Signs of disease shown as early as 26 years old
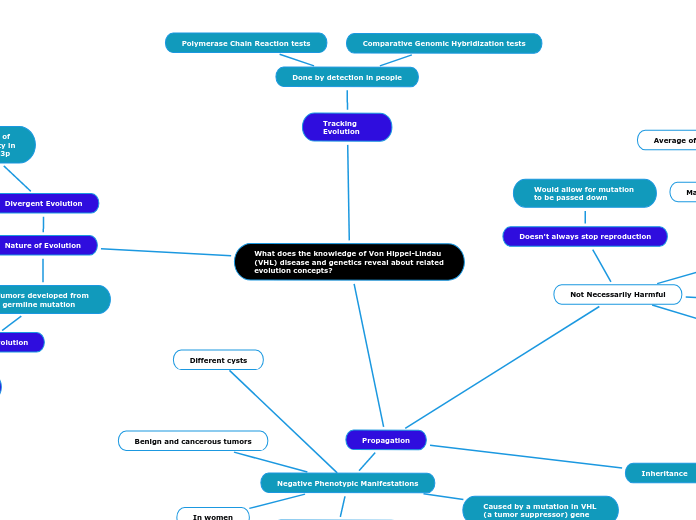
Different cysts
What does the knowledge of Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease and genetics reveal about related evolution concepts?
Propagation
Inheritance
Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Pattern
50% for a parent to pass it to their child
Not Necessarily Harmful
Inheriting Germline Mutation
These might never manifest negative phenotypes
Second mutation required may not occur
Phenotypic manifestations may skip generations
Adequate life expectancy for reproduction
Females
Average of 48.4 years
Males
Average of 59.4 years
Doesn't always stop reproduction
Would allow for mutation to be passed down
Negative Phenotypic Manifestations
Caused by a mutation in VHL (a tumor suppressor) gene
Leads to VHL protein abnormalities
Protein Evolution
pVHL30 is conserved less
pVHL19 is conserved more
Associated with tumors in different organs
Tumor Phylogeny
Some parallel evolution observed
Early Truncal Events
Mutation in chromosome 3
Inactivation of the VHL gene
Evolution of Disease in Particular Organs
Renal Cysts and Carcinomas
May progress to clear cell renal cell carcinomas
Evolve further through additional genetic alterations
Leads to intra-tumour heterogeneity
Following evolutions occur after about 1 to 2 years
First progression after approximately 7 years
Brainstem Hemangioblastomas
Median evolution time of 1.5 years
Progress after 7 years
Cerebellar Hemangioblastomas
3.5-year median evolution time
In women
Pregnancy complications
Stop reproduction
Benign and cancerous tumors
Nature of Evolution
Tumors developed from a germline mutation
DNA Variance and Mutation
Impact
Not on sequence of evolving disabilities
Not on number of evolving disabilities
Convergent Evolution
Different tumors becoming similar as evolution occurs
Divergent Evolution
Requires loss of heterozygosity in chromosome 3p
Tracking Evolution
Done by detection in people
Comparative Genomic Hybridization tests
Polymerase Chain Reaction tests