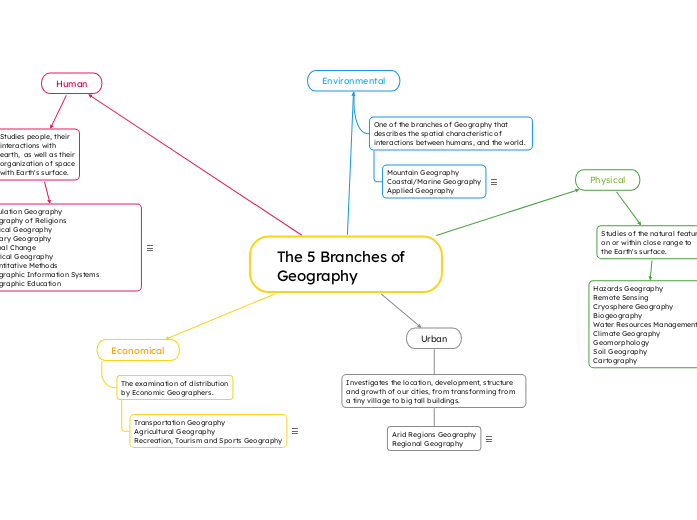
The 5 Branches of Geography
Human
Studies people, their
interactions with
earth, as well as their
organization of space
with Earth's surface.
Population Geography
Geography of Religions
Medical Geography
Military Geography
Global Change
Political Geography
Quantitative Methods
Geographic Information Systems
Geographic Education
Population Geography: Populations geographers not only study births or deaths, but also the distribution, migration and the expansion of populations in geographic locations/areas.
Geography of Religions: Studies of the disbursement of religions around the world, looking at their cultures and their built environments.
Medical Geography: Studies of the geographic distribution of diseases like pandemics or epidemics, as well as illness, death and health care.
Military Geography: Looks at the distribution of military facilities, troops, and tools.
Global Change: Research based on the long-term changes on our planet due to human impacts on the environment.
Political Geography: Investigates every aspect of country, state, nation development, boundaries, diplomacy, international organizations, internal country subdivisions, voting, etc..
Quantitative Methods: Use of mathematical models and techniques to help test theories.
Geographic Information Systems: Develops data-based geographic systems and information to show geographic data in a map-like format, like google maps or google earth.
Geographic Education: The education that provides teacher with the understanding and skills they need to help teach geographic illiteracy, as well as to help develop future geographers.
Urban
Investigates the location, development, structure and growth of our cities, from transforming from a tiny village to big tall buildings.
Arid Regions Geography
Regional Geography
Arid Regions Geography: Study of dry surfaces or deserts around the world. Researchers explore how humans, animals and plants use resources in this type of environment.
Regional Geography: Mainly focused on the studies of areas that are as small as a urban area, or as big as a continent.
Physical
Studies of the natural features
on or within close range to
the Earth's surface.
Hazards Geography
Remote Sensing
Cryosphere Geography
Biogeography
Water Resources Management
Climate Geography
Geomorphology
Soil Geography
Cartography
Hazards Geography: Combines the work of physical and human geography. Research of events like disasters, and studying how us people respond and interact with this sort of event.
Remote Sensing: Uses satellites and sensors to help examine features close or on earth's surface from a specific distance. Remote sensing helps develop the understanding of a place that is not capable of having direct observation.
Cryosphere Geography: Exploration of the glaciers and ice sheets on earth, and their past distributions or the causes.
Biogeography: Studies of the geographic disbursement of animals and plants.
Water Resources Management: When geographers look into the distribution and use of water around the world within what is known as the hydrologic cycle, as well as human-developed systems for distribution, storage or use.
Climate Geography: Studies of distribution of long-term weather activities/patterns from the earth's atmosphere.
Geomorphology: Studies of the landforms on earth, from both development or disappearance whether to erosion or other physical processes.
Soil Geography: Studies of the upper layer (soil) of the lithosphere and it's distribution patterns and categorization.
Cartography: The main focus of developing and improving technologies in map-making. Cartographers are trained to create high-quality maps that show geographical info in a useful manner.
Environmental
One of the branches of Geography that describes the spatial characteristic of interactions between humans, and the world.
Mountain Geography
Coastal/Marine Geography
Applied Geography
Mountain Geography: Study of the development of mountain systems and the people that live in those higher altitudes and how they adapted to that environment.
Coastal/Marine Geography: Research on not only the coastal environments, but how coastal life and humans interact with it.
Applied Geography: Applied geographers are taught specifically to use geographic skills, techniques and knowledge to help solve problems with everyday societies. These geographers are typically employed in a private firm or a government agency, instead of a academic environment.
Economical
The examination of distribution
by Economic Geographers.
Transportation Geography
Agricultural Geography
Recreation, Tourism and Sports Geography
Transportation Geography: Research of transportation networks- whether they are private or public, and the uses of moving products or people.
Agricultural Geography: Studies of the disbursement of agriculture in rural settlements and land use in rural areas, as well as accessibility to agricultural products.
Recreation, Tourism and Sports Geography: The study of leisure-time games/activities and their impacts on our local environments. With sports being one of the largest industries, making people temporarily migrate from one place to another.. which geographers seem to find fascinating.