimated date of delivery
Menstruation
Party blood and party tissue from inside the uterus
Vagina bleeding occurs every month as a cycle.
Normally called a 'period'
Implantation
The egg must attach to the uterus to become a viable pregnancy.
The egg is pushed back towards the uterus by the cilia (1).
It takes about 6-12 days for the fertilized egg to travel to the uterus and attach to the uterus in a process known as implantation (1,8).
Implantation is defined as the process by which the embryo attaches to the endometrial surface of the uterus and invades the epithelium and then the maternal circulation to form the placenta.
A canal through the cervix allows sperm to enter and menstrual blood to exit.
The uterus is divided into two parts: the cervix, which is the lower part that opens into the vagina, and the main body of the uterus, called the corpus.
The corpus can easily expand to hold a developing baby.
The uterus is a hollow, pear-shaped organ that is the home to a developing fetus.
Bartholins Glands
These glands are located next to the vaginal opening on each side and produce a fluid (mucus) secretion.
Labia Minora
The labia minora (“small lips”) can have a variety of sizes and shapes.
This skin is very delicate and can become easily irritated and swollen.
They lie just inside the labia majora, and surround the openings to the vagina (the canal that joins the lower part of the uterus to the outside of the body) and urethra (the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body).
Labia Majora
The labia majora (“large lips”) enclose and protect the other external reproductive organs.
During puberty, hair growth occurs on the skin of the labia majora, which also contain sweat and oil-secreting glands.
Vagina
It also is known as the birth canal.
The vagina is a canal that joins the cervix (the lower part of uterus) to the outside of the body.
Increases in size overtime.