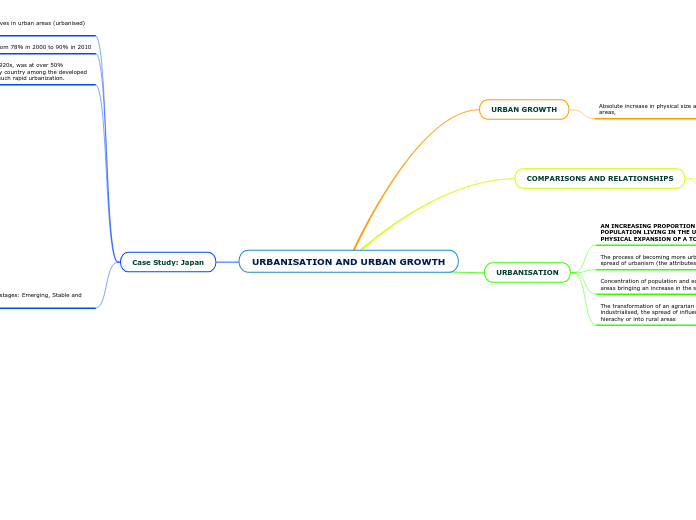
URBANISATION AND URBAN GROWTH
Case Study: Japan
Urbanisation occured in three stages: Emerging, Stable and Mature
Phase 3: Mature - Further rejuvenation and modernisation of the population toward a 'city of the future'
Increase in inter-connectedness and accessibilty of transport system, with both privately owned public transport systems and PPP systems used.
Gentrification and the pursuit of better Quality of Life in the CBD district (1991): Buildings and Land lots were redeveloped into a more efficient multi-purpose design, spreading out the concentration of business and commercial areas by injecting entertainment and education options within the CBD
Phase 2: Stable - urbanisation rate begins to slow, focus begins to shift to maintaining sustainable growth, influenced by the 1973 oil crisis. Land prices were high and CBDs were inefficient
Redevelopment Plan released in 1988 in order to readjust land uses and maximise efficiency
Japan's land area is only about 378 km^2, with 70% of the land area covered by forest. Thus, land is divided into irregular sections privately owned by locals, which can slow development as they have to deal with all the landowners before development. Under the Land Redevelopment Scheme, landowners have to agree to give up a certain portion of their land, used to reshape the land into a more efficient layout and build public infrastructure.
Energy Conversation Act was passed in 1979 to allow for efficient use of resources such as fossil fuels, by the establishment of designated resource management factories and guidelines to reduce wasted power or fuel.
Phase 1: Emerging - High urbanisation rate - Many greenfield sites had to be completely developed and built on, high rate of industrialisation after WWII, leading to excessive concentration of population and industry in the larger metropolitan regions, causing overpopulation and socio-economic decline in rural areas as well as increased pollution levels
1970 Water Pollution Control Law aimed at preventing pollution of public water bodies, thus protecting human health and conserving the living environment of the area.
To protect the victims of such discharge by assessing liability against factory and business owners who are responsible. Compensation to persons suffering from health problems related to discharges can be assessed against the factories and businesses.
2nd National Development Plan created in 1969 to construct a nationwide transportation network of motor ways and rapid national railways ('Shinkansen') system together with the implementation of large-scale industrial development projects. Business were also shifted out of over-concentrated areas (removal areas) to less developed areas (promotion areas)
1st National Development Plan created in 1962 using 'Growth Pole' strategy, encouraging the growth of industrial and commercial nuclei away from the existing major metropolises, while 15 new industrial cities were later designated in 1964, decreasing overpopulation and economic decline in more rural areas while increasing economic diversity.
Solutions: Urban Zoning, creation of Public-Private Partnerships for transport (Partnership between private companies and the government to faster create infrastructure)
High-quality towns and retail shops built along newly built railway lines increase accessiblity and allow for urban growth
1960 - The Income-Doubling Plan, aimed at doubling Japan's GDP from 7000 per capita by investing heavily in urban infrastructure, enabling rapid growth and industrialisation
Japan started to urbanize in 1920s, was at over 50% urbanisation in 1970s, the only country among the developed nations that has experienced such rapid urbanization.
Experienced rapid growth from 78% in 2000 to 90% in 2010
91.7% of Japan's population lives in urban areas (urbanised) [2019]
In 2017, about 117 million people lived in urban areas of Japan, compared to eleven million people in rural areas.
URBANISATION
The transformation of an agrarian economy to one more industrialised, the spread of influences down the settlement hierachy or into rural areas
Concentration of population and economic activities into urban areas bringing an increase in the size of settlements
The process of becoming more urban or the growth and spread of urbanism (the attributes of city dwellers)
AN INCREASING PROPORTION OF A COUNTRY'S POPULATION LIVING IN THE URBAN AREAS AND THE PHYSICAL EXPANSION OF A TOWN
COMPARISONS AND RELATIONSHIPS
Urbanisation and urban growth in any country tends to occur at different rates, typically driven by demographical, political or economic influences
MEDCs that urbanised many decades ago tend to have lower rates of urban growth, while LEDCs have much more rapid urbanisation rates
URBAN GROWTH
Absolute increase in physical size and total population of urban areas,