EL REINO ANIMAL
Global warming is the ongoing rise of the average temperature of the Earth's climate system which has various negative effects.
Cordados
Vertebrados
Mamíferos
Euterios
Vivíparos, placentarios.
Pinnípedos
Foca, morsa, león marino
Desdentados
Armadillo, perezoso
Proboscídeos
Elefante
Perisodáctilos
Cebra, caballo, rinoceronte
Artiodáctilos
Camello, jirafa, alce
Cetáceos
Ballena, delfín
Carnívoros
León, oso, lobo
Lagomorfos
Conejo, liebre
Roedores
Ratón, lirón, ardilla
Primates
Gorila, mmono, lemur
Quirópteros
Murciélago, vampiro
Insectívoros
Musaraña, erizo, topo
Metaterios
Vivíparos, marsupiales.
Canguro, koala
Prototerios
Ovíparos.
Ornitorrinco, equidna
Aves
Impennes
Con aletas natatorias.
Pingüino
Carenadas
Voladoras.
Pelícano, cigüeña, loro
Rátidas
Corredoras, no voladoras.
Avestruz, kiwi
Reptiles
Crocodilios
Cocodrilo, caimán y gavial
Quelonios
Tortuga y galápago
Ofidios
Serpiente, culebra
Saurios
Lagartija, salamanquesa
Anfibios
Urodelos
Salamandra y tritón
Anuros
Rana y sapo
Ápodos
Cecilia
Peces
Osteíctios
Atún, salmón, trucha
Condrictios
Tiburón, manta, raya
Lampreas y mixines
Cefalocordados
Anfioxos
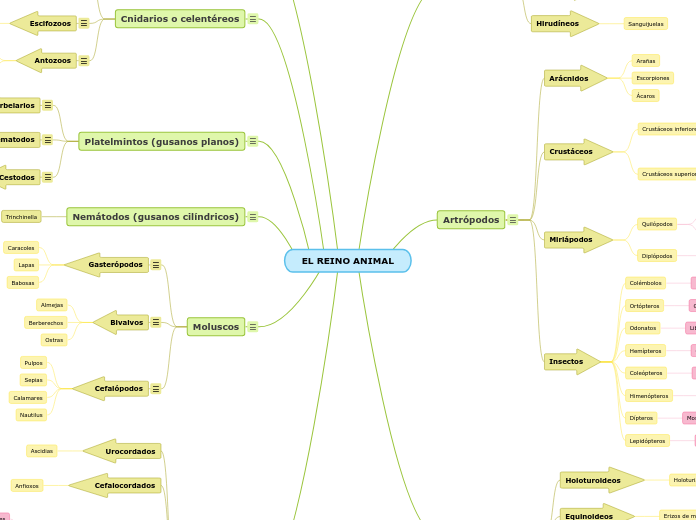
Urocordados
Ascidias
Moluscos
- Simetría bilateral
- Triblásticos
- Celomados
Cefalópodos
Nautilus
Calamares
Sepias
Pulpos
Bivalvos
Ostras
Berberechos
Almejas
Gasterópodos
Babosas
Lapas
Caracoles
Nemátodos (gusanos cilíndricos)
- Simetría bilateral
- Triblásticos
- Pseudocelomados
Son de vida libre o parásitos
Trinchinella
Platelmintos (gusanos planos)
- Simetría bilateral
- Triblásticos
- Acelomados
Overpopulation creates an increased demand for energy as well as having negative effects on our environment and ecosystems.
Cestodos
Parásitos del tubo digestivo.
Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish from a body of water at a rate that the species cannot replenish, resulting in those species becoming underpopulated in that area.
This will lead to a Marine Ecosystem imbalance with time.
Solitaria
Tenia
Trematodos
Parásitos internos de vertebrados.
Water is essential for agricultural production and food security. It is the lifeblood of ecosystems, including forests, lakes, and wetlands.
Overpopulation affects our water and this has negative outcomes.
Fasciola hepática
Turbelarios
De vida libre.
Over-cultivation is the practice of excessive farming on a piece of land to the point of degradation of the soil as well as the land itself.
Planarias
Cnidarios o celentéreos
- Simetría radial
- Diblásticos
Climate change is likely to both increase electricity demand for cooling in the summer and decrease electricity, natural gas, heating oil, and wood demand for heating in the winter.
Antozoos
No tienen fase medusa.
Corales
Anémonas
Escifozoos
Alternancia pólipo y medusa o sólo medusa.
Finding reusable energy sources can be our first step towards conserving our environment.
Aurelia aurita
Hidrozoos
Alternancia generaciones pólipo y medusa.
How will climate change affect the production of clean energy?
e.g.: solar, wind, water
Carabela portuguesa
Obelia
Hydra
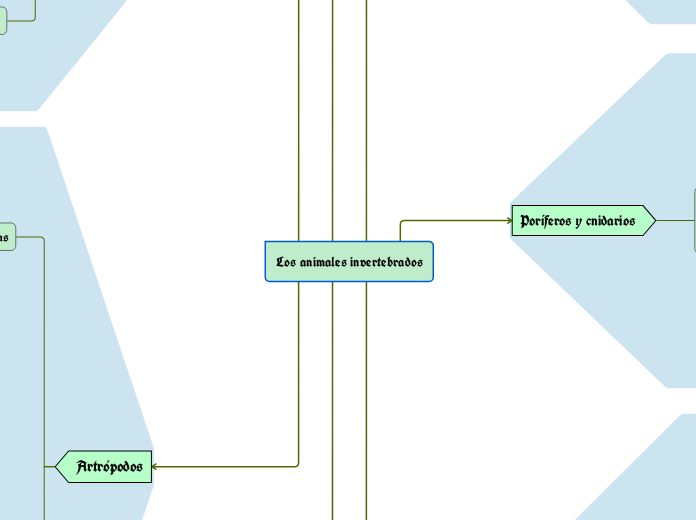
Poríferos (esponjas)
- Simetría radial o asimétricos
- Diblásticos
Equinodermos
- Simetría bilateral en larvas; simetría pentaradial adultos
- Triblásticos
- Celomados
Healthy ecosystems and rich biodiversity are fundamental to life on our planet.
Even small changes in average temperatures can have a significant effect upon ecosystems.
Ofiuroideos
Ofiuras
Asteroideos
The inter-connected nature of ecosystems means that the loss of species can have knock-on effects upon a range of ecosystem functions.
e.g. bees go extinct
Estrellas de mar
Equinoideos
Climate change will affect mountain and lowland ecosystems, the diversity of wildlife, and the distribution of freshwater.
e.g.: forest fires
Erizos de mar
Holoturoideos
Climate change is affecting the habitats of several species, which must either adapt or migrate to areas with more favorable conditions.
e.g.: natural habitat disappearing
Holoturias
Artrópodos
- Simetría bilateral
- Triblásticos
- Celomados
- Metamería
Climate change is supported by scientific evidence.
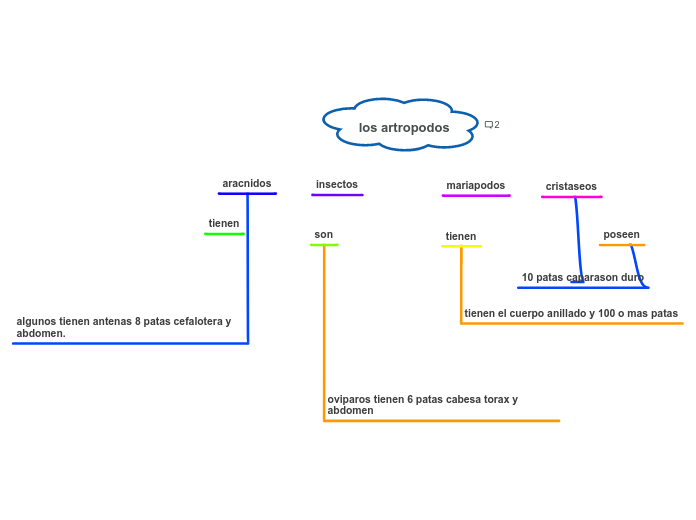
Insectos
Lepidópteros
Mariposas o polillas
Dípteros
Mosca o mosquito
Himenópteros
Hormigas, abejas o avispas
Coleópteros
Escarabajo
Hemípteros
Chinche
Odonatos
Libélulas
Ortópteros
Grillo o saltamontes
Colémbolos
Piojo de papel o pulga de nieve
Miriápodos
Write down the consequences caused by this issue and how it will affect our lives and the environment in the future.
e.g.: flooding, rainfall increase
Diplópodos
Milpies
Quilópodos
Escalopendras
Cienpies
Crustáceos
Write down the consequences caused by the melting of the ice-caps and how it will affect our lives and the environment in the future.
e.g.: decreasing of polar bear habitat
Crustáceos superiores (decápodos)
Braquiuros
Abdomen debajo del tórax y aplanado.
Centollo, buey de mar, cangrejo de mar
Macruros
Abdomen largo que sirve para nadar.
Gamba, langosta, cangrejo de río
Crustáceos inferiores
Percebes
Cochinillas
Arácnidos
Write down the consequences caused by this issue and how it will affect our lives and the environment in the future.
e.g.: decreasing of land surface
Ácaros
Escorpiones
Arañas
Anélidos
- Simetría bilateral
- Triblásticos
- Celomados
- Cuerpo segmentado
Hirudíneos
Sanguijuelas
Oligoquetos
Lombrices
Poliquetos
Gusanos tubícolas