Tissues of the body
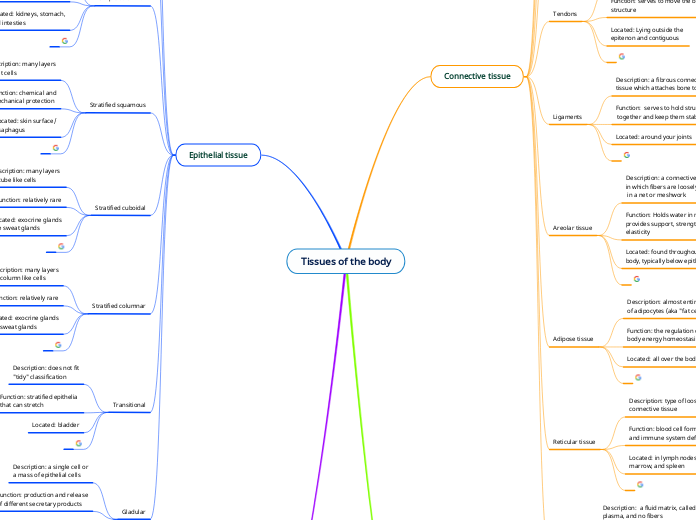
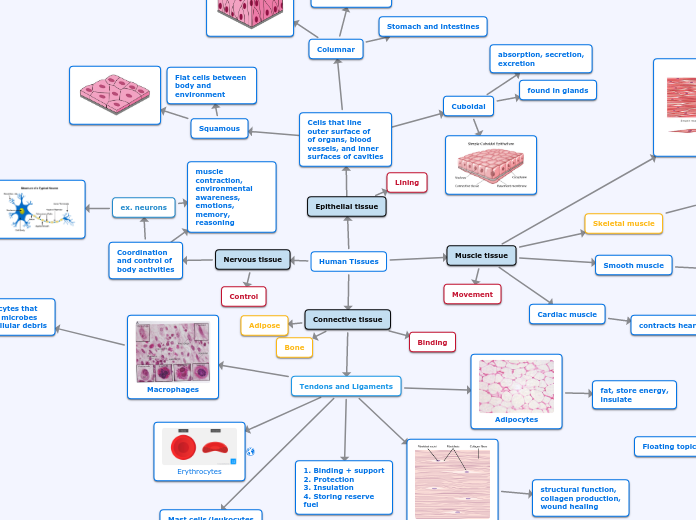
The provided content highlights various types of epithelial and connective tissues in the human body, emphasizing their descriptions, functions, and locations. Epithelial tissues are categorized into types like stratified cuboidal, stratified squamous, glandular, stratified columnar, transitional, simple squamous, simple columnar, and simple cuboidal.
Megnyitás
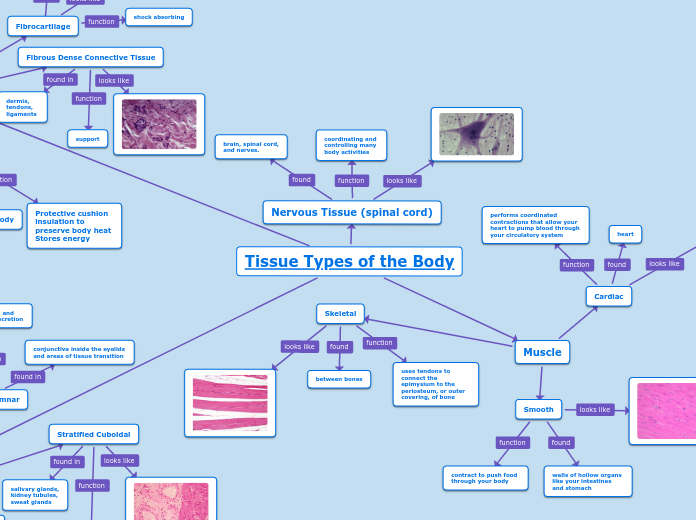
Tissues of the body Muscle tissue Smooth muscle Located: walls of hallow organs. Function: propels substances,
slower (ex. Peristalsis) Description: smooth like, spindle
like, not cylindrical, uni-nucleated,
not striated. Cardiac muscle Located: heart Function: must generate ATP
continuously. Description: much shorter,
uni-nucleated, striated, fit close
together at junctions called
"intercalated discs" Skeletal muscle Located: attached to bones. Function: pulls on bones to make
gross body movements or
cause changes in facial movements. Description: long and thin,
multi-nucleated, striated. Subtopic
Connective tissue Blood Located: inside the blood vessels Function: transportation, regulation,
and protection Description: a fluid matrix, called
plasma, and no fibers Reticular tissue Located: in lymph nodes, bone
marrow, and spleen Function: blood cell formation
and immune system defenses Description: type of loose
connective tissue Adipose tissue Located: all over the body Function: the regulation of whole-
body energy homeostasis Description: almost entirely
of adipocytes (aka "fat cell") Areolar tissue Located: found throughout the
body, typically below epithelial Function: Holds water in matrix,
provides support, strength and
elasticity Description: a connective tissue
in which fibers are loosely arranged
in a net or meshwork Ligaments Located: around your joints Function: serves to hold structures
together and keep them stable Description: a fibrous connective
tissue which attaches bone to bone Tendons Located: Lying outside the
epitenon and contiguous Function: serves to move the bone or
structure Description: fibrous connective tissue
which attaches muscle to bone Elastic cartilage Located: in external ear and epiglottis Function: provides strength, and elasticity Description: most springy Fibrocartilage Located: found between vertebrae
and knee joint Function: provides the tough
material of the intervertebral discs Description: most tensile
strength Hyaline cartilage Located: in the nose, trachea,
larnyx, and bronchi Function: provides mechanical
support for the respiratory tree,
nose, articular surface, and
developing bones. Description: pearl gray
semitranslucent matrix Bone Located: ends of bone Function: protects and supports
body Description: white and sturdy Nervous tissue Supporting cells Located: the central nervous system
(brain and spinal cord) Function: maintaining homeostatic
control and immune surveillance in
the nervous system. Description: non-neuronal cells
of the nervous system. Neurons Located: the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. Function: send and receive signals. Description: branches or spikes extending
out from the cell body. Epithelial tissue Gladular Located: a mixture of bone
endocrine (ductless, hormones
are secreted into the blood Function: production and release
of different secretary products Description: a single cell or
a mass of epithelial cells Transitional Located: bladder Function: stratified epithelia
that can stretch Description: does not fit
"tidy" classification Stratified columnar Description: many layers
like column like cells Stratified cuboidal Located: exocrine glands
like sweat glands Function: relatively rare Description: many layers
of cube like cells Stratified squamous Located: skin surface/
esaphagus Function: chemical and
mechanical protection Description: many layers
of flat cells Simple columnar Located: kidneys, stomach,
and intesties Function: secretion and
absorption Description: single layer of
column like cells Simple cuboidal Located: kidneys and secretary
glands Function: involved in secretion
and absorption Description: single layer of cube-
like cells Simple squamous Located: lungs for gas exchange Function: allows rapid diffusion
of substances. Description: single layer of flat
cells of substances.