Microrganismi
A microorganism is an organism so small that people cannot see them with the naked eye.
Microorganisms can be harmful and useful organisms.
Microrganismi nocivi che causano malattie importanti: Bacillus anthracis, Clostridium botulinum, Salmonella spp, virus dell'influenza, virus dell'HIV, virus dell'epatite, Candida albicans, Plasmodium falciparum, Giardia lamblia.
Harmful microorganisms include fungi, bacteria, protozoa, etc.
They cause several diseases in human beings, animals, and plants, which can even lead to death.
The harmful microorganisms not only can damage the human body, but also the food we eat.
Malattie
What diseases can they cause?
Malattie parassitarie
Micosi
Infezioni virali
Infezioni batteriche
Prevenzione
Give examples of how the spread of harmful organisms can be prevented.
Pratiche igieniche: lavaggio mani, pulizia superfici, vaccinazione.
Diffusione
Give examples of how harmful organisms can spread.
Contatto diretto con soggetto infetto o oggetto contaminato
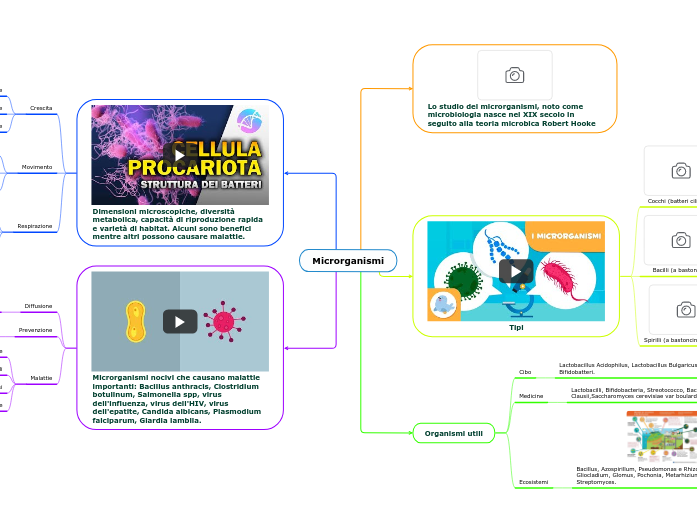
Dimensioni microscopiche, diversità metabolica, capacità di riproduzione rapida e varietà di habitat. Alcuni sono benefici mentre altri possono causare malattie.
Research about the main characteristics of the microorganisms and give examples!
Respirazione
Respirazione anaerobica
Fermentazione
Respirazione aerobica
Movimento
Pseudopodi
Ciglia
Flagelli
Crescita
Formazione di spore
Gemmazione
Divisione cellulare
Organismi utili
Microorganisms help in the production of many food items, making medicines, keeping the environment clean, in manufacturing, and in research.
Ecosistemi
Microorganisms have a role in waste disposal, agriculture, and nutrient recycling.
Give examples of these types.
Bacillus, Azospirillum, Pseudomonas e Rhizobium, Beauveria, Gliocladium, Glomus, Pochonia, Metarhizium e Trichoderma, Streptomyces.
Medicine
Give examples of bacteria used in the pharmaceutical industry.
Lactobacilli, Bifidobacteria, Streotococco, Bacillus Clausii,Saccharomyces cerevisiae var boulardii.
Cibo
Give examples of Microorganisms in food production.
Lactobacillus Acidophilus, Lactobacillus Bulgaricus e Bifidobatteri.
Tipi
There are five types of microorganisms. Out of these five, four can be free-living or parasitic.
There is one that can be only parasitic since it always reproduces inside other living things.
After enumerating them, click on the flags below to mark the ones which can be free-living and the ones that cannot.
can be free-living
only parasitic
Spirilli (a bastoncino spiralato)
Bacilli (a bastoncino)
Cocchi (batteri cilindrici)
Lo studio dei microrganismi, noto come microbiologia nasce nel XIX secolo in seguito alla teoria microbica Robert Hooke
Name the study of microorganisms.